Serbian Genetics Society
THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia June 08-11, 1994

Serbian Genetics Society
THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia June 08-11, 1994

Chairmanship
Vukica DIKLIĆ
Janko DUMANOVIĆ
Dragoslav MARINKOVIĆ
Aleksandar KRSTIĆ
Ana SAVIĆ
Bogosav SOLDATOVIĆ
Aleksandar TUCOVIĆ
Organizing Committee
Kosana KONSTANTINOV, president
Marija Kraljević-Balalić
Nada BARJAKTAREVIĆ, secretary
Marko Anđelković
Dragan ALAVANTIĆ
Vasilije Isajev
Mile IVANOVIĆ
Vesna LAZIĆ-JANČIĆ
Miroslava MICIĆ
Teodora PAPIĆ-PALJIĆ
Gojko SAVIĆ
Draga SIMIĆ
Vitomir VIDOVIĆ
Ljubiša TOPISIROVIĆ
Branka TUCIĆ
Secretariat
Miodrag DIMITRIJEVIĆ
Jelena KNEŽEVIĆ
Desmir KNEŽEVIĆ
Vera ROBOVIĆ
Goran SARATLIĆ
Ljiljana VAPA
Mladen VUJOŠEVIĆ
Serbian Genetics Society
THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia June 08-11, 1994
Symposium 1. CYTOGENETICS
B. Soldatović
A retrospective evaluation of development of cytogenetics
Jovanka Atlagić
A cytogenetic study of interspecific sunflower hybrids (H. annum L. x H. occidentalis Riddelt)
Jelena Blagojević i Vujošević M.
N. Đelić, B. Soldatović i M. Anđelković
Svetlana Fišter i B. Soldatović
Drinka Merčap, A. Đujić, Z. Magić i M. Simović
Different responses to genotoxic agents depending on the genetic constitution
Snežana Mezei, L. Kovačević i N. Čačić
The effect colchicine on some quantitative characters of sugar beet
B.P. Pavlović
A method for making numerical karyotype etalons
B.P. Pavlović
Numerical karyotype etalons Erinaceus europaeus europaeus
B. Pavlović, i Nevenka Pavlović
Slavica Simović i G. Marković
The chromosome complements of some fish species from the Cyprinidae family
Z. Stanimirović, Mirjana Vučinić, B. Soldatović, E. Herzog
S. Šesek
N. Tanić, Olivera Spasić, Jelena Blagojević i M. Vujošević
Chromosomes of frogs from the family Ranidae (Anura, amphibia) - a comparative analysis
Marijana Vučinić, Z. Stanimirović, B. Soldatović
"ROSOL", as an eventual inducor of polyploid type chromosome aberrations
M. Vujošević i Jelena Blagojević
Symposium 2. MEDICAL GENETICS
Slavenka Adžić, Stefanija Marković, D. Plećaš, N. Radunović i Z. Pilić
Chromosome aberrations found by cordocentesis
Nevenka Aleksić
In vitro genotoxicological characterisation of ivermectin and praziquantel
M. Babić i M. Micić
A cephalometric analysis of patients with Klinefelter's syndrome
S. Branković i G. Savić
Suzana Cvjetičanin i D. Marinković
N. Dedović, J. Milašin, V. Petrović, G. Stamenković, M. Gavrić, Z. Nikolić
A high incidence of H-ras gene point mutations in two types of head and neck neoplasias
Vukosava Diklić, Marija Kosanović, Milica Todorić, M. Vukotić, S.P. Stojković
The role of genetic factors in the etiopathogenesis of cardiovascular disorders
Nada Dimković, Vitana Kostić, Dragan Jovanović i Nada Barjaktarović
Cytogenetic analyses reveal "atypical cells" in the peritoneal dialysis effluent
B. Đorđević, D. Mihailović, D. Stojanović, C. Kutlešić, M. Čekerevac, Z. Popović i Z. Stanković
Histologic findings in the ovary of a Turner's syndrome patient
Slobodanka Grković i Vesna Ivanović-Deretić
A report of a 9p/10p family translocation
Marija Guć-Šćekić, Dragana Anđelković, V. Jurukovski i Gordana Pilić-Radivojević
Genetic determinants in the prognosis of neuroblastoma
Vesna Ivanović-Deretić, Slobodanka Grković i B. Garzičić
A report of autosomal whole arm translocation
Zorica Janakova
Zorica Janakova
Zorica Janakova
Humoral factors in the variability of allergic reactivity
Gordana Jokšić
Dragana Jovanović i D. Marinković
J. Jovanović-Privrodski, A. Krstić, F. Popić-Paljić, R. Aleksić i G. Raca
J. Jovanović-Privrodski, A. Krstić, F. Popić-Paljić, Z. Pilić
Vesna Knežević, Vukosava Diklić, Marija Kosanović i N. Vojvodić
Genetic investigations of cardiovascular diseases
M. Krajinović, K. Ivanović, L. Mestroni, V. Diklić i J. Nikoliš
A. Krstić, M. Kovačević, G. Raca, F. Popić-Paljić, J. Jovanović-Privrodski, R. Aleksić, N. Čamber, R. Madžar, V. Čihi, Lj. Gaćina, N. Mitrovčan i Lj. Malešević
The registration of chromosomal aberrations using the methodology of D.S.Borgoankar
M. Krstić, Stefanija Marković i Slavenka Adžić
Moral and ethical aspects of prenatal diagnosis in hereditary diseases
Živana Laca
Cytogenetic investigations in medical genetics
Milena Ludoski, Ljiljana Lalić, Vera Popović, V. Jurukovski i Angelina Novak
B. Lukić, Nada Barjaktarović, Nada Todorović i Vitana Kostić
Ljiljana Luković, Jelena Milašin, N. Arsenović i Vukosava Diklić
Chromosomal aberrations in three ovarian tumors
D. Marinković, D. Jovanović, S. Cvjetičanin i S. Branković
Genetic homozygosity and normal vs. pathological human variation
Miroslava Mićić
The influence of sex chromosomal anomalies on spermatogenesis
D. Mihailović, Z. Stanković, B. Đorđević, V. Mihailović i M. Čekerevac
The nuclear volume in Patau's syndrome
V. Mihailović, Z. Stanković, D. Mihailović i D. Stojanović
The frequency of acrocentric associations in women with spontaneous abortus
Jelena Milašin, Nasta Dedović, S. Mićić, B. Dimitrijević, Vukica Diklić
H-ras gene mutations in human urinary tract tumors
Olivera Milošević-Đorđević i Nada Barjaktarović
The reaction of human T limphocytes to mafosfamide and 5-fluorouracil in vitro
S. Minić, M. Kosanović i B. Petrović
A citogeneticinvestigation of chromosomes in patiens with incontinentio pigmenti
J. Nikoliš, V. Kekić, S. Mićić, V. Diklić, M. Ristanović
Ag- NORs in normal human population
Angelina Novak, Đ. Kokai, Vera Popović, Milena Ludoški, V. Jarukovski
Ivana Novaković, Olga Antonović, Slavenka Adžić i Svjetlana Maglajić
V. Novosel
A genetic survey of a family with repeated polydactylism
Vesna Pendić, Vera Popović i Angelina Novak
Familial 46,xy gonadal dysgenesis
D. Pešut, D. Marinković
ABO blood type frequency in some lung diseases
F. Popić-Paljić, A. Krstić, J. Jovanović-Privrodski, R. I Aleksić i G. Raca
Genetic counselling of married couples in cases of effects of harmful environmental noxes
F. Popić-Paljić, A. Krstić, J. Jovanović-Privrodski, G. Raca i R. Aleksić
The use of modern software in diagnosing rare syndromes
Branka Popović, B. Garzičić i Biljana Spremo
Fragile sites and oncogenes as a possible risk for neoplasia in carriers of balance translocations
G. Raca, A. Krstić, B. Garzičić, F. Popić-Paljić, J. Jovanović-Privrodski, R. Aleksić, N. Čamber, R. Madžar, V. Čihi, Lj. Gaćina, N. Mitrovčan i Lj. Malešević
An induction of fragile sites on human chromosomes by aphidicoline and cytosine-arabinoside
Dragica Radojković, Ana Savić, J. Savić, P. Minić i B. Brukner-Dabović
An application of the recombinant DNA method in the prenatal diagnostic of cystic fibrosis
S. Radulović, Nada Barjaktarović i Vitana Kostić
A rare variant of karyotype 47,XY,13 in AML (M2 type)
O. Ristić, Ž. Laća, S. Nikšić, N. Aranđelović i I. Timotijević
Biljana Spremo i B. Garzičić
L.N. Stojanović, E. L. Nassonov i M. Stanić
Nada Todorović, B. Lukić i Nada Barjaktarović
Cytogenetic parameters during different treatments in perinatology
Symposium 3. MOLECULAR GENETICS AND GENETIC ENGINEERING
Desanka Božin i Gordana Cerović
Desanka BOŽIN, Gordana CEROVIĆ i RADMAN
Desanka Božin, Gordana Cerović i RADMAN
Mismatch recognition efficiency. II. Mismatch recognition efficiency in the mammalian nucleus
Sanja Glišić, Ivana Savić i Alavanić
The use of multiallelic human apoB gene DNA polymorphism (3'HVR) for DNA typing
Sanja GLIŠIĆ, Ivana SAVIĆ i ALAVANTIĆ
Sanja Glišić, Ivana Savić i Alavantić
Sanja Glišić, Ivana Savić, Nadežda Radoja i Alavantić
An insertion/deletion polymorphism in the signal peptide of the apoB gene
Đ. Fira, M. Kojić, A. Banina i Lj. Topisirović
Extracellular proteinases of mesophilic lactobacilli
Radmila V. Ivanišević, Mirjana M. Milić, Dragana S. Ajdić, Milija Z. Jovičić, Mila J. Janković i J. Savić
Mila J. Janković, Mirjana M. Milić, Radmila V. Ivanišević, Z. Jovičić i J. Savić
Replication and mutagenesis: Analysis of a highly mutable sequence from the hisC gene of E. Coli
Z. Jovičić, Mirjana M. Milić, Radmila V. Ivanišević, Mila J. Janković i D. Savić
lieS and glnF (ipoN) mutants of E. coli show an increased resistance to novobiocin
Knežević-Vukčević, B. Čuljković, M. Vulović, B. Vuković-Gačić i D. Simić
The effect of bioantimutagens on intrachromosomal recombination in Escherichia coli K12.
M. Kojić, Lj. Topisirović
Kojić, Topisirović, Branka Vasiljević
Regulation of the expression of the sgm gene from Micromonospora zionensis
Kosana Konstantinov, Snežana Mladenović, Snezana Gošić, G. Saratlić, N. Delić, R. Petrović
Recombinant DNA technology in plant variety patenting and protection of authors rights
Konstantinović, Sanja Ivković i Glišin
Temperature - dependent activities of hybrid Escherichia coli promoters
Koviljka Krtolica, Nadežda Urošević, Dobrila Nešić, Ljiljana Tukić, Z. Magić i B. Dimitrijević
The activation of oncogenes in human myeloid neoplasta
Vesna Lazić-Jančić, D. Kovačević, A. Steed i S.A. Quarrie
Genotype-specific accumulation of BAR17MRNA in maize leaves during drought stress
Vesna Lazić-Jančić, C. Lebreton, A. Steed i S.A. Quarrie
Investigation on qtl for abscisic acid production using RFLP markers
Z. Magić, Svetlana Matić i G. Poznanović
Radiation induced expression of acute phase protein genes in rat liver
Vesna Maksimović, Svetlana Radović, Erika Varkonji i Ana Savić
Analysis of mRNAs in developing buckwheat seeds
Jelena Marjanović, V. Glišin i Zvezdana Popović
The anemic Belgrade rat 67kd erythrocyte membrane protein
N. Miladinov, B. Bojović, M. Kojić, A. Banina i Lj. Topisirović
Analysis of the regulator domain of the prt gene in Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis BGIS29
Mirjana M. Milić, M.Z. Jovičić, Radmila V. Ivanišević, Mila J. Janković i J. Savić
A new cysB regulated gene that modifies novobiocin rezistance in cysB mutanats of Escherichia coli
Snežana Mladenović, Kosana Konstantinov, Bojana Tadić i G. Saratlić
The influence of bacterial on multiple allele polimorphism in maize
Sonja Pavlović, Tatjana Mitrović, Glišin i Zvezdana Popović
An analysis of the distal promoter of the rat bminy - globin gen
S. Radoja, M. Konstantinović i V. Glišin
Svetlana Radović, Vesna Maksimović i Ana Savić
Characterization of the 13 S globulin of buckwheat seed
Ivana Savić, Sanja Glišić, Nadežda Radoja i D. Alavantić
Ivana Savić, Sanja Glišić, Nadežda Radoja i D. Alavantić
S. Stanković, J. Knežević-Vukčević, B. Vuković-Gačić i D. Simić
An investigation of repair mechanisms in different Bacillus thuringiensis subspecies
Milena Stevanović i P.N. Goodfellow
Cloning and characterisation of the human SOX3 gene
I. Stojanović, M. Vujičić i Lj. Topisirović
A study of the segregational stability of plasmid pAl from Lactobacillus plantarum A112
J. Svirčević, M. Kojić, A. Banina i Lj. Topisirović
Nataša Trutić, Koviljka Krtolica, M. Čolić i Z. Mugić
Branka, M. Kojić, Lj. Topisirović
Resistance to hygromycin B in Micromonospora strains
Miloš Vujanac, Vesna Todorović, Snežana Kojić, Ana Savić i Dragana Stefanović
Extrachromosomal replication of plasmids in Drosophila embryos
Nataša Vukov, Snežana Kojić, Lj. Topisirović i Branka Vasiljević
Analysis of the pMZl plasmid from Micromonospora zionensis
Symposium 4. BREEDING OF ORGANISMS
D. S. Adamović, B. Pekić i Z. Lepojević
J. Boćanski, M. Stojaković
V. Bogdanović, D. Radojković, Radica Vidić-Dedović i P. Stojić
Methods for evaluating additive genetic effects
Jelena Bošković i M. Bošković
R. Cerović
A study of microgametogenesis in vitro in sour cherries
N. Čačić, L. Kovačev i Snežana Mezei
Combining abilities for the leaf area index of sugar beet (Beta vulgaris L.)
M. Dimitrijević, Sofija Petrović i Marija Kraljević-Balalić
Analysis of the gene effect in the inheritance of the number of kernels per spike in wheat
B. Dozet, R. Marinković
Recurrent phenotype selection of protein sunflower (Helianthus annum L. var. macrocarpus Ckll.)
G. Drinić, M. Ivanović i Jelena Vančetović
Genetic gain from selection based on hs progenies in two synthetic populations of maize
D. Đokić, S. Lomović, M. Milovanović i R. Ognjanović
D. Đokić, S. Lomović, M. Milovanović i R. Ognjanović
D. Đokić, S. Lomović, M. Milovanović i R. Ognjanović
D. Đokić, M. Kostić, S. Lomović i M. Jelić
Some parameters of mineral nutrition efficiency as an indicator in wheat selection
D. Đokić, M. Kostić, S. Lomović i M. Milovanović
The efficiency nitrogen nutrition as a genotype characteristic of wheat
D. Đokić, M. Kostić, S. Lomović i M. Milovanović
J. Đorđević i M. Ivanović
R. Đorđević, Z. Marković, V. Pešić i I. Đinović
The influence of "afila" genes on the forming of pods in Pisum sativum L.
Matilda Đukić i Dragica Obratov
Genetic specificity of morphological characters of hybrid plane half-sib progeny
Ž. Gajić i A.E. Bell
M. Grbić
Growth characteristsics of Siberian elm (Ulmus pumula L.) rooted cuttings from dwarf parent trees
Branislava Grbović i Biljana Nikolić
Differences between 6 varieties of mulberry (Morus alba, L.) propagated in vitro
Đ. Gvozdenović, Marija Kraljević-Balalić, I. Mihaljev i A. Takač
Components of genetic variance for the length and width of pepper fruits (Capsicum annuum L.)
V. Guzina, S. Orlović i G. Abramović
V. Isajev, A. Tucović i Mirjana Šijačić
Developments in the improvement of austrian pine (Pinus nigra Arn.) in Serbia
Đ. Jocković, J.R. Vilcox, H.J. Xu, Milica Hrustić i M. Stojaković
J. Joksimović, R. Marinković i M. Mihaljčević
Combining ability for yield components of F1 hybrids of sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.)
B. Jovanović, S. Prodanović i D. Stevanović
D. Knežević
Identification of wheat varieties by Gli- allele composition
D. Knežević, Mirjana Menkovska i Dragica Zorić
Allelic variation at Gli- loci in some Macedonian wheat cultivars
D. Knežević, M. Pavlović, Marija Kraljević-Balalić i Veselinka Zečević
Genetička analiza površine lista zastavičara kod pšenice (Triticum aestivum L.)
D. Knežević, Ljiljana Vapa i Aleksandra Yurievna Novoselskaya
Genetic analysis of the area of the flag leaf in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.)
L. Kovačev, N. Čačić i Snežana Mezei
Polu sib test kros rekurentna selekcija multigermnih tetraploidnih oprašivača šećerne repe
B. Kovačević, Snežana Mezei i Marija Kraljević-Balalić
Half-sib tests cross recurrent selection of multigerm tetraploid pollinators of sugar beet
Mirjana Kraljević-Balalić, M. Dimitrijević i Sofija Petrović
Combining ability analysis for grain number in wheat
M. Kuburović, M. Pavlović i D. Knežević
Combining ability and gene effects for root volume in wheat
Nevenka Kuprešanin i Snežana Mezei
Induction of haploid callus in sugar beet
D. Latinović, Lj. Lazarević, P. Stojić, G. Trifunović i M. Katić
Possibilities of the application of restricted selection indexes in dairy cattle populations
Vera Lavadinović, V. Isajev
The phenotype - physiological variability of 29 Douglas fir provenances in test plantations
Lj. Lazarević
Possibilities and limits in the genetic improvement of milk characteristics in cattle
Lj. Lazarević, D. Latinović, G. Trifunović, M. Katić i P. Stojić
The influence of the level of milk production on the genetic variation
Milomirka Madić i M. Pavlović
Inheritance of stem height in barley hybrids (Hordeum vulgare L.)
R. Marinković, D. Škorić, J. Crnobarac i N. Dušanić
Correlations and path analysis in castor beans (Ricinus communis L.)
Ljiljana Merkulov, Jadranka Ivezić i Marija Kraljević-Balalić
Danica Mićanović, Zora Sarić, M. Sarić i V. Mitrović
Genetic variability of wheat in making natural associations with free-living diazotrophs
N. Mišić R. Cerović i Gordana Đurić
Atrophy opovules in flowers with an interrupted development in the plum (P. domestica L.)
N. Mićić, R. Cerović i Gordana Đurić
Ovary deformities in plums due to irregular carpel fusion
M. Mihaljčević
Yellow spots on sunflower leaves (H. annum L.) are caused by nuclear and extranuclear factors
I. Mihaljev, Marija Kraljević-Balalić, P. Dorić i S. Petrović
Future needs for cchanges of conceptions and methods in plant breeding
M. Milutinović, Ružica Džamić, L. Avramov, D. Nikolić i M. Nikolić
M. Milutinović, Gordana Šurlan-Momirović, N. Ralević, Ivana Ralević i Vera Rakonjac
Multivariate analysis in different populations of wild sweet cherry (Prunus avium L.)
A.M. Mirković, R.R. Todorović, P.D. Mišić, Z.V. Pavlović i N.G. Zec
Selection of Persian wallnut, Juglans regia L. in Serbia
M. Mitrović
Economic and biological properties of some walnut selection
Nastasija Makovački, Snežana Mezei i L. Kovačev
Compatibility between sugar beet hybrids and Azotobacter strains
S. Orlović, V. Guzina
An assessment of the possibility of utilization of leaf-blade anatomic structure in poplar selection
Zorica Pajić i M. Babić
Popcorn hybrids - development and utilization
M. Pavlović, M. Kuburović, D. Knežević i Veselinka Zečević
Genetic effects and inheritance of the size of the sclerenchymous layer in the wheat stem
V. Pešić i Dragica Zorić
Inheritance of stem height in wheat hybrids of the F3 and F4 generations
R. Petrović, N. Delić i M. Vidaković
Sofija Petrović, Marija Kraljević-Balalić i M. Dimitrijević
The inheritance and phenotypic variability for the number of kernels per spike in wheat
M.M. Petrović, R. Lazarević, Lj. Lazarević S. Vasović, B. Miščević, S. Aleksić, D. Radosavljević
Genetical parameters of traits of body development in young female cattle
Lj. Prijić, Mirjana Jovanović i M. Mladenović
Application of genetic male sterility to the soybean breeding program
Vera Rakonjac, T. Živanović i D. Nikolić
Varijability and heritability components of some sweet cherry fruit characteristics
G. Saratlić, K. Konstantinov, I. Verešbaranji, Snežana Mladenović, J. Dumanović, B. Kerečki
Genetic control of the oil quality in the maize kernel
P. Sklenar, J. Boćanski i Marija Kraljević-Balalić
The mode of inheritance of leaf area in maize (Zea mays L.)
A. Stančević i M. Nikolić
M. Stanisavljević
In vitro germination and storage of blackberry pollen
Tatjana Stevanović Janežić i V. Isajev
M. Stojaković, D. Jocković, J. Boćanski, G. Bekavac i R. Popov
A study of combining abilities for grain yield in maize (Zea mays L.)
Vidosava Šećerov-Fišer
Mode of inheritance for plant height in ornamental sunflowers
Gordana Šurlan-Momirović, Zorica Tomić, Ivana Ralević i N. Ralević
Evalluation of germplasm collection of Agrostis stolonifera L. through multivariate analysis
Zorica Tomić
Improvement of italian ryegrass (Lolium multiflorum Lam.) by chromosome duplication
Z. Tomović i S. Orlović
The variability and heredity of leaf morphological parameters in poplar clones, section leuce
G. Trifunović, Lj. Lazarević , D. Latinović, P. Stojić i M. Katić
B. Trifunović, V. Trifunović, Gordana Radović i D. Jelovac
Selection progress and divergence in local synthetic populations of maize (Zea mays L.)
A. Tucaković i V. Isajev
Polyploid complexes, diploidization and improvement of trees and shrubs
A. Tucović, V. Isajev i Mirjana Šijačić
Sex variability and its significance in the improvement of the black poplar (Populus nigra L.)
A. Tucović, V. Isajev i Mirjana Šijačić
Mass and individual selection of the white bark pine (Pinus heldreichii Chrisst.) in Serbia
Ljiljana Vapa, S. Denčić, Erika Rakk-Šoltes i S. Kevrešan
RFLP at the Glu-1 loci and the bread-making quality of wheat cultivars
Mirjana Vasić
Genetic analysis of the number of seeds per plant in white bean crosses
Dragana Vasić, Ana Marjanović i B. Dozet
Dragica Vilotić, Mirjana Šijačić i V. Isajev
Jasmina Zdravković, Z. Marković, M. Damjanović i M. Zdravković
Inheritance of stoutness of the pericarp in tomato fruits (Lycopersicon escukntum Mill.)
Veselinka Zečević, M. Pavlović, D. Knežević i B. Vulić
Genetic analyses of productive tillering in wheat
Marija Zlokolica i I. Gerić
Isozyme variation among maize collections from Yugoslavia
T. Živanović, Gordana Šurlan-Momirović, Ivana Ralević i N. Ralević
Numerical taxonomy of ZPSin populations of maize based on quantitative traits
Symposium 5. POPULATION AND EVOLUTIONARY GENETICS
N. Tucić
Population genetics and two great syntheses of modern biology
I. Aleksić
Genetic components of variation in size and shape during ontogeny in the lizard Lacerta oxycephala
S. Avramov i Branka Tucić
Quantitative genetics of the juvenile traits in Iris Pumila: The structure of phenotypic variation
C. Cekuš
Presence of fossa mentalis and dimples in samples, from the area surrounding Subotica
G. Cekuš
Variations of hair limits on the forehead in samples from northern Serbia
Jelka Crnobrnja-Isailović i I. Aleksić
Ivana Gliksman
The quantitative genetic basis of increased longevity in the bean weevil (Acenlhoscelides obtectus)
V. Kekić, Sofija Pavković-Lučić, Aleksandra Čvoro i N. Milošević
Sexual selection and body size in Drosophila melanogaster
D. Knežević, D. Marinković, Lj. Agramović
A population genetic study of left-handedness in citizens of Prokuplje
Stanislava Mikuljanac i O. Stojković
Mirjana Milanović i M. Anđelković
Dragana Milanović i Sofija Karaulić
N. Milošević, V. Kekić, Sofija Pavković-Lučić i Aleksandra Čvoro
Learning in Drosophila melanogaster implications on the genetic structure
Milica Milošević, Z. Magić, Č. Radojičić i D. Marinković
V. Novosel
D. Paunović, R. Simonović, I. Stolić i M. Dokić
Calculating the risk factor for transfusion-associated graft-versus-host disease
B.P. Pavlović
The potential number of cells and system size of individuals and populations
R. Simonović, D. Paunović, I. Stolić i V.D. Miletić
Disequilibrium pattern analysis between A and B loci of the HLA system in Serbia
M. Stamenković-Radak, J.B. Clark i M. Kid Well
Snežana Stanić i D. Marinković
Selection for a different time until the first mating in Drosophila melanogaster
Vesna Stojiljković
Individual variability of a-amylase activity in Drosophila subobscura
O. Stojković
Darka Šešlija i D. Blagojević
Tatjana Terzić i M. Anđelković
Ljiljana Vapa, Ivana Karanović, Dragana Radović, J. Purger i M. Bokorov
The genetic distance between three species of the genus Apodemus
G. Živanović, Mirjana Milanović i M. Anđelković
Correlation of structural complexity of o chromosome and the genetic load in Drosophila suboboscura
Jelena Živanov-Čurlis i Estera Mrčarica
The effect of the aging on the in Drosophila melanogaster genetic load
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
A RETROSPECTIVE EVALUATION OF DEVELOPMENT OF CYTOGENETICS
B. SOLDATOVIĆ
Veterinarski fakultet, Beograd
Recent advances in general and animal cytogenetics, and the significance of fundamental and applied research results, as well as modern trends in genetic research were presented in this paper. A retrospective view shows that the development of the science was accomplished by a justified introduction and improvement of cytogenetical techniques and methods. The results obtained were applied and helped in the understanding of philogenic relationships, evolution of species, biomonitoring as a method of conservation of authentic genofounds of species and the ecosystem. Cytogenetic achievements were used in the diagnostics of aberrant genetical forms and in the prevention of their distribution throughout the population. The development of information system has given rise to a new approach in Cytogenetic research and at least 10 megaprogram systems have been developed for detailed cariotype analyses. The introduction of new methodology and technics could secure precise cytogenetical analyses, detailed gene mapping and a fruitful application of genetic advances in biotechnology and embryotechnology.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
A CYTOGENETIC STUDY OF INTERSPECIFIC SUNFLOWER HYBRIDS (H. annum L. x H. occidentalis Riddel)
Jovanka ATLAGIĆ
Institut za ratarstvo i povrtarstvo, Novi Sad
H. occidentalis is a diploid, perennial sunflower species whose phylogenetic origin and genetic relationship has not been as adequately as studied other species from the genus Helianthus. The objective of this paper was to study the possibility of crossing H. occindentalis with cultivated sunflower. The meiosis of the species and the HF1 hybrid was analyzed by the aceto-carmine method (Georgieva, 1976) and pollen vitality by the method of coloring (Alexander, 1969). Three hybrid combinations were obtained from the cross between cultivated sunflower and H. occidentalis. A low percentage of irregularities (fast and lagging chromosomes) occurred during the meiosis of H. occidentalis. Chromosome bridges and fragments were not detected. Chromosome pairing in diakinesis was normal (17 bivalents). High pollen vitality (90.81-97.68%) was observed. In the HF1 interspecific hybrids, several irregularities occurred during meiosis. The average number of bivalents per meiocile was 13.39. The percentage of meiocites with bivalents was 82.35%. Besides bivalents, univalents (9.19% of meiocites) and multivalents (8.46% of meiocites) were also detected in diakinesis. Fast chromosomes in metaphase I, lagging chromosomes in anaphase I and telophase II were detected in a high percentage of meiocites. Chromosome bridges and fragments were detected in 10.52% of meiocites. Pollen vitality in the HF1 hybrid was low (3.72-52.94%). The results obtained show that, although these are species with an identical number of chromosomes, differences exist in the chromosome structure. This indicates that the genome of diploid, perennial species differs from the genome of annual species. The question remains open whether the basic number of chromosomes (17) in the sunflower represents a single genome or several genome.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
THE DISTRIBUTION OF CONSTITUTIVE HETEROCHROMATIN AND NUCLEOLUS ORGANIZERS IN LIZARDS OF THE FAMILY LACERTIDAE (SAURIAJ)
Jelena BLAGOJEVIĆ i VUJOŠEVIĆ M.
Odeljenje za genetiku, Institut za biološka istraživanja "Siniša Stanković", Beograd
The family Lacertidae is characterized by karyotipic uniformity. Almost all species have the same number and morphology of chromosomes, 36 acrocentric macrochromosomes and 2 microchromosomes. The structure of chromosomes of eight species from the family Lacertidae (Podarcis sicula, P.muralis, Lacerta viridis, L. trilineala, L. meliscllensis, L. taurica, L. agilis and Alroides nigropunctatus) was analyzed regarding the distribution and amount of constitutive hetcrochromatin, and the presence and localization of nucleolus organizers. Interspecies variability in the number and position of nucleolus organizers was detected. The presence of constitutive heterochromatin in the centromeric region was the same for all species while terminal and interstitial localization of constitutive heterochromatin characterized only some of them. Phylogenetic relationships between species in the light of results obtained were considered.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
THE INFLUENCE OF OXYTOCIN ON MITOTIC ACTIVITY AND ACCURRENCE OF CHROMOSOMAL ABERRATIONS IN HUMAN PERIPHERAL BLOOD LIMPHOCYTE CULTURES
N. ĐELIĆ 1, B. SOLDATOVIĆ
1 i M. ANĐELKOVIĆ 2
1 Katedra za biologiju, Veterinarski
fakultet, Beograd
2 Katedra za genetiku, Biološki fakultet PMF, Beograd
The influence of oxytocin (SyntocinonR) on the occurrence of structural and numerical chromosomal aberrations was examined in cultures of human peripheral blood. The limphocyte cultures were treated with four concentrations of oxytocin (0.01 IU/ml, 0.02 IU/ml, 0.05 IU/ml and 0.1 IU/ml) and a negative as well as a positive control was included. The occurrence of chromatid and chromosomal breaks and gaps was evaluated among structural aberrations, and the occurrence of heteroploid and polyploid cells was deceted as measure of numerical aberrations. Within the range of the tested concentrations, oxytocin did not induce significant alterations in the occurrence of structural and numerical aberrations, compared to the negative control level. The level of structural aberrations in the positive control (10 MNNG) was significantly raised, whereas the level of numerical mutations was not significantly changed. In order to evaluate some possible cytotoxic effects, a mitotic index was established for each experimental concentration, negative and positive controls. No statistically significant alterations of the mitotic index values were observed in relation to the control level. On the basis of the results obtained oxytocin did not show genotoxic effects in the tested concentrations.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
THE FREQUENCY OF THE GAP AND BREAK TYPE OF STRUCTURAL CHROMOSOME CHANGES IN INDIVIDUALS OF THE FISH SPECIES STIZOSTEDION VOLGENSE /PERCIDAE/, CAUGHT AT SOME LOCALITIES OF THE RIVER DANUBE
Svetlana FIŠTER i B. SOLDATOVIĆ
Veterinarski fakultet, Beograd
The karyotype of Slizostedion volgense / Pisces, Percidael is presented, together with the number and morphology of chromosomes. The frequency of structural chromosome changes of gap- and break types in individuals caught at four localities of the river Danube: Beška, Zemun, Višnjica and Grocka, was analyzed. The highest mean values of gap- and break types of chromosomal changes were established in fishes from localities m the Danube that were placed downstream from the mounth of the river Sava at Belgrade: at Višnjica and Grocka. The results obtained revealed the presence of genotoxical agents in some of investigated localities. The water of the Danube at the cited localities could be marked as a point of periodic or permanent hazard from a genotoxical point of view.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
DIFFERENT RESPONSES TO GENOTOXIC AGENTS DEPENDING ON THE GENETIC CONSTITUTION
Drinka MERĆEP 1, A. ĐUJIĆ 2, Z. MAGIĆ 2 i M. SIMOVIĆ 2
1 Veterinarski fakultet, Beograd
2 Institut za medicinska istraživanja VMA, Beograd
Ionizing radiation as an undoubtedly genotoxic agent is suitable for comparing responses in different strains of the same animal species. The most competent biological indicator for radiation damage is the presence of dicentric and "ring" chromosomes, wich arc a confident sign that the organism was irradiated. The BALB/C mouse strain is very sensitive, while C57BL/6 is more resistant to ionizing radiation measured with LD50/30. This phenomenon could be explained by genetic factors controlling special physiological functions, which suppose the existence of genetic predispositions for resistance to radiation trauma. The experiment was performed on BALB/C mice which are radiosensitive and whose LD50/30 is 5.98 Gy, and strain C57BL/6 which is more resistant and whose LD50/30 is 8.308 Gy. Animals were sacrificed at different intervals after irradiation: on the first, the fourth and the tenth day. Six animals for each term and from each strain were used. A classical cytogenetic method was used to obtain chromosomes. The results obtained support the fact that an important element in the response of an organism is its genetic constitution.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
THE EFFECT COLCHICINE ON SOME QUANTITATIVE CHARACTERS OF SUGAR BEET
Snežana MEZEI, L. KOVAČEVIĆ i N. ČAČIĆ
Institut za ratarstvo i povrtarstvo, Novi Sad
Triploid sugar beet hybrids are produced by converting diploid genotypes to a tetraploid level. Induced polyploids represent a source of new genetic variability. In sugar beet breeding, multigerm tetraploids obtained by the action of colchicine were used as pollinators for sterile diploids, and monogerm tetraploids as maternal components for diploid and tetraploid multigerm populations. The induction of autotetraploids is based on the mutagenic effect of colchicine on spindule fibres. The function of the colchicine effect on apical mcristcmcs is to convert a high percent of the original genotype to the tetraploid level. Since not all cells were in the phase of active mitotic division, a certain percentage of original genotypes remained at the diploid level. The aim of this study was to compare original diploids and diploids which were under treatment with colchicine but did not change their ploidy level; to determine whether colchicine affected only the spindle fibres or the complex of genes which carry different quantitative characters (root yield, sugar content, yield of polarized and white sugar). An aqueons solution of colchicine was applied to the apical points of growth of the genotypes studied under greenhouse conditions. Cytological analysis was performed according to the aceto-carmine squash method. Sugar beet roots with 36 and 18 chromosomes were analyzed the following year and all plants with mixoploid tissues were removed from the trial. The results of the study showed that differences exist between the genotypes studied and between the original diploid populations, the diploid population which was not transformed to the tetraploid level and the induced autotetraploids with respect to the yield of root and white sugar. Regarding the other quantitative characters studied, the sugar content, K, Na, alpha-N and yield of polarisation sugar, the differences established were not statistically significant.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
A METHOD FOR MAKING NUMERICAL KARYOTYPE ETALONS
B.P. PAVLOVIĆ
Institut za šumarstvo, Beograd
The quantity of chromosome material joined to the centromere is called the "centromere load" (CO). The chromosome length is proposed as a possible measure for intrakarytype comparison of centromere loads. The base for calculating centromere load indices is the arithmetic mean of chromosome lenghts of the karyotype (specific centromere load - SCO). These index values can be used in comparisons of Karyotypes. A mathematical; statistical method has been developed for karyotype analysis. A complex of measured lenghts, calculated single analytical and composed indices that presents a quantity state of one typical chromosome set (karyotype), is called a numerical karyotype ctalon. In addition three subsets of index values are calculated on the basis of means of arms (long, short, or, long and short) lengths. These data subsets represent simulated karyotypes that originate from deletions of all short, or long arms, as well as by centric fissions of all chromosomes. Symbols and formulations for measuring and calculating quantities are given in an algebraic table form of the numeric karyotype etalon.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
NUMERICAL KARYOTYPE ETALONS Erinaceus europaeus europaeus
B.P. PAVLOVIĆ
Institut za šumarstvo, Beograd
The chromosomes of the published male and female karyotypes of ssp. Erinaceus europaeus europaeus (Folio 52 in An atlas of mammalian chromosomes, eds. Hsu, Benirschcke 1968) have been measured. The data were used for karyometric analysis that is presented in two table sets - numeric karyotype etalons. The ratio of lengths (W) of the longest chromosome to the shortest one in the male karyotype (W=8.4194) was smaller then in the female karyotype (W=9.7079). The indices of centromere loads (H) in the male karyotype decreased from H1 = 1,7988 to H48 = 0,2136 (Y-chromosome was not the shortest one), and in the female karyotype from H1 = 1,8744 to H48 = 0,1931. Unit index values (H=l) were located between H24 and H25 (male), or H26 and H27 (female). Long arm karyotype proportions were PL = 0.6527 (male) and PL = 0.6506 (female). Correlations of sister chromatid lengths in the karyotype were high, male and female: r = 0.9S7 and ρ = 0.986 respectively. The components of H-index variations (male sH =0,577 and female sH =0,573) were higher than for the long arms on Lindices (male sL =0,438 and female sL =0,426), or for the short arms (K-indices) in the karyotypc, (male sK =0,262 and female sK =0,255). Simulations of deletions of all short arms, or long arms, resulted in increased values of the corresponding components of variation similary to simulations of centric fissions of all chromosomes.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
THE RELATION OF VARIATION COMPONENTS INSIDE THE KARYOTYPE OF MAMMALIA AND PISCES: INDICES OF PARTIAL CENTROMERE ARM LOADS AND INDICES OF CENTROMERE LOADS
B. PAVLOVIĆ, i Nevenka PAVLOVIĆ
Prirodno-matematički fakultet, Sarajevo
Each unpublished numeric etalon for the 270 mammalian and piscian karyotypes (B. Pavlović) consists of a value for the relation (PsA=sA/sH) between the chromosome arm variation and the chromosome variation given in units of mean chromosome length for each karyotype. The parameters (PSA) have been compared among taxa and related to 2n value of the karyotypes. The arithmetic mean value of PSA is 1.005, or 1.434 for piscian, and 0.939 for mammalian karyotypes. The parameters ranged from 0.530 to 2.985, or 0.636 to 2.985 (Pisces), and 0.530 to 2.183 (Mammalia). There were several values of 2n with wide ranges of the relation PSA. Specific relations of 2n, PSA have been shown for the represented mammalian orders.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
THE CHROMOSOME COMPLEMENTS OF SOME FISH SPECIES FROM THE CYPRINIDAE FAMILY
Slavica SIMOVIĆ i G. MARKOVIĆ
Agronomski fakultet, Čačak
In this paper the results from a study of the chromosome complements of five fish species from the Cyprinidae family are presented. These species are common in the waters of the Danube basin. Our studies showed that diploid chromosome sets of the analyzed species consisted of 50 chromosomes (2n=50) as follows: Chondrostoma nasus 15 metacentrics, 15 submctacentrics, 12 subtelocentrics and 8 telocentrics; Alburnoides bipunctatus - 8 pairs of metacentrics, 7 pairs of submetacentrics, 6 pairs of subtelocentrics and 4 pairs of telocentrics; Blicca bjoerkna -6 pairs of metacentrics, 7 pairs of submctacentrics, 6 pairs of subtelocentrics and 6 pairs of metacentrics; Abramis sapa - 12 metacentrics, 14 submetacentrics, 10 subtelocentrics and 14 telocentrics and Abramis ballems - 15 metacentrics, 10 submctacentrics, 12 subtelocentrics and 13 telocentric chromosomes when compared with data from the literature. Certains differences regarding the morphological types of chromosome of certain fish species were established.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
A LARGE ACROCENTRIC CHROMOSOME IN THE FIRST PAIR OF AUTOSOMES IN NATURAL POPULATIONS OF Mus musculus, Linne 1758
Z. STANIMIROVIĆ 1, Mirjana
VUČINIĆ 2, B. SOLDATOVIĆ E. HERZOG 1
1 Veterinarski fakultet, Beograd
2 Poljoprivredni fakultet, Beograd - Zemun
In this study, polymorphism of chromosomes in natural populations of Mus musculus was examined. The investigations were conducted in 5 different localities (Sevarice, Glušci, Lipolist, Bogatić, Sremska Mitrovica) in North-West Serbia, around the Sava and Danube. Besides the frequent finding of a Robertsonian type of chromosomal polymorphism, the presence of one large acrocentric chromosome in the first pair of autosomes, unusual for the mouse karyotype, was observed in a large number of investigated animals. By the application of appropriate cytogenetical methods, it was established that the altered chromosome had two additional insertions, located in ICs and IE regions. Based on the results obtained from the karyotype tests in mice and data from the literature, it can be concluded that the observed acrocentric chromosome resulted as an adaptation of mice to an increased quantity of environmental, agrochemical and industrial pollutants in the localities investigated.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
CYTOGENETIC CHARACTERISTICS OF PLANTLETS REGENERATED BY IN VITRO WHEAT (Triticum aestivum L.) ANTHER CULTURE
S. ŠESEK
Institut za ratarstvo i povrtarstvo, Novi Sad
Cytogenctic analysis of 189 green plantlets regenerated by in vitro Triticum aestivum L. anther culture was performed. A haploid number of chromosomes (2n=3X=21) was found in 49.2% of the studied plantlets, while 41.3% of plantlets had a diploid number of chromosomes (2n=6X=42) in somatic cells. This means that 90.5% of green plantlets were either polyhaploids or hexaploids. Haploaneuploids, i.e. polyhaploids with 2n=19, 20 or 23 chromosomes, occurred with the frequency of 2.1%, while the frequency of diploaneuploids (hexaploids with 2n=40, 41, 43 or 44 chromosomes) was 4.2%. Only 2 polyploids were found: one with 2n=8X=56 and one with 2n=9X=63 chromosomes, which was 1.1% of the total number of analyzed plantlets. There was 2.1% of mixoploids, i.e., of plantlets with cells with a haploid and diploid number of chromosomes.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
CHROMOSOMES OF FROGS FROM THE FAMILY RANIDAE (ANURA, AMPHIBIA) -A COMPARATIVE ANALYSIS
N. TANIĆ, Olivera SPASIĆ, Jelena BLAGOJEVIĆ i M. VUJOŠEVIĆ
Odeljenje za genetiku, Institut za biološka istraživanja "Siniša Stanković", Beograd
Chromosomes of a few species of the genus Rana (Anura, Amphibia) from different localities have been compared concerning the number and position of the nucleoli organizer region (NOR), as well as the amount and distribution of constitutive heterochromatin regions. All species had the same number of chromosomes (2n=26), but there were differences in their morphology. Polymorphism in the number and position of NORs in chromosomes has been found. It was shown that polymorphism in the distribution and amount of C-bands also existed. In spite of the variability of these chromosome characteristics in the genus Rana, we can generally say that constitutive heterochromatin is most commonly present in centromeric and telomeric regions, and rarely in the interstitial region. In most species NOR is localized in a single pair of small submetacentric chromosomes.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
"ROSOL", AS AN EVENTUAL INDUCOR OF POLYPLOID TYPE CHROMOSOME ABERRATIONS
Marijana VUČINIĆ 1, Z. STANIMIROVIĆ 2, B. SOLDATOVIĆ 2
1 Poljoprivredni fakultet, Beograd - Zemun
2 Veterinarski fakultet, Beograd
Rosol (VZ-Zemun) is an anticoagulant rodenticide, with sodium-warfarin as the active substance. The appearance of cytogenetical changes in meiotic testicular cells of experimental mice, during a seven day treatment with "Rosol" was studied. The substance was administered by gastric tube in a dose of 0.13 mg per kilogramme of body weight. Cytogenetical tests revealed an induction of structural and numerical aberrations of the polyploid type in cells of the germinative epithelium. The results obtained supply additional information on the effects of anticoagulant rodenticides and to explain the appearance of resistant strain of rodents.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
INTERPOPULATION POLYMORPHISM OF B-CHROMOSOMES IN YELLOW NECKED WOOD MICEAPODEMUS FLAVICOLLIS (MAMMALIA, RODENTIA)
M. VUJOŠEVIĆ i Jelena BLAGOJEVIĆ
Odeljenje za genetiku, Institut za biološka istraživanja "Siniša Stanković", Beograd
Populations of yellow necked wood mice (Apodemus flevicollis) are often characterized by the presence of B-chromosomes. Samples from nine localities (total of 669 animals) were compared for the presence of Bs. In all samples, except one, Bs were present, but in significantly different frequencies (0.11-0.64). It was found that the difference in the frequency of animals with Bs was dependent on the type of environment, altitude and the sex. Significant differences in the frequency of animals with Bs were associated with the sampling time, and the age category.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
CHROMOSOME ABERRATIONS FOUND BY CORDOCENTESIS
Slavenka ADŽIĆ 1, Stefanija MARKOVIĆ 2, D. PLEĆAŠ 2 N. RADUNOVIĆ 2 i Z. PILIĆ 2
1 Institut za ginekologiju i akušerstvo, Beograd
2 Institut za ginekologiju i akušerstvo KCS, Beograd
Along with other methods, in the Institute of Gynecology and Obstetrics, cordocentesis is used. The indications arc: the age of pregnant women (36-47), foetus malformations, a slowing down if intrauterine development, oligoamnion, hydroamnion, etc., which are detected by ultrasound at regular check ups. In the group of older pregnant women (173), 21 (12.14%) chromosome aberrations were found. In 88 pregnancies with disordes discovered by ultrasound 13 (14.77%) chromosome aberrations were detected. In all cases of abnormal karyotype termination of the pregnancies was performed.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
IN VITRO GENOTOXICOLOGICAL CHARACTERISATION OF IVERMECTIN AND PRAZIQUANTEL
Nevenka ALEKSIĆ
Veterinarski fakultet, Beograd
The effects of the antiparasits ivermectin and praziquantel in PHA-stimulated human lymphocyte cultures were observed. Genetic effects were evaluated by the determination of sister-chromatid exchange frequencies (SCE). Both drugs proved to be genotoxic in certain concentrations in our test system. Ivermectin was tested in the concentrations 0.15, 0.30, 0.60, 1.20 and 2.40 ug/ml of medium. Concentrations higher than 0.15/ug/ml induced a statistically significant increase of SCE. Praziquantel was added in the doses of 2.84, 5.68, 11.36, 22.72 and 45.44 ug/ml of medium. The drug statistically increased the SCE frequency in the concentrations of 2.84, 5.68 i 11.36 ug/ml; in higher doses it produced mitotic arrest.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
A CEPHALOMETRIC ANALYSIS OF PATIENTS WITH KLINEFELTER'S SYNDROME
M. BABIĆ i M. MICIĆ
Institut za biologiju i humanu genetiku, Stomatološki fakultet, Beograd
Sex chromosomal aneuploidy has an influence on cranial growth and the shape and position of craniofacial structures. Twenty-eight adult males with Klinefelter's syndrome were analysed and compared with a control group. Linear and angular measurements were taken from the lateral cephalograms of all subjects under the same conditions. Reduced cranial growth and a specific craniofacial morphology in men with an extra X chromosome was recorded. The influence of the extra X chromosome on cranial base growth, facial height, maxilla, mandible and intermaxillary relations were analysed. The effects of sex chromosomes imbalance on craniofacial structures was discussed.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
THE DEGREE OF GENETIC HOMOZIGOSITY IN A SAMPLE OF PSYCHIATRIC CLINIC PATIENTS AND IN HEALTHYREPRESENTATIVES OF PRIŠTINA INHABITANTS
S. BRANKOVIĆ i G. SAVIĆ
Prirodno-matematički fakultet, Priština
The presence of homozygously recessive characters ("HRC-TEST') has been verified for 29 qualitative morphophysiological systems, and compared in a sample of /A/ 140 patients from the Psychiatric Clinic in Priština, and /B/140 healthy individuals as a control sample. The average presence of HRC's was found to be significantly greater in the A-group, amounting to 8,8 (i.e. cca. 30%), whereas it was much lower among healthy individuals, both of Albanian (6,2) and of Serbian (6,5) nationality (i.e. 22% of studied traits). The frequency distribution of the analysed characteristics was also significantly different, suggesting a population-genetic difference between samples A and B. This difference was especially emphasized in 8/29 of the traits studied.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
THE DEGREE OF GENETIC HOMOZYGOSITY AMONG PATIENTS WITH CONGENITAL HIP DISLOCATION AND A CONTROL SAMPLE CONSISTING OF SCHOOL CHILDREN FROM BELGRADE
Suzana CVJETIČANIN i D. MARINKOVIĆ
Biološki fakultet, Beograd
Assuming that congenital dislocation of the hip (CDH) is a genetically controlled disease, we made a hypothesis that an increased homozygosity level, as well as decreased variability in the patients, could be a population-genetic parameter for the prediction of the illness. Taking into consideration the experience of numerous scientists who studied the nature of the inheritance of mono- and oligogenically controlled qualitative traits, we applied a methodology to estimate the proportion of such homozygosly recessive characters ("HRC-TEST") in samples of diseased and healthy/control individuals. After analysis of 21 HRC's, it was found that 17 of them were significantly more frequent among 93 children from Belgrade. The average number of HRC's in the two samples was 7.1 + 1 and 5.2 + .1, respectively. The described methodology can be used for further analyses, with the hope that it can be applied as an early prognosis for decreased resistance to different diseases.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
A HIGH INCIDENCE OF H-ras GENE POINT MUTATIONS IN TWO TYPES OF HEAD AND NECK NEOPLASIAS
N. DEDOVIĆ 1, J. MILAŠIN 2, V. PETROVIĆ 3, G. STAMENKOVIĆ 1, M.
GAVRIĆ 3, Z. NIKOLIĆ 3
1 Institut za nuklearne nauke, Vinca
2 Institut za biologiju i humanu genetiku, Stomatološki fakultet
3 Klinika za oralnu i maksilofacijalnu hirurgiju, Stomatološki fakultet, Beograd
The DNA from 17 specimens of pleomorphic adenomas of the salivary glands (PA) and 9 specimens of squamos cell carcinomas of the lip (SCC) has been screened for the presence of activating mutations in the H-ras gene (codon 12,13 and 61), known to be involved in the pathogenesis of various human neoplasias. Using a sensitive technique of hybridization with synthetic oligonucleotide probes on an in vitro amplified tumor DNA, point mutations, mainly in codon 12 of the H-ras gene, were detected in 6 specimens of PA (35%) and 5 specimens of SCC (55%). G->C and G->T transversions at the first position of codon 12 were the predominant base substitutions in PA and SCC, respectively. This high incidence of mutated ras genes suggests that their alteration may play an important role in the pathogenesis of some head and neck neoplasias, benign as well as malignant.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
THE ROLE OF GENETIC FACTORS IN THE ETIOPATHOGENESIS OF CARDIOVASCULAR DISORDERS
Vukosava DIKLIĆ 1, Marija KOSANOVIĆ 1, Milica TODORIĆ 2, M. VUKOTIĆ 2, S.P. STOJKOVIĆ 2
1 Institut za biologiju i humanu genetiku
Medicinskog fakulteta Univerziteta u Beogradu, Beograd
2 Dom zdravlja Rakovica, Beograd SM
Our genetically oriented study is a part of the Rakovica study of CVD (RASCO). Having in the mind that the appearance of early CVD is grouped in families in a way that strongly indicates the importance of genetic factors, our intention was to identify high risk individuals and families for preventive measures. A study was undertaken of 176 probands (69 men and 107 women) who had some of risk factors of CVD or CVD itself before the age of 55 (men) and 65 (women). The control group consisted of 45 young and, healthy men and 28 women. Family grouping of CVD risk factors and CVD was investigated among 944 relatives of probands and 450 relatives of control subjects. The prevalence of the CVD risk factors: hipertension, dyslipidaemia, diabetes mellitus and CVD in relatives of probands was significantly higher (p< 0.001) than in relatives of controls. A positive correlation between the clinical phenotype of probands and the prevalence of CVD risk factors and CVD in their relatives was evident. Male and female probands, with hypertension as a single risk factor, had 43.3% and 46.0% relatives with CVD. In probands who had two or more CVD risk factors, or risk factors combined with CVD, this percentage was higher, 50.9% and 54.0% respectively. The mortality of CVD risk factors or CVD was significantly higher (p<0.005) in relatives of probands than in relatives of controls. Our study confirms the general agreement that genetic factors are operative in CVD as well as in the three major risk factors for the development of CVD.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
CYTOGENETIC ANALYSES REVEAL "ATYPICAL CELLS" IN THE PERITONEAL DIALYSIS EFFLUENT
Nada DIMKOVIĆ, Vitana KOSTIĆ, Dragan JOVANOVIĆ i Nada BARJAKTAROVIĆ
Kliničko-bolnički centar "Zvezdara", Beograd
Cytogenetic analyses were performed on dividing cells from the peritoneal effluent of 26 patients (pts) undergoing chronic peritoneal dialysis (CPD). Numerical and structural abnormalities of the karytype served as diagnostic criteria for "atypical cells". The following cytogenetic abnormalities were observed in 7 patients: hyperdiploidy (in 6 pts), hypodiploidy (in 2 pts) and marker chromosomes (in 2 pts). In three patients more than one chromosome abnormality was present. Dividing cells with normal mitoses were observed in 11 patients while in the remaining eight patients no dividing cells could be found. There were no differences in age, sex, duration of dialyses and the incidence of peritonitis between patients with pathological mitoses and those without them. The question of whether this unexpected finding is a consequence of an immunosuppressed uremic status, dialysis procedure or some other factor(s) remains to be elucidated.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
HISTOLOGIC FINDINGS IN THE OVARY OF A TURNER'S SYNDROME PATIENT
B. ĐORĐEVIĆ, D. MIHAILOVIĆ, D. STOJANOVIĆ, C. KUTLEŠIĆ, M. ČEKEREVAC, Z. POPOVIĆ i Z. STANKOVIĆ
Institut za patologiju, UKC, Niš
The 45,XO karytypc is characterized by Turner's syndrome. Typical clinical features of 45,XO Turner's syndrome arc short stature, primary hypogonadism, infantile genitalia, pterygium collu, cubitus valgus, a shield-like chest with widely spaced nipples, lymphedema and a variety of congenital malformations such as a horseshoe kidney and coaretation of the aorta. In this paper, histologic finding in the ovary of a 16-year-old girl with Turner's syndrome arc presented. Histologically, the ovary consisted only of the stroma and structures which are normally found in the ovarian hilus: rete tubules and clumps of cells that closely resamble Leydig cells. Follicles are totally absent.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
A REPORT OF A 9p/10p FAMILY TRANSLOCATION
Slobodanka GRKOVIĆ i Vesna IVANOVIĆ-DERETIĆ
Dečja klinika Medicinskog fakulteta, Beograd
This report describes a family in which two members of the same generation, both phcnotypically normal, had a balanced translocation carrier 9p/10p. In this family four children were malformed. One of them had an unbalanced karytype: 46,XY,-9 +der/9/t/9:10/p22;q24/pat. In this report we have discussed the clinical manifestation of partial monosomy 9p- and partial trisomy 10p+. Prenatal diagnosis was done in the next two pregnancies. Healthy children were borrn.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
GENETIC DETERMINANTS IN THE PROGNOSIS OF NEUROBLASTOMA
Marija GUĆ-ŠĆEKIĆ, Dragana ANĐELKOVIĆ, V. JURUKOVSKI i Gordana PILIĆ-RADIVOJEVIĆ
Institut za zdravstvenu zaštitu majke i deteta RS, Beograd.
Neuroblastomas are characterized by distinct genetic features. Human neuroblastoma cells often carry cytogenetic abnormalities signalling an amplification of the gene N-myc. In most cell lines amplified N-myc is localized in homogeneously staining regions (HRSs) of chromosomes and on double minute chromosomes (DMs). Neuroblastomas arc genetically complex and there are at least two distinct loci for the putative suprcssor gene (Ip and 14q) that are deleted independently. Both of them are associated with advanced stages of the disease. 40 NB patients were subjected to cytogenetic analysis and 2 of them were analysed both aytogenetically and by fluorescent in situ hybridization for the presence of the amplified N-myc gene. In 19 cases cytogenetic analysis revealed normal karyotypes. Near-tetraploid cells were found in mosaic with normal cells in 14 cases and were correlated with advanced stage of the disease. HSRs were present in karyotypes of 4 patients and were correlated with a poor prognosis. Deletion or loss of hetcrozygosity (LOH) for the short arms of chromosomes 1 and 11 in mosaic with normal cells or near-tetraploid cells were found in 2 patients in stages III and IV. The cytogenetical analysis in one case with an advanced stage of disease revealed LOH for Ip and 3p. FISH performed in two patients with HSRs showed the presence of the amplified N-myc gene.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
A REPORT OF AUTOSOMAL WHOLE ARM TRANSLOCATION
Vesna IVANOVIĆ-DERETIĆ, Slobodanka GRKOVIĆ i B. GARŽIČlĆ
Dečja klinika Medicinskog fakulteta, Beograd
This report deals with the possibility of the identification, segregation and transmitting of an autosomal whole arm translocation based on a case of 46,XY, t/2p5p;2q5q/. Two pregnancies were miscarried. In the third pregnancy an unbalanced karyotype was found. In the fourth pregnancy prenatal diagnostic was done and the karyotype was balanced: 46,XY, t/2p5p;2q5q/.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
A POPULATION GENETICIST IN (PRE) CLINICAL PRACTICE CONCERNING CHRONIC WIDE-SPREAD NONCONTAGIOUS DISEASES
Zorica JANAKOVA
Dom zdravlja, Jagodina
This review presents the work of our medical workers (population geneticist, doctor-assistant, nurse and laboratory technician) that is based on continuous control of chronic wide-spread noncontagious diseases. It is based on, sistematical, primary and rational prediction and prevention of: allergic diseases particularly bronchial asthma in childhood, diabetes and related diseases, and other diseases with polygene multifactorial etiology. Besides laboratory tests and consultations. This center also includes a population-genetic, laboratory and (pre)clinical educational treatment of the individual and families with hereditary liabilities and a genetical high-risk factor. Population-genetictreatment includes the selection of individuals (families) with established genetical and environmental factors of risk. Selection is systematically performed among pregnant women and women who have just given birth and relatives of patients, who arc, in endangered business firms, schools and other groups and also at high-risk ages in order to diagnose the susceptibility. The first person (family) who is selected significantly rationalised further laboratory treatment, even if it concerns a high degree of atopy, immunological defects, homozygote elevated genotype, or other aspect of family susceptibility to diseases with allergic reactions, or to the early stages of diabetes. Such an approach to this massive pathology, makes it possible that early stages become available for further (pre)clinical-educational treatment and continuous monitoring aimed at prediction or dela of the clinical manifestation.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
THE SIGNIFICANCE OF PRELIMINARY
SELECTION OF PERSONS ATRISK IN SYSTEMATIC CHECKUPS FOR THE DETECTION OF EARLY
STAGES OF DIABETES MELLITUS
Zorica JANAKOVA
Dom zdravlja, Jagodina
From the aspect of population genetics and medical practice, genetical, constitutional, physiological and environmental parameters for the most effective selection of individuals with a decreased tolerance to glucose (DGT) neve been established in order to diagnose liability to diabetes mellitus we also wish to emphasize the high efficiency and economy of the suggested method of systematic checkups for the detection of early stages of diabetes mellitus which included preliminary selection of individuals for OGTT. For example every third person (adult) should take the OGT-test. As a result, 40% of the tested persons will be found to decreased tolerance to glucose. Moreover, only every seventh woman who has just given birth or pregnant woman would need to be tested in order to detect gestational diabetes in one third of the tested women. Using the experience of the genetic counselling office for small groups of medical workers in public medical centres in order to search for latent stages of diabetes, to prevent its clinical manifestation, and to suppress other wide-spread noncontagious diseases.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
HUMORAL FACTORS IN THE VARIABILITY OF ALLERGIC REACTIVITY
Zorica JANAKOVA
Dom zdravlja,
Jagodina
A group of 300 children with allergic reactivity (AR) have been observed clinically, genetically and in the laboratory (IgE, IgA, IgM, IgG, IgD, alfalantitrypsin, transferrin, haptoglobin, coeruloplasmin, alfa2-macroglobin i C3-and C4-complement). In the genetic counselling unit for chronic common noninfectious diseases. Increases in the degree of atopy and severity of allergic diseases were not followed by continued changes of the frequency of pathological levels of serum immunoglobulins, plasma-proteins and components of complement, but with a high degree of heterogenezity and individual variability. Humoral imunodeficiency and amplified chronic nonallergic inflammation take part in the appearance of AR with moderate severity and with a moderate or normal degree of atopy. High AR and it severest clinical forms are etiopathogenitically relatively autonomous and primarily depend on the high degree of atopy. A moderately high AR is more frequently followed with extreme deviations of the lavels of the plasma proteins and components of complement, or there are moderate deviations from normal values. There are two exceptions: alfal-antitrypsin (extremely low values are characteristic for the highest level of AR) and hepatpglobin (increased and decreased values often follow high AR). The form of the variability of humoral factors follows the other forms of genetic and environmental variability of AR.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
CHROMOSOME ABERRATION AND THE CB MIKRONUCLEI TEST AS COMPARATIVE METHODS FOR BIOLOGICAL DOSIMETRY OF IONISING RADIATION
Gordana JOKŠIĆ
Klinički centar Srbije Institut za medicinu rada i radiološku zaštitu "Dr Dragomir Karajović", Beograd
The cytochalasin B micronuclei test as a new method in biological dosimetry is based on the fact that many chromosomal aberrations (dicentric chromosome, ring chromosome, excess eccentrics, chromosome breaks, incomplete chromatid type of aberrations, triradials and isochromatid deletions) pose problems during anaphase resulting in the formation of micronuclei. There is an almost ideal congruity of results on the chromosome aberration frequency and the CB micronuclei test, in the aberration yield after acute irradiation. For low X and gamma irradiation doses (0.1-05 Gy), the calibration curve is linear in character (defined by the mathematical expression y=c+aD. The lowest dose hat could be determined by this method for X-irradiation is 0.1 Gy, and for gamma irradiation 0.15 Gy. For irradiation doses of 0.1-4 Gy, X and gamma calibration curves have a linear-quadratic shape defined by the mathematical expression y=c+aD+/3D . The highest irradiation dose which can be reliably determined is 4 Gy. The CB micronucleus test has an advantage as a method because from one sample several thousand lymphoblasts can be analysed and therefore a more objective pattern of radiation damage from non-uniform irradiation and internal contamination with radionuclides can be obtained. The specificity of dicentric chromosomes as chromosome aberration representing the most reliable indicator that has been irradiated a cell should be further retained as an irreplaceable biodosimetric parameter in accidental overexposures and occupational pathology.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
A FREQUENCY ANALYSIS OF GENETICALLY CONTROLED QUALITATIVE CHARACTERISTICS AMONG WOMEN WITH BREAST CANCER IN THE HIGH RISK GROUP AND CONTROL INDIVIDUALS
Dragana JOVANOVIĆ i D. MARINKOVIĆ
Biološki fakultet univerziteta u Beogradu, Beograd
A study of patients with a family syndrome (PFS=26), patients without a family syndrome (PWFS=44), a high risk group (HR=70) and a control sample (C=70') has shown the existence of population - genetic differences in the presence of 10 selected homozygously recessive characteristics (HRC-test) and observed dermatoglyphic characteristics. We found a statistically significant difference between the PWFS and C sample, also between the PWFS and HR group for two traits. PFS and HRC samples showed in comparison with the C group a significant difference for only one characteristic. We also detected a significant difference in the number (0-6/6) of HRC's between the PWFS and C group, as well as between the PWFS and HR sample. The comparison between PFS and control values was almost statistically significant. PWFS on the average had a decreased number of HRC s (1.9) similar to PFS (2.0), while the HR group had on average 2.4 HRC s, and for the C sample the average homozigosity was detected as 2.7. A dermatoglyphic study also showed a difference between the studied groups. We noticed a difference in the frequency distribution of 28 observed dermatoglyphic patterns between PFS and the control, also between PWFS and the control sample. Three dermatoglyphic patterns did not appear in group C, but they were present among patients and the HR sample with a frequency of about 3%. The percent of individuals containing six or more whorls was highest in the PWFS (16%), next in the HR group (14%} and in PFS (11%), and lowest in the control sample (7%). Comparison of ABO and Rh blood group frequencies among the four samples did not show statistical significance.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
EUROCAT IN VOJVODINA
J. JOVANOVIĆ-PRIVRODSKI, A. KRSTIĆ, F. POPIĆ-PALJIĆ, R. ALEKSIĆ i G. RACA
Medicinski fakultet, Institut za zdravstvenu zaštitu dece i omladine, Novi Sad
Today the European standard for registration of congenital anomalies is EUROCAT wich starlet to be used 1979 in West Europe. EUROCAT registration was used in Vojvodina in 1992. Of 15,025 newborns 404 malformed cases were found wich gave an incidence of 2.68%.Thc EUROCAT register shows:
1) epidemiological data and the geographical distribution of malformed persons,
2) environmental agents which give malformations (level of teratogenesis) and mutations (level of mutagenisis)
3) the malformed newborns who need treatment
4) the measures for a preventive program
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
THE HLA SYSTEM - A GENETIC MARKER FOR PRENATAL DIAGNOSIS OF INUSLIN DEPENDENT DIABETES MELLITUS (IDDM) - Case report
J. JOVANOVIĆ-PRIVRODSKI, A. KRSTIĆ, F. POPIĆ-PALJIĆ, Z. PILIĆ
Medicinski fakultet, Institut za zdravstvenu zaštitu dece i omladine, Novi Sad
Prenatal classification of the HLA system DR locus and its association with HLA DR3, DR4 and DR3,4 for insulin dependent diabetes mellitus is used in genetic consultations for the determination of genetic risk. Our patient was a pregnant woman who had a child with diabetes (HLA classification DR3\4). She wanted to know the possible risk for the next child. She was recommended a prenatal classification of the HLA system by the method of cordocentesis in the 20th week of pregnancy. The HLA classifications in fetal blood was DR 4,6. The risk for this locus was 29% but if the DR locus had been 3, 4 the risk would be doubled (68%). The patient was informed of the risk and she decided to have the child.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
GENETIC INVESTIGATIONS OF CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASES
Vesna KNEŽEVIĆ 1, Vukosava DIKLIĆ 2, Marija KOSANOVIĆ 2 i N. VOJVODIĆ 3
1 Medicinski centar, Mladenovac
2 Institut za biologiju i humanu genetiku, Medicinskog fakulteta, Beograd
3 Gradski zavod za gerontologiju, Beograd
Familial grouping of Cardiovascular Diseases (CVD) and CVD risk-factors is a well known phenomenon. Our family study was undertaken in 132 young women who had a hypertension and some of them had other CVD risk factors as well. The control group consisted of 74 young of 74 young women without hypertension. Familial grouping of CVD risk factors and CVD was investigated among 642 first degree relatives and 1039 second degree relatives of probands and 378 first degree relatives and 654 second degree relatives of control subject. The prevalence of hypertension in the first and second degree relatives of patients was significantly higher than in the relatives of control subject (p<0.001, rr 1.7; p<0.002, rr 1.6). The prevalence of CVD was significantly higher only in the mothers of patients (p<0.02). Comparisons of the lipid status in examined and control groups showed that in the hypertensive group mean values of triglycerides were significantly higher and levels of HDL-cholesterol significantly lower, while levels of both serum total cholesterol, and LDL cholesterol were not significantly higher. The part of these investigations which relates to the association of lipid levels and DNA polymorphisms for apo B was published in Genetika, Vol 25, 1, 1-19, 1993.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
THE PARENTAL ORIGIN OF THE X CHROMOSOME IN A PATIENT WITH A ROBERTSONIAN TRANSLOCATION AND TURNER'S SYNDROME
M. KRAJINOVIĆ 1,2, K. IVANOVIĆ 3, L. MESTRONI 2, V. DIKLIĆ l i J. NIKOLIŠ l
1 Institut za biologiju i humanu genetiku, Medicinski fakultet, Univerzitet u Beogradu, Beograd
2 Internacional Centre for Genetic
Engineering and Biotechnology, UNIDO, Trieste, Italy
3 Pedijatrijsko odeljenje Opšte bolnice, Pančevo,
We give a report on a proband with both a paternally inherited Robertsonian translocation and Turner s syndrome. A study of the parental origin of the X chromosome performed by microsatellite analysis indicates paternal origin of the X chromosome (Xpat). The occurrence of chromosome aberrations as a consequence of interchromosomal interactions is discussed.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
THE REGISTRATION OF CHROMOSOMAL ABERRATIONS USING THE METHODOLOGY OF D.S.BORGOANKAR
A. KRSTIĆ, M. KOVAČEVIĆ, G. RACA, F. POPIĆ-PALJIĆ, J. JOVANOVIĆ-PRIVRODSKI, R.
ALEKSIĆ, N. ČAMBER, R. MADŽAR, V. ČIHI, Lj. GAĆINA, N. MITROVČAN i Lj. MALEŠEVIĆ
Data about chromosomal aberrations from cytogenetic laboratories from all over the world has been collected and registered for more then 25 years in a computer center at the University of Delaware. The idea about the registration system comes from Prof. D.S. Borgoankar, who is the Head of the Cytogenetic laboratory at the Medical Center in Delaware. In order to benefit from the advantages of this efficient system for registration, we developed practical software for PC and PC compatible computers. This software is designed to register, sort and print data about chromosomal aberrations. It uses the methodology of D.S. Borgoankar and has functioned since 1993. Information about most chromosomal abnormalities diagnosed so far in the cytogenetic laboratory of the Children's Hospital in Novi Sad are already stored in its data base (total of 554 cases for the period from 1969 until March 1994). Work on the registration goes on continuously and data for the year 1993 were sent to the World's Registry in Delaware. Using REPOS (from the English word REPOSITORY) we obtained a good insight into the result of our work. We also have capability for a better follow-up in the future. We have improved our communication with the World's Central Register so that we can use all of its advantages. This software can be used for the registration of chromosomal aberrations diagnosed in all laboratories on the territory of Yugoslavia.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
MORAL AND ETHICAL ASPECTS OF PRENATAL DIAGNOSIS IN HEREDITARY DISEASES
M. KRSTIĆ, Stefanija MARKOVIĆ i Slavenka ADŽIĆ
Institut za ginekologiju i akušerstvo KCS, Beograd
Prenatal diagnosis of inherited diseases includes interventions which have ethical and logical concerns. When disorders of the foetus are found, a decision about its fate needs to be made. It is usually made on the basis of genetic analysis and the knowledge that the disorders will become apparent during later life. According medical to ethics, prenatal diagnosis and the decision about the termination of the pregnancy, fall within the domain of genetic counselling. The decision is usually made on the basis of doctor's and geneticist’s opinions, as well as the attitude of parents who are told about which disorders are expected in their child. Doctors and geneticists have many dilemmas about their standpoint and attitude in counselling the parents to terminate the pregnancy. These problems concerning the treatment of chromosome constitution XYY, XXX and other variants including different types of mozaicisms, appear at the Institute of Genecology and Obstetrics. The authors want to stress the difficulties in decision making in the mentioned cases including moral dilemmas and the question of who is, in general, to judge whether a life is worth living or not.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
CYTOGENETIC INVESTIGATIONS IN
MEDICAL GENETICS
Živana LACA
Centar za Medicinsku genetiku
Institut za mentalno zdravlje, Beograd
Cytogenetic methods are widely used in various studies in our Center for Medical Genetics. 1. Investigates of the etilogy of certain diseases and syndromes. The development and application of differential staining of chromosomes anabled the detection of a large number of numerical and structural chromosomal aberrations in certain diseases and syndromes. In research of this type we are faced with structural changes which require the involvement of experts in different fields (cytogeneticst, molecular biologist, endocrinologist, etc.). 2. The prevention of the birth of children with chromosomal aberrations - Prenatal analysis of fetal karyotype is made in all cases where indications exist. It is rather difficult to give advice regarding certain findings and their interpretation. 3. The prevention of malignancy - In the group of patients with gonadal dysgenesis and dysfunction, cytogenetic analysis reveals the presence of a male karytype in some female patients with gonadal dysgenesis or testicular feminisation. This enables timely surgical intervention and elimination of nondifferentiated gonads which show a tendency to malignancy. 4. An explanation of the development of certain disturbances at a chromosomal level - Analysis of chromosomal polymorphisms and particularly the application of the NOR staining method enables a checking of the origin of the chromosomal non-disjunction. 5. A follow-up of some processes at the cell level like mitotic division of aberrant chromosomes, cell kinetics in some syndromes, etc. 6. Testing hypotheses about the genesis of chromosomal aberrations. 7. Investigation of the mutagenic effects of some agents. Cytogcnctic analysis significantly contributes to problem solving in ontogenetics, evolution genetics, etc.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
THE USE OF FLUORESCENT IN SITU HYBRIDIZATION FOR MARKER CHROMOSOME IDENTIFICATION IN PATIENTS WITH TURNER'S SYNDROME
Milena LUDOSKI 1, Ljiljana LALIĆ 2, Vera POPOVIĆ 2, V. JURUKOVSKI 4 i Angelina NOVAK 1
1 Laboratorija za Humanu Genetiku Instituta za Hematologiju i Instituta za Endokrinologiju, Univerzitetsko - kliničkog centra, Beograd,
3 Laboratorija za Citogenetiku, Vojno - medicinske Akademije, Beograd
4 Inslitut za Molekularnu Genetiku i Genetičko inženjerstvo, Beograd
During the identification of marker chromosomes in patients with congenital disorders cytogenetists have been faced with a lot of difficulties, despite progress in various specialized staining techniques. However, the new method, fluorescent in situ hibridization (FISH) with chromosome-specific DNA probes offered a solution to this problem. The two patients, described below, have phenotypes of Turner's syndrome and mosaic karyotypes. Only slightly more than naif of the patients with Turner's syndrome are monosomic for the X chromosome. Most of the remaining patients have a second lineage of cells which contain a structurally normal or abnormal X chromosome. Cytogenetic analysis performed by HG-banding techniques, revealed mosaic karyolypes, 45,XO/46,X,r(?), in both patients. Also, in both cases the discovered marker chromosome resembled ring chromosomes. The only differences were in the percentage of abnormal cells and size of ring chromosomes. Fluorescent in situ hybridization was performed on the same slides after cytogenetic analysis. The biotinylated probe, pBam X5, was composed of alphoid, tandemly repeated sequences unique to the X-chrornosome centromere. The ring chromosomes were shown to be derived from the X chromosome in both female patients. Routine cytogenetic studies, using the Q-banding technique, excluded the presence of the brilliantly fluorescent end of the Y-chromosome long arm on these two ring chromosomes. In conclusion, a combination of cytogenetic methods and FISH with chromosome-specific DNA probes significantly increases marker chromosome identification and provides a means for more accurate diagnosis.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
RING (15)-A CASE REPORT
B. LUKIĆ, Nada BARJAKTAROVIĆ, Nada
TODOROVIĆ i Vitana KOSTIĆ
Kliničko-bolnički centar "Zvezdara", Beograd
The authors present the case of a female newborn with a low body weight of 2300g at birth, two weeks before term. Body length was 43cm, head circumference 30cm. There were two signs of malnutrition, visible stigmata occurred only on the extremities which were short, especially the upper arms, and both feet were with an outstanding metatarsus various. There was a small umbilical hernia. All analyses were within physiological limits. Neurological status O.K. Cytogenetic analysis showed the karyotype 46,XX,r(15)(pl2,q26). Literature data of this syndrome are very few, but the clinical features reported arc in agreement with our case. Except for an obvious deformity of both feet, other phenotypic changes were not present. For the ring formation to appear, a double deletion has to occur, both on "p" and "q" arms, which means that some deficit of genetic material certainly exists.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
CHROMOSOMAL ABERRATIONS IN THREE OVARIAN TUMORS
Ljiljana LUKOVIĆ 1, Jelena MILAŠIN 2, N. ARSENOVIĆ 3 i Vukosava DIKLIĆ 1
1 Institut za Biologiju i Humanu genetiku, Medicinskog i
2 Stomatološkog fakulteta, Beograd,
Ginekološko-akušerska klinika, KBC, Beograd
Three samples of ovarian carcinomas were subjected to cytogenetic analysis. Two were histological serous adenocarcinomas and one a cystadenocarcinoma. The patients were not under chemo- or radiotcraphy. Chromosomes were obtained by direct preparation and stained using the GTG technique. Extensive and complex numerical and structural alterations were seen in all specimens. Chromosomal numbers were in the range of 27-29 (in one mitosis 400 chromosomes). Gross marker chromosomes characterized all tumours. We were able to indentify always, partially or completely, the origin of marker chromosomes, due to complex rearrangements involving small portions of chromosomes. Chromosomes #1, #3, #6, #7, and #11 were most frequently involved in structural aberrations. Double minute chromosomes (DMs) were seen in one patient and a homogeneously staining region (HSR) was found in another.
The chromosomal aberration 6q- described as a specific change in ovarian tumours, was found in 2 cases. Furthermore, the recurrence of specific regional chromosome losses and breakpoints suggests a localization of genes that play a role in the formation and progression of some ovarian tumours.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
GENETIC HOMOZYGOSITY AND NORMAL vs. PATHOLOGICAL HUMAN VARIATION
D. MARINKOVIĆ, D. JOVANOVIĆ, S. CVJETIČANIN i S. BRANKOVIĆ
Biološki fakultet Univerziteta u Beogradu, Beograd.
The degree of individual genetic homozygosity has been estimated according to the presence of cca. 30 qualitative homo-recessive characters ("HRC-TEST") in sample of healthy and diseased individuals. In the majority of such studies a significant increase in HRC's has been determined among patients with a number of diseases (e.g., Endemic nephropathy, Muscular dystrophy, Diabetes mellitus, Chronic lymphcytic leukaemia, Congenital hip dislocation, Ca uteri). A similar or lower mean homozygosity has been established in samples of patients with Acute appendicitis, Bronchial asthma, Bronchogenic carcinoma, Breast cancer, showing, however, a significant difference in the frequency distribution of the studied traits. Further applications of HRC-testing may have a practical use in genetic counselling, since they seem to be in correlation with the individual's resistance to different diseases.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
THE INFLUENCE OF SEX CHROMOSOMAL ANOMALIES ON SPERMATOGENESIS
Miroslava MIĆIĆ
Institut za biologiju i hum. genetiku, Stomatološki fakultet, Beograd
Sex chromosomal abnormalities were found among males treated for infertility. Different deletions of Yq were the most frequent structural anomaly usually affecting the patient's fertility. Other structural aberrations are rare and we have observed the following: 47,XisoXqY; 45,X 46,XisoYq; 45,X 46,XringY; 46,Xt(Y;13). All patients had azoospermia. Testicular biopsy showed the presence of a spermatogenic process in all cases except in the patient with the 47,XisoXqY karyotype. Patients with anomalies of Y chromosome and X monosomy cell line had all spermatogenic stages with a lower number of cells in the later stages of the process. The 45,X cell line was not observed in dividing testicular cells. Analysis of diakinesis-Metaphase I showed bivalent anomalies which affected the later stages of spermatogenesis. The influence of Y chromosome aberrations on the spermatogenic process and fertility of patients is discussed.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
THE NUCLEAR VOLUME IN PATAU'S SYNDROME
D. MIHAILOVIĆ, Z. STANKOVIĆ, B.
ĐORĐEVIĆ, V. MIHAILOVIĆ i M. ČEKEREVAC
Institut za patologiju Medicinskog fakulteta, Niš
Kariometric parameters have sometimes been used in histopathology, because of the well-documented correlation between the nuclear volume and the quantity of DNA. In this study, the mean nuclear volume of various cells was estimated in trisomy 13 patients (patau's syndrome). From 3 newborn infants, an unbiased estimate of the mean nuclear volume (Vv) was obtained after standard formalin fixation, paraffin-embedding, sectioning and hematoxylin-eosin staining, using the equation VV=I03∙π/3 where I0 is the length of an intercept measured in a random direction trough a test point, which hits a nucleus. Compared with control newborn infants, there was a significantly lower mean nuclear volume of hepatocytes and endocrine cells of the pancreas in patients with Patau's syndrome. These results indicated that DNA content and mean nuclear volume may provide partly independent biological information.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
THE FREQUENCY OF ACROCENTRIC ASSOCIATIONS IN WOMEN WITH SPONTANEOUS ABORTUS
V. MIHAILOVIĆ, Z. STANKOVIĆ, D. MIHAILOVIĆ i D. STOJANOVIĆ
Institut za patologiju Medicinskog fakulteta, Niš
In the human karyotype 5 pairs of acrocentric chromosomes have been show to carry nucleolar organizer regions and have a tendency for intragroup associations or clustering. It has been reported that the frequency of associations of acrocentric chromosomes decreases in older individuals, as compared to middle aged persons. The aim of this paper was to investigate the incidence of acrocentric associations in women with spontaneous abortions. Metaphases from lymphocyte cultures were studied. The frequency of satellite associations were higher in women with spontaneous abortions, compared to controls. We conclude that the frequency of satellite associations may indicate the possibility of nondisjunction of chromosomes during mitosis.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
H-ras GENE MUTATIONS IN HUMAN URINARY TRACT TUMORS
Jelena MILAŠIN 1, Nasta DEDOVIĆ 2, S. MIĆIĆ 3, B. DIMITRIJEVIĆ 2, Vukica DIKLIĆ l
1 Institut za biologiju i humanu genetiku,
Stomatološki fakultet, Beograd
2 Institut za nuklearne nauke, Vinča, Beograd
3 Urološka klinika Medicinski fakultet, Beograd
Alternation of ras oncogenes and subsequently of the encoded p21 proteins, has been implicated in the pathogcnesis of various human malignancies. Members of the ras gene family (H, K and N ras) become activated, i.e. acquire the transforming potential, by point mutations in codon 12, 13, and 61. The DNA from 32 urothelial cancers (transitional cells carcinomas of the bladder, urether and pelvis) and 22 kidney cancers (renal cell carcinomas) was screened for the presence of Ha-ras gene mutations. Using the technique of oligonucleotide hybridization on in vitro amplified tumor DNA, H-ras mutations at 12 and 13 were detected in 7 out of 32 transitional cell carcinoma specimens (22%) and in 3 out of 22 renal cell carcinoma specimens (13.6%) The predominant mutations were G->A transitions at codon 12, precisely GGC->AGC (glycine->serine) and GGC->GAC (glycine->aspartic acid) in urothelial tumors, and at codon 13 in kidney tumors (GGT->GAT, i.e. glycine-> asparagine). The 18 % overall incidence of mutated ras genes suggests that ras gene activation docs not represent the crucial event in urinary tract tumor development, at least not in the major part of the tumor population.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
THE REACTION OF HUMAN T LIMPHOCYTES TO MAFOSFAMIDE AND 5-FLUOROURACIL IN VITRO
Olivera MILOŠEVIĆ-ĐORĐEVIĆ l i Nada BARJAKTAROVIĆ 2
1 Prirodno matematički fakultet, Univerzitet u Kragujevcu, Kragujevac ,
2 Klinička bolnica grada Beograda, Beograd
The effects of the alkylating agent: mafosfamide and the nucleic acid analog 5-fIourouracil were tested, as they are the most frequently used drugs for chemotherapy of cancer. It is known than cyclophosphamidc does not act per se as an alkylant, but in vivo undergoes metabolic activation. Mafosfamide is a derivative of 4-hydrooxycyclophosphamidc and it is active in vitro and in vivo. We tested the ability of these agents to induct chromosomal aberrations in human lymphocyte cultures which were PHA activated or not. The drugs were tested in the cone, of 9 ug/ml for mafosfamide and 11,4x10 M for 5-fluorouracil. Analysis of the frequency of chromosomal aberrations in control nontreated lymphocyte cultures from the same persons was carried out concomitantly. Maosfamide and 5-flourouracil induced significant increases of chromosomal aberrations frequency in cultures which were not PHA activated in the period of treatment (5,7*** and 6,9***). In contrast to 5-flourouracil, mafosfamid induced a significant increases of chromosomal aberration frequency also in cells which were PHA stimulated in the period of treatment by the agents (9,9*** and 1.2). Mafosfamide significantly induced the following types of aberrations: chromosomal (49%) and chromatid breaks (36%), achromatid lesions (30,5%) and dicentric (2%). 5-fluorouracil induced aberrations only of the break type.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
A CITOGENETICINVESTIGATION OF CHROMOSOMES IN PATIENS WITH INCONTINENTIO PIGMENTI
S. MINIĆ 1. M. KOSANOVIĆ 2 i B. PETROVIĆ 2
1 Klinika za kožne bolesti, UKC, Beograd ,
2 Institut za biologiju i humanu genetiku, Medicinski fakultet, Beograd
Incontinentio Pigmenti (IP), also known as Block-Sulzberger syndrome or Bloch-siemens syndrome, Bloch Siemens syndrome, is a rare, complex genodermatosis, in which skin changes are often combined with other organ and structure anomalies of ectodermal origin. It occurs nearly exclusively in females. The high percentage of heredity (55,4%) and female to male ratio of 17:1 suggest that some genome anomalies could be the cause of the sickness. Although a many questions concerning IP have not been solved, our investigation of the family pedigrees of our probands attempts to confirm its heredity and discover the way it is inherited. We also examined their karyotypes (probands and their family members) in order to determine if they were positive for IP which), and whether it was due to chromosome aberrations or gene mutations. Our results indicated that 10 out of eleven affected examines came from families in which more than one family member was affected which confirmed the heredity of the disease. A pedigree analysis was in favour of the X linked do minant type of heredity. IP is transmitted from mother to daughter. There are no affected males in the proband's pedigrees. Although heredity has been proved, cytogenetical analysis of all affected examines showed a normal karyotype.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
Ag- NORs IN NORMAL HUMAN POPULATION
J.NIKOLIŠ 1, V. KEKIĆ 2, S. MIĆIĆ 3, V. DIKLIĆ 1, M. RISTANOVIĆ l
1 Institut za biologiju i humanu genetiku Medicinskog fakulteta Univerziteta u Beogradu, Beograd
2 Biološki fakultet, Univerzitet u Beogradu,
Beograd
3 Urološka Klinika UKC u Beogradu, Beograd
The activity of nucleolus organizers regions (NORs) in lymphocytes of 49 males aged 11-74 years and 48 females aged 18-74 years was analysed. The aim of this study was to examine if there are any variations in the frequency of Ag-stained NORs in different age and sex groups. The results obtained indicate a significant difference in the number of active NORs between males and females. There is no correlation, however, between the number of active NORs and the age of the individual.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
INTERPHASE CYTOGENETICS: THE DETECTION OF THE GENOMIC CONSTITUTION OF THE OVARY (PARAFFIN-EMBEDDED SECTIONS) IN A PATIENT WITH TURNER'S SYNDROME AND CHROMOSOMAL MOZAICISM
Angelina NOVAK 1, Đ. KOKAI 2, Vera POPOVIĆ 3, Milena LUDOŠKI l, V.
JARUKOVSKI 4
1 Laboratorija za Humanu Genetiku, Institut za Hematologiju, Beograd
2 Odeljenje Patologije Ginekološko-Akušerske klinike, Beograd
3 Institut za Endokrinologiju, Univerzitetsko-Kliničkog Centra, Beograd i
4 Institut za Molekularnu genetiku i Genetičko inženjerstvo, Beograd
The difficulty of detecting sex chromosome mosaicism cytogenetically hinders the establishment of an acceptable explanation for the phenotype-genotype discrepancy amongst these patients. Fluorescence In Situ Hibridization (FISH) permits the genomic identification of patients with mosaic karyotypes in interphase nuclei by utilising the X-chromosomc-specific DNA probe ("interphase cytogenetics"). We evaluated the efficiency of "interphase cytogenetics" in the detection of the genomic constitution of the ovary from a patient with Turner's syndrome with mosaicism (46,XX/46,XO) that was previously established by blood limphocyte karyotyping. We used alphoid rcpctitative sequences specific for the X chromosome and a biotin-labclled probe, PBamXS. An examination of ovarian sections and blood lymphocytes by FISH showed persistence of both cell lines 46,XX/45,XO in each. The genomic constitution of the germ cell/oocyte in an ovarian primordial follicle was shown to be normal (46,XX). Our results: l. showed a high applicability of interphase cytogenetics on paraffin sections, 2.indicatcd the possibility of genomic screening of diverse tissues for routine cytogenetic investigation, 3.offered a reliable methodological approach for defining an accurate percentage of abnormal karyotypes in mosaicism of different organs and non-dividing tissues.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
A CASE OF MONOSOMY 22
Ivana NOVAKOVIĆ 1, Olga ANTONOVIĆ 2, Slavenka ADŽIĆ 2 i Svjetlana MAGLAJIĆ 3
1 Institut za biologiju i humanu genetiku, Medicinski fakultet
2 Institut za ginekologiju i akušerstvo, KCS, Beograd
Univerzitetska dečja klinika, Beograd
A new case of monosomy 22 is described in a female newborn. The child had facial dysmorphy, bilateral corneal opacity, elongated, disproportional toes and muscular hypotony; a systolic heart murmur was detected. Chromosome analysis showed the karyotype 45,XX,-22,inv(9)mat. The newborn died shortly after birth. A post-mortem examination showed a persistent truncus arteriosus type HI, an atrial septal defect and a persistent left superior vena cava. Our case is compared with other cases of monosomy 22 with or without mosaicism.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
A GENETIC SURVEY OF A FAMILY WITH REPEATED POLYDACTYLISM
V. NOVOSEL
Medicinski institut Univerziteta Crne Gore, Podgorica
A case of a family with a marked frequency of occurrence of polydactylism on both hands and feet has been described. Anamnesic data indicate that the occurrence of this phenomenon originates from the second (II) generation, and it is completely developed in the fourth (IV) generation in three sisters, who were subject of our examination. This anomaly becomes apparent in the form of a sixth finger; from the x-ray one can clearly sec the developed metacarpal bone from the distal side of their arms and legs. The analysis of metaphase chromosomes and sex chromatin indicates this to be a normal karyotype with 46,XX. From the data given one can conclude that this anomaly has occurred as a consequence of a gene mutation which became apparent in the fourth generation.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
FAMILIAL 46,XY GONADAL DYSGENESIS
Vesna PENDIĆ 1, Vera
POPOVIĆ 2 i Angelina NOVAK 1
1 Laboratorija za Humanu Genetiku, Institut
za Hematologiju, Beograd
2 Institut za Endokrinologiju, Univerzitetsko-Kliničkog Centra,
Beograd
The Swyer syndrome, in its complete form is characterized by female phenotype (bilateral tubes, a uterus and a vagina), primary amenorrhea and 46,XY karyotype. This prevalence of gonadal neoplasms: gonadoblastoma and germinoma, is high. We present a patient with a normal female phcnotype, primary amcnorrhea and 46,XY karyotype. This patient, also, had a unilateral ovarectomy with the diagnosis of disgcrminoma. Cytological investigation, using the Q-tcchnique, confirmed that epithelial cells from the patient's buccal smear contained a brilliantly fluorescent "Y-body". Cytogenetic investigation, with HG-banding, of blood lymphocyte metaphases revealed the 46,XY karyotype without any structural rearrangements on the Y chromosome. The discrepancy between genotype and phenotype may be explained by investigations of the patient's sister with the same clinical (normal female with primary amenorrhea) and cytological (46,XY) status. Finally, all these facts indicate that 46,XY, gonadal dysgenesis is a familial disease inherited as an X-linked recessive trait.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
ABO BLOOD TYPE FREQUENCY IN SOME LUNG DISEASES
D. PEŠUT 1, D.
MARINKOVIĆ 2
1 Institut za plućne bolesti i tuberkulozu, Klinički centar
Srbije, Beograd
2 Biološki fakultet P.M.F. Univerzitet u Beogradu, Beograd
The frequency of ABO blood types was analysed among patients (Pts) with lung tuberculosis (LTB), hydatid lung disease (HLD) and bronchogenic carcinoma (BC). The diagnoses had been established at the Institute of Lung Diseases and Tuberculosis of Serbia and all of the cases. The frequency variations of ABO blood types in Pts's groups were compared to those found in Yugoslav population and the differences tested using the χ2 test. In the group of Pts operated on for HLD (N=84) blood type A was significantly decreased comparing to the frequency found in the Yugoslav population. Blood type B and AB frequencies were increased but without significance. In the group of LTB Pts including 79 individuals with both the fibrocaseous cavernous (FC) form and specific pleural disease (PD), blood type O was significantly decreased compared to the frequency in the general type population. A significantly increased frequency of blood type B was found among LTB Pts with the FC form of the disease, while blood type O was increased in LTB Pts with PD. In the group of BC Pts (N=105) there was no significant difference in ABO blood type frequencies compared to that in the Yugoslav population, i.e, the differences decrease with increase Pis' number. The result favour genetic predisposition / resistance to LTB as well as to the form of the disease and are an addition to controversial findings in the last two decades which have not taken into account the form of the disease. This study speaks in favour of a genetic influence even in parasitic lung disease. Individuals with blood type A seem to be more resistant to HLD than those with B and AB types.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
GENETIC COUNSELLING OF MARRIED COUPLES IN CASES OF EFFECTS OF HARMFUL ENVIRONMENTAL NOXES
F. POPIĆ-PALJIĆ, A. KRSTIĆ, J. JOVANOVIĆ-PRIVRODSKI, R. I ALEKSIĆ i G. RACA
Institut za zdravstvenu zastitu dece i omladine, Novi Sad
The main purpose of genetic counselling work is the prevention of the birth of children with hereditary and congenital anomalies. In order to estimate the quantity of teratogenous environmental effects, we have made conducted an analysis of couples who visited our genetic counselling service in a four year period because of the effects of harmful environmental noxes during pregnancy. Out of the total of 995 couple's, 362 visited us because of possible harmful environmental effects. Due to the use of medications and work with harmful chemicals 159 couples come to see us, which accounted for 16,75% of the total number of women examined in our service. Out of that number 30,82% took antibiotics, 17,6% sedatives and anxiolytics, 13,8% analgetics. Antiallergies were used less (6.28%), antieptileptics 4,4%, hypnotics 1,25%. Medications which could not be included in these groups made up 21,38%. Because of harmful chemicals, paints and lacquer, 4,4% women came to see us. Pregnancy infections or contacts with infectious agents brought 127 women (13,29% from the examined group). The most common causes of their coming to our service were rubella infections (15,74%), varicella (14,96%) and herpes simplex type I 13,4%. Influenza was frequent (18,11%), as well as other infections (bacterial sore throat, sinusitis, urinary infection and respiratory tract infection 27,55%. there were no cases of AIDS and Hepatitis B. Due to the fear of X-Rays or other radiation exposure 76 couples came (7.96%). The fetus was directly radiated only in the case of pelvic X-ray diagnostic procedures in 22 (28,95). Considering the number of pregnant women who are exposed to teratogenic stimuli (according to data in the literature), we think that the number of women coming for this reasons should be greater.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
THE USE OF MODERN SOFTWARE IN DIAGNOSING RARE SYNDROMES
F. POPIĆ-PALJIĆ, A. KRSTIĆ, J. JOVANOVIĆ-PRIVRODSKI, G. RACA i R. ALEKSIĆ
Institut za zdravstvenu zaštitu dece i omladine, Novi Sad
In our everyday work in the genetics department of our Institute we use two SOFTWARE PROGRAMMES which are of grca help to us in diagnosing rare syndromes. They are LDDB (London Dysmorphology Data Base) of British authors and POSSUM (Pictures of Standard Syndromes and Undiagnosed Malformations) by Australian authors. The SOFTWARE functions as follows: all the patients symptoms are fed in and the machine offers a certain number of syndromes on the basis of the given symptoms. As the given syndrome is frequently unknown, on can use the syndrome vocabulary that contains a detailed syndrome description, data with references from the world literature, examples of patients with a corresponding syndrome, at different ages including patients photographs and their X-rays. Diagnosis is made by detailed analysis and comparison of the patient understudy to those obtained from the software. In addition to the syndrome vocabulary, the software contains a symptom dictionary as well. Both of them play an important part in education. In one of our patients born on September 11, 1986 in Bugojno, who was hospitalized because of a chest deformity with frequent respiratory infections, the diagnosis of Spondylothoracic dysplasia was made thanks to POSSUM. On the basis of the given symptoms: postnational growth arrest, abnormal rib number (ribs 3-8 are absent), scoliosis and udescended tests, the software offered these diagnoses: l. Jarcho-Levin syndrome(Spondilothoracic dysplasia) and 2.Simpson-Colahi Behmel syndrome. After careful comparison we chose the diagnosis of Spondilothoracic dysplasia which is autosomal-recessively inherited.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
FRAGILE SITES AND ONCOGENES AS A POSSIBLE RISK FOR NEOPLASIA IN CARRIERS OF BALANCE TRANSLOCATIONS
Branka POPOVIĆ, B. GARZIČIĆ i Biljana SPREMO
Institut za onkologiju i radiologiju Srbije, Laboratorija za kliničku i eksperimentalnu onkologiju, Beograd
The hereditary theory of oncogenesis observes the development of neoplasia as a microevolution cither at the oncogene level or at the chromosome level. One type of primary translocation of cells is chromosome translocation (HGL, BURKITT LYMPHOMA etc.). Since primary translocations in cancer include reciprocal translocation on fragile sites (fra), the question is: are FRE a risk for the development of cancer in the human population? We detected translocation sites on chromosomes 1,2,6 and 7 in 1000 constituve balanced cariotypes, and in 100 leukemic cariotypes, and we wished to know if FRA and ONC are present? In 1000 constitutive balanced cariotypes we found an average of 70% translocations on FRA, and 30% on FRA and ONC. Most of the primary translocations in 100 leukemic cariotypes were on sites with FRA and ONC, but break points in oncogenesis may or may not include sites with FRA. The same break points on chromosomes can produce different phenotypes, but the main condition for malignant expression is the break region on a specific site within the ONC itself.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
AN INDUCTION OF FRAGILE SITES ON HUMAN CHROMOSOMES BY APHIDICOLINE AND CYTOSINE-ARABINOSIDE
G. RACA, A. KRSTIĆ, B. GARZIČIĆ, F. POPIĆ-PALJIĆ, J. JOVANOVIĆ-PRIVRODSKI, R. ALEKSIĆ, N. ČAMBER, R. MADŽAR, V. ČIHI, Lj. GAĆINA, N. MITROVČAN i Lj. MALEŠEVIĆ
The capacity of nucleoside - analog 1-bcta-arabinofuranosyl cytosine to induce fragile sites of the aphidicoline type (type 4) on human chromosomes is well documented. Our goal was to check if some fragile sites from this group show special sensitivity to cytosine-arabinoside. We wanted to ascertain if some fragile sites show different expression depending on the agent used for induction (aphidicolin or cytosine-arabinoside). The fragile site most sensitive to induction by aphidicoline was fra 3(pl4.2). The fragile site at Xp22 turned out to be the most sensitive to cytosine-arabinoside. There is a possibility that these differences are based on different molecular composition of DNA segments at different fragile sites (fragile sites especially sensitive to cytosine-arabinoside are expected to be rich in GC base pairs). These results are especially important for the development of more efficient techniques for cytogenetic diagnosis of fragile X. Since we know today that the mutation in fragile X patients consists of amplification of CGG isles, we consider that cytosine-arabinoside is one of the substances that should be tested for its capacity to induce fragile X.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
AN APPLICATION OF THE RECOMBINANT DNA METHOD IN THE PRENATAL DIAGNOSTIC OF CYSTIC FIBROSIS
Dragica RADOJKOVIĆ 1, Ana SAVIĆ 2, J. SAVIĆ 1, P. MINIĆ l i B. BRUKNER-DABOVIĆ
1 Institut za zdravstvenu zaštitu majke i deteta Srbije, Beograd
2 Institut za molekularnu genetiku i genetičko inženjerstvo, Beograd
Cystic fibrosis (CF) is one of the most common autosomal recessive diseases (1 in 2500 live births gives rise to an affected child). Affected persons are homozygous for the mutated CF gene. Regarding the severity of this disease and the high risk (1:4) of couples who are hcterozygons for the mutated gene to have an affected child, it is essential to perform prenatal diagnosis of CF. Genetic prenatal diagnosis of CF can be performed in the first and second trimester of pregnancy. It is possible to perform diect and indirect genetic analysis of the presence of the mutated gene. Direct detection is performed by searching for known mutations within the CFTR gene (F508 is the most frequent one). Indirect detection is performed using RFLPs (Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism) closely associated with the CFTR gene. The development of recombinant DNA techniques, particularly PCR (Polymerase chain reaction) provide precise and fast prenatal diagnosis of CF (within 48 hours). We present our results of the prenatal diagnosis of CF using recombinant DNA methods in the first and second trimester of pregnancy. We discuss the advantages, problems and a proper approach to prenatal diagnosis if this disease.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
A RARE VARIANT OF KARYOTYPE 47,XY,13 IN AML (M2 TYPE)
S. RADULOVIĆ, Nada BARJAKTAROVIĆ i Vitana KOSTIĆ
Kliničko - bolnički centar "Zvezdara", Beograd
A 74 year old patient was diagnosed as ANLL (M2) based on: peripheral blood and bone marrow findings, cystochemical staining and immunophenotyping. Cytogenetic analysis was performed before introducing cytogenetic therapy, both conventional and G-banding techniques on 50 bone marrow metaphases. Trisomy 13 was found as the only disbalance of the karyotype. Neither numerical nor structural changes of remaining chromosomes were noticed. According to the literature data, chromosome 13 is seldom present in chromosome rearrangements in AML, so just the conclusion that this variant of karyotype is connected with poor prognosis is of great importance.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
THE SEGREGATION TYPE, CHROMOSOME AND BREAKPOINT DISTRIBUTION IN PROGENY OF CARRIERS OF RECIPROCAL TRANSLOCATIONS
O. RISTIĆ, Ž. LAĆA, S. NIKŠIĆ, N. ARANĐELOVIĆ i I. TIMOTIJEVIĆ
Institut za mentalno zdravlje, Beograd
A follow-up study for 15 years, resulted in the detection of 35 reciprocal translocations (RT), among 1567 couples with a fertility problem (2,2%). The segregational analysis was done using the Jalbert and Sclc model. Out of the 35 RT the adjaccnt-1 (A-l) type was predicted in 88,5% adjaccnt-2 (A-2) in 3% and 3:1 segregation type in 8,5%. The 3:1 segregational type was significantly less frequent in comparison with similar studies. Regarding the progeny with unbalanced karyotypes, confirmation between the predicted and obtained model was detected in all 8 possible cases. Concerning the chromosome distribution, the most frequent were 2,4,21 which is consistent with Davis RT sample. Chromosome 22 was even less frequent than chromosome 21 leading to discrepancy concerning Davis sample. Break point (BP) positioning was determined using Neri's model in which chromosomes were divided into terminal (T), medial (M) and centromeric (C). A T/S combination was present in 60%, S/S in 17,2%, T/T in 11,4% and C/S and C/T in 5,7% each. The probability of obtaining a normal phenotype and malformed progeny was estimated regarding the total number of pregnancies, liveborn infants and the sex of the carrier parent. Concerning liveborn infants, the risk for an unbalanced karytype was 14,3% while the percentage of infants with normal and balanced karyotypes was equal at 42,8% each. The spontaneous risk rate was 54,5%.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
APHIDICOLIN FRAGILE SITES AS TARGET POINTS FOR IONIZING RADIATION
Biljana SPREMO i B. GARZIČIĆ
Institut za onkologiju i radiologiju, Laboratorija za kliničku i eksperimentalnu onkologiju, Beograd
The application of therapeutical doses of ionizing radiation in 13 patients with Carcinoma Portio Vaginalis Uteri (Ca PVU), indused chromosome mutations in peripheral T lymphocytes. These changes included the occurrence of a high percentage of: dicentric, polycentric and ring chromosomes, acentric fragments and heteroploidy with aberrant chromosomes. Quantification of chromosome aberrations during radioteraphy, showed an increase of their percentage. The quality of chromosome rearrangements was detected by the G-band technique and we used it to find out the break regions on chromosomes which produced dicentrics as the most frequent type of aberrations. We analyzed more than 1300 mitoses in 13 patients during radiotheraphy and found that the break points were not random. Most of the detected break points were on fragile sites of the aphidicolin type.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
LUPUS ANTICOAGULANT ANTIBODIES TO CARDIOLIPIN AND THEIR CLINICAL MANIFESTATION IN SLE PATIENTS AND MEMBERS OF THEIR FAMILIES
L.N. STOJANOVIĆ 1, E. L. NASSONOV 2 i M. STANIĆ 1
1 Institut za reumatologiju Akademije medicinskih nauka Rusije, Moskva
2 Institut za biologiju Medicinskog fakulteta, Beograd
The problem of the discovery of different immune disorders in normal family members of SLE patients and the increased concentration of rheumatic diseases in these families is one of the most difficult aspects in the understanding of SLE pathogenesis. Taking into account the increasing interest in lupus anticoagulant (LA), considered to be an acquired autoantibody-inhibitor of the prothrombinase complex , we included in our study 5 probands with cer SLE (2 male, 3 female) all LA-positive. Probands were 23-34 (mean value 27) yrs old with a disease duration of 2-20 (mean value 8,4) yrs. Three of them (1 male, 2 female) had kidney involvement (during 0,5-11 yrs). Inn all patients elevated levels of anti-DNA, anticardiolipin antibodies were revealed, and 3 had positive ANA. We studied 11 relatives of the 1st degree, and the following clinical symptoms were revealed: Raynaud's phenomenon (5), SLE (1+1 not included in the study who died from SLE in 1969), cryoglobulinemic hemalytic syndrome (1), varication (1), ankylosing spondyloarthritis (1), osteoarthrosis (1) , hypertension (1). Two relatives had noclinical symptoms (but 1 had laboratory changes). We also discovered the following laboratory disorders: 6 certain and 1 doubtful positive LA out of 10, 3 certain and 1 doubtful for positive anticardiolipin antibodies out of 9. We also found such immune disorders as: elevated anti-DNA antibody(S), ANA (2), cryoproteins (l), rheumatoid factor(l). The obtained data permit us to suggest that there can be a correlation between different clinical immunogenetical subtypes of SLE and the possibility of finding clinical and/or laboratory changes in the relatives of SLE patients. Therefore a concrete division of SLE in such subtypes may be helpful for prophylaxis and prognosis in SLE relativies.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
CYTOGENETIC PARAMETERS DURING DIFFERENT TREATMENTS IN PERINATOLOGY
Nada TODOROVIĆ, B. LUKIĆ i Nada BARJAKTAROVIĆ
Kliničko - bolnički centar "Zvezdara", Beograd
The authors present the results of an investigation of the level of sister-chromatid exchanges (SCE) after Progesterone treatment in pregnancy, after Syntocinon treatment in labor, and Luminal + phototherapy treatment in hyperbilirybinemia in newborns. A control group of healthy newborns had a SCE level of 5,55 ±0.62. the results of our investigations were: after Progesterone: 7,99±0.88 and in experiments in vitro up to 13.20±5.07. After Syntocinon treatment both in vivo and in vitro systems showed no significant increase of SCE-s. Luminal therapy also did not show any damage at the genetic level: 5.39±1.84, but phototherapy elevated the level of SCE-s to 7,66±2.18. Taking these results into account, the authors suggest a high censure in the application of Progesterone, and serious evaluation of indications for the use of phototherapy and also its duration.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
MISMATCH RECOGNITION EFFICIENCY. III. MISMATCH RECOGNITION EFFICINECY IN PLANT SUBCELLULAR ORGANELLES
Desanka BOŽIN i Gordana CEROVIĆ
Institut za nuklearne nauke Vinča, Beograd
Chloroplasts and mitochondria of most land plants, have their own DNA which is different from nuclear DNA. They have their own systems for DNA replication, transcription and translation. In fact most of the proteins found in chloroplasts are coded by nuclear genes, synthesized in the cytoplasm and imported into the plastids. A minority of chloroplast proteins are in fact of chloroplast origin, leading to questions about the organization and information content of chloroplast DNA. The studies of DNA repair in plants were limited to the repair of pyrimidine dimmers, strand breaks and alkylating agents damage. Very recently, we demonstrated in vitro mismatch-stimulated and mismatch-specific DNA breakdown in a nuclear extract from normal and transformed Nicotiana tobaco callus. These observations raise some intriguing questions: docs the mismatch repair activity exist in chloroplasts and how docs it function? Like bacterial systems? The same as nuclear? Therefore we sought for a mismatch-specific DNA breakdown in an extract from Triticum sp. ethyoplast. For this purpose we used the same model system as described in the two previous abstracts. Synthetic oligonucleotides were prepared in such a way that C • A and C • C mispairings were formed. We detected mismatch-stimulated and mismatch-specific activity in the extract from Triticum sp. ethyoplast with a reactivity order of preference: G:C <<< C • A << C • C. These findings are different from those which were demonstrated in our previous studies of plant nuclear extract recognition efficiency.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
MISMATCH RECOGNITION EFFICIENCY. I. MISMATCH RECOGNITION EFFICIENCY IN THE MAMMALIAN NUCLEUS
Desanka BOŽIN, Gordana CEROVIĆ i RADMAN
Institut za nuklearne nauke Vinča, Beograd
Institut Jacques Monod, 2 place Jussieu, 75251 Paris Cedex 05, France
A DNA base pair mismatch can be defined as any noncomplementary base pair in the DNA duplex. Mismatched base pairs arise in DNA in the course of DNA replication, recombination and deamination of 5-methyl-cytosine. The mechanisms for mismatch correction of replication errors have been postulated in well studied systems of E. coli, S. typhimurium and S. pneumoniae. Mismatch repair in eukaryotic cells is less well understood. Mismatch rectification has been demonstrated in Saccharomyces cerevisiae, vertebrate organisms and in higher plants. Therefore we sought for a mismatch-stimulated and mismatch-specific DNA breakdown of the DNA in the nuclear extract of rat liver. For this purpose we selected well studied K-ras gene and the vicinity of the frequently mutated gly-12 codon as the model system. Synthetic oligonucleotides were prepared in such a way that the gly-12 triplet was in the middle. A set of 19-mcr oligonucleotides was designed to allow for the concentration, upon annealing, of C • A G:A and C • C mispairings in the middle of the molecule. These elementary duplexes were legated into a size ladder which was the substrate in the in vitro mismatch recognition and mismatch-specific DNA breakdown assays in the nuclear extract of rat liver. We detected mismatch-stimulated and mismatch-specific activity in the nuclei of rat liver cells. An enzymatic analysis yielded a reactivity order of preference at physiological pH: G:C - G:A < C • C <<< C.A. Biochemical analysis suggested that it might be a functional homologue of the bacterial correction system(s).
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
MISMATCH RECOGNITION EFFICIENCY. II. CONFORMATION-DEPENDENT MISMATCH RECOGNITION EFFICIENCY IN THE MAMMALLIAN NUCLEUS
Desanka BOŽIN, Gordana CEROVIĆ i
RADMAN
Institut za nuklearne nauke Vinča, Beograd,
Institute Jacques Monod, 2 place Jussieu, 75251 Paris Cedex 05, France
Very recently, NMR spectroscopy and UV light melting studies have been used to probe the variability in the conformation and stability of the CA, GA and CC mismatches as a function of pH. These analyses have shown the presence of apH-dependent conformation and stability of noncomplementary base pairs. On the other hand, the presence of enzymatic systems specialized in the repair of noncomplementary DNA base pairs is well established. In order to understand the mechanism of mismatch recognition by the repair system, we have studied different pH-dependent conformations of CA, GA and CC containing heteroduplexes, corresponding to the sequence 25-43 of the K-ras gene by enzymatic assays. We detected conformation-dependent differences in the mismatch-specific recognition; efficiency. At pH 4.5, C:A, G:A, and C:C noncomplementary base pairs are protonated, G:A has GSyn: Aanti conformation and all base pairs have two hydrogen bondes. We have detected recognition efficiency and DNA breakdown with the order of preference: G:C = C:C - C:A < < G:A. At pH 7.5 C • A, G:A and C • C noncomplementary base pairs are not protonated. G:A has a Gami '• Aanti conformation and two hydrogen bonds. C • A and C • C have just one hydrogen bond respectively. We have detected the recognition efficiency and DNA breakdown with the order of preference: G:C = G:A < C • C <<< C • A. It is clear that mismatches provoke and promote their own repair.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
THE USE OF MULTIALLELIC HUMAN apoB GENE DNA POLYMORPHISM (3'HVR) FOR DNA TYPING
Sanja GLIŠIĆ, Ivana SAVIĆ i ALAVANIĆ
Institut za nuklearne nauke "Vinča", Laboratorija za radiobiologiju i molekularnu genetiku, Beograd
DNA polymorphism of the hypervariable region on the 3' end of the human apoB gene is a potent genetic marker, because of high heterozygocity (more than 80%). Previously, we found 16 different HVR alleles in the Belgrade population. The hypervariable region is located about l00 bp downstream of the second polyadenyl signal containing tandem repeats 30bp long. DNA was extracted from whole blood, dried blood spots or hairs. DNA fragments were synthesized using specific oligonucleotides and optimal conditions for Taq polymerase. Answers to the questions posed about DNA typing were known after 1,5% agarose gel electrophoresis. Considering both the human diploid chromosomal set and codominant inheritance of HVR alleles, it is a fast, easy and accurate identification in cases with a limited number of persons, for example relatives in the first and the second degree of kinship. The use of this polymorphism in forensic medicine for an accurate establishment of kinship and for other purposes is demonstrated, for example evaluation of the success of bone marrow transplantation, etc.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
APOLIPOPROTEIN B GENE DNA POLYMORPHISMS (EcoRI and MspI) AND SERUM LIPID LEVELS IN A SERBIAN NORMOLIPIDAEMIC POPULATION: INTERACTION OF RARE ALLELES AND SMOKING WITH CHOLESTEROL LEVELS
Sanja GLIŠIĆ, Ivana SAVIĆ i ALAVANTIĆ
Institut za nuklearne nauke "Vinča", Laboratorija za radiobiologiju i molekularnu genetiku, Beograd
The frequency of restriction fragment length polymorphisms (RFLPs) of the apolipoprotein B gene, detected by EcoRI and MspI, and their influence on serum lipids were studied in a total of 239 normolipidaemic subjects from the Belgrade area. The influence of the interaction between different genotypes and smoking was also studied. The relative frequency of both rare R2 and M2 alleles (lacking the cutting site) was similar to that reported in other groups of Caucasians (0.16 and 0.11 respectively). No association was observed between the apoB genotypes/haplotypes and serum lipid levels adjusted by age, BMI and blood pressure, either in the whole sample or in either women or men. When smokers and non-smokers were considered separately, smoking had a significant impact on total cholesterol variability in all individuals with genotype M1M2, and HDL cholesterol variability in women with genotype R1R2. It was shown that the presence of rare alleles of these two polymorphisms in smokers leads to a decrease of lipid levels, either in the whole sample or in both women and men analyzed separately, except for an increase of the HDL cholesterol level in men smokers, heterozygous for EcoRI polymorphism (R1R2).
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
MULTIALLELIC DNA POLYMORPHISM AT TH E 3' END OF THE apoB GENE (3'HVR) AND SERUM LIPID LEVELS IN NORMOLIPIDEMIC INDIVIDUALS
Sanja GLIŠIĆ, Ivana SAVIĆ i ALAVANTIĆ
Institut za nuklearne nauke "Vinča, Laboratorija za radiobiologiju i molekularnu genetiku, Beograd
The influence of the presence of various hypervariable region (HVR) alleles at the 3' end of the apoB gene, the main protein constituent of LDL, on serum lipid levels was studied. The sample from the Belgrade area included 293 normolipidemic persons (162 women and 131 men) chosen randomly. DNA was extracted from whole blood. A Polymerase Chain Reactin (PCR) method was performed for the amplification of the specific sequence, and reaction products were analyzed on agarose gel. Statistical analysis was made considering risk factors such as age, sex, smoking, blood pressure and body mass index. 16 different alleles whose sizes depend on the number of repeats (from 26 to 54) containing 15 predominantly A and T nucleotides were found. The most frequent alleles contained 34 and 36 repeats (34HVR and 36HVR). The association of the particular genotype and serum lipid variation was analyzed after the sample was divided into 6 groups depending on allele combinations which have an equal, higher or lower number of repeats than 36 (36HVR, > 36HVR AND < 36HVR). It was shown that DNA polymorphism of this region has a significant influence on LDL cholesterol variation in women. Also, women with genotype > 36HVR/ = 36HVR have the highest values of both total and LDL cholesterol, as well as triglycerides.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
AN INSERTION/DELETION POLYMORPHISM IN THE SIGNAL PEPTIDE OF THE apoB GENE
Sanja GLIŠIĆ, Ivana SAVIĆ, Nadežda RADOJA i ALAVANTIĆ
Institut za nuklearne nauke "Vinča", Laboratorija za radiobiologiju i molekularnu genetiku, Beograd.
The signal peptide of human apolipoprotein B (apoB) gene shows a polymorphism resulting in the variable peptide length. Because the signal peptide is involved in the translocation of apoB across the membrane of the endoplasmic reticulum, a loss of hydrophobic aminoacids could affect apoB translocation and quantity of lipoprotein particles. The purpose of our work on this polymorphism was: I. to detect Ins/Del polymorphism in the Belgrade population, the number of alleles and their frequencies, 2. to register an association between this polymorphism and the variation in lipid levels. DNA was extracted from whole blood of 237 normocholestcrolemic and 52 hypercholestcrolemic persons. A Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) with specific oligonucleotides (ID14'CAGCTGG CGATGGACCCGCCGA3' and ID25'ACCGGCCCTGGCGCCCGCCA GCA3') in optimal conditions for Taq polymerase in the presence of 10%DMSO resulted in two DNA fragments with different lengths. A longer fragment with 93bp, coding 27 aminoacids, named Ins (insertion) allele and a shorter one with a length of 84bp, coding 24 aminoacids, called Del (deletion) allele were found. Visualization of PCR products on 8% polyacrylamide gel after silver staining enabled the detection of 19.7-49,2% more heterozygote’s for the Ins/Del polymorphism tahn in all other normolipidaemic populations that have been studied. Also, the frequency of the Del alclle in the Belgrade population was higher than in other populations. However, statistical analysis (TC test) showed that there was no significant difference in frequencies of tch two alleles (Ins and Del) between the normolipidemic and hyperlipidemic population. There was a linear dependence of Ins allele frequencies among 6 groups of normocholesterolemic persons with ascending lipid values. This tendency was confirmed by a comparison with hypercholesterolemic individuals with high LDL-cholesterol levels.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
EXTRACELLULAR PROTEINASES OF MESOPHILIC LACTOBACILLI
Đ. FIRA, M. KOJIĆ, A. BANINA i Lj. TOPISIROVIĆ
Inslitut za molekularnu genetiku i genetičko inženjerstvo, Beograd.
Strains of mesophilic lactobacilli which produce extracellular proteinases are identified by screening a large collection of natural isolates. In order to determine the substrate specificity of these proteinases, their activity against major casein fractions (asi, β and κ-casein) has been tested. The majority of strains synthesize acid proteinases which predominantly hidrolyse - βcasein. The exception is Lactobacillus divergens 742, a strain which produces a proteinase that hydrolysis all three casein fractions, with the optimum at basic pH values. All proteinses tested are of the serine-type, since their action is inhibited by a specific inhibitor (phenyl methyl sulfonyl fluoride). It was shown in hybridization experiments that total DNA isolated from these strains in most of the cases hybridizes with probes from the lactococcal protcinase gene regions. On the basis of hybridization experiments, preliminary restriction maps of proteinase gene regions of several strains of mesophilic lactobacilli have been constructed, indicating the high level of homology with the lactococcal protcinase gene regions. Among strains which do not hybridize with the lactococcal proteinase probes, the strain Lactobacillus paracasci EN1 is very interesting since it produces exopolysacharide besides extracellular proteinase. The derivative of this strain, obtained by the plazmid curing treatment, besides loss of the capability of exopolysacharide synthesis, also showed increased proteolytic activity.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
THE NUCLEOTIDE SEQUENCE AND TRANSCRIPTIONAL ANALYSIS OF THE nov GENE WHICH AFFECTS THE RESPONSE OF E. coli K12 TO THE ANTIBIOTIC NOVOBIOCIN
Radmila V. IVANIŠEVIĆ, Mirjana M. MILIĆ, Dragana S. AJDIĆ, Milija Z. JOVIČIĆ, Mila J. JANKOVIĆ i J. SAVIĆ
Institut za molekularnu genetiku i genetičko inženjerstvo
The target of the coumarin group of antibiotics in E. coli is the enzyme DNA gyrase (GyrB subunit), which is involved in the control of bacterial DNA supercoiling. Most of the mutants conferring resistance to coumarins map within the gyrB gene (encoding for GyrB protein). In our laboratory the now gene was discovered that affects the response of E. coli K12 to novobiocin (Molecular Microbiology, 1992. 6: 1547-1553). The nucleotide sequence of the nov gene was determined. Nucleotide sequence analysis revealed the presence of an open reading frame 1461 base pairs long. Transcription is driven from the promotor sequence which is recognized by the subunit of RNA polymerase. Two A nucleotides (6 to 7 nucleotides away from the "40" sequence, respectively) were determined as transcriptional start sites.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
REPLICATION AND MUTAGENESIS: ANALYSIS OF A HIGHLY MUTABLE SEQUENCE FROM THE hisC GENE OF E. Coli
Mila J. JANKOVIĆ, Mirjana M. MILIĆ, Radmila V. IVANIŠEVIĆ, Z. JOVIČIĆ i J. SAVIĆ
Institut za molekularnu genetiku i genetičko inženjerstvo
Our previous studies showed that an E. coli strain deficient in DNA polymerase I is a very strong mutator creating mutations of exclusively minus frameshift and deletion types. The hotspot is located within the hisC gene, in the sequence consisting of four consecutive GCTG quadruplets (Mol Gen Genet, 1990. 223:481-486). The analysis of the sequence showed that it contains a four times repeated 3'GTC 5' triplet that is recognized by the E. coli primase. A possible relationship between DNA replication and a very high frequency of mutations arising at this site was analysed using fusions of the relevant fragment from the hisC gene with the lacZ gene, galactosidase is synthesized only if a particular frameshift mutation happens and the sequence recognized by the primase is located either in the leading or lagging strand during plasmid replication.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
lieS AND glnF (ipoN) MUTANTS OF E. coli SHOW AN INCREASED RESISTANCE TO NOVOBIOCIN
Z. JOVIČIĆ, Mirjana M. MILIĆ, Radmila V. IVANIŠEVIĆ, Mila J. JANKOVIĆ i D. SAVIĆ
Institut za molekularnu genetiku i genetičko inženjerstvo, Beograd.
Novoboicin is a coumarin antibiotic which inhibits the enzymatic activities of the GyrB subunit of the topoisomcrase II enzyme. Topoisomerase II is a bacterial enzyme responsible for converting circular DNA to a negatively supercoiled form. It is known that gyrB mutanats and some cysteine (cysB and cysE) mutants show increased levels of resistance to novobiocin (Mol Gen Genet, 1991. 228:307-311). We have isolated isoleucine and glutamine novobiocin resistant auxotrophs by direct selection on novobiocin plates. It has been demonstrated, by monitoring the efficiency of plating of parental strains and isoleucine and glutamine mutants that they do not exhibit resistance to other large hydrophobic antibiotics. Isoleucine and glutamine mutations were mapped by PI transduction experiments. Glutamine mutants carried mutations in the glnF (rpoN) gene and isoleucine mutants carried mutations in the lieS gene. The glnF (rpoN) gene codes the subunit of RNA polymerase and lieS gene codes isoleucyl-tRNA synthetase. Complementation of isoleucine mutants with a plasmid which carries the WT lieS gene has also shown that these mutations in the lieS gene are responsible for novobiocin resistance.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
THE EFFECT OF BIOANTIMUTAGENS ON INTRACHROMOSOMAL RECOMBINATION IN Escherichia coli K12
KNEŽEVIĆ-VUKČEVIĆ, B. ČULJKOVIĆ, M. VULOVIĆ, B. VUKOVIĆ-GAČIĆ i D. SIMIĆ
Katedra za mikrobiologiju, Institut za botaniku i Botanička bašta, Biološki fakultet, Univerzitet u Beogradu, Beograd
The main goal of the expanding research area of antimutagenesis/anticarcinogenesis is to detect inhibitors or modulators of environmental genotoxic agents and to elucidate the mechanisms of their action. There is already considerable evidence for the antimutagenic effect of certain naturally-occurring compounds affecting DNA repair and replication in bacteria and mammalian cells. Antimutagens act through different mechanisms: by chemical or enzymatic inactivation of the mutagen (desmutagens) or by interfering with cellular processes of the mutation fixation (bioantimutagens). The bacterial short-term tests, routinely used to detect environmental mutagens, are recommended for identifying antimutagens. By using the E. coli reversion assay system we have previously found that among differently prepared extracts of cultivated and wild typesage (Salvia officinalis L.) only the CO2, re-extract of cultivated sage, prepared without distillation of ethereal oils (Extract 1), specifically reduced the frequency of UV-induced mutations in the repair proficient strain. In this work we used a set of E. coli K12 strains with different alleles of the recA gene to test whether the bioantimutagenic effect of Extract 1 is due to the enhancement of error-free recombination repair. We measured intrachromosomal recombination between nonoverlapping deletions in the lac operon by monitoring lac recombinants on McConkey lactose plates with or without the plant extract. Two model bioantimutagens, coumarin and tannic acid which enhance recombination and excision repair, respectively, were used to validate the assay system. Extract 1 enhanced the formation of Iac+ recombinants in UV-irradiated or untreated recA+ and recA730 strains, suggesting that its antimutagenic effect is due to the stimulation of recombination.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
A MOLECULAR ANALYSIS OF A LARGE PLASMID pS50-290 IN Lactococcus lactis subsp. laclis biovar. Diacetylactis
M. KOJIĆ, Lj. TOPISIROVIĆ
Institut za molekularnu genetiku i genetičko inženjerstvo, Beograd.
Lactococcus lactis subsp. laclis biovar. diacetylactis was isolated from a buter starter culture. It was established that strain S50 is able to synthesize bacteriocin S50 with a narrow antibacterial spectrum. In addition, it synthesized a proteinase of the Pl-type. Genetic analysis showed that agents encoding proteins and bacteriocin production as well as resistance to bacteriocin are located on a large plasmid pS50-290 (290 kb). Besides this plasmid, strain S50 contained three smaller plasmids of which the smallest had a size of 7 kb (pS50-7). Plasmid pS50-7 is a cryptic one, since derivative S70-20, cured of this plasmid, retained the same growing characteristics as the original strain S50. Hybridization experiments (labelled pS50-7 was used as a probe) revealed that plasmid pS50-2909 contained a sequence homologous to that of pS50-7. In addition, homology between plasmid pS50-7 and a plasmid of approx. 20 kb, present in strain S50, was found. In the conjugation cross between donors S50 Rif, Bac+, Bacr and recipients MG7284 FusR, SpcR, BacS (selection for the resistance to bacteriocin S50 was applied), the transfer of plasmid pS50-290 most probably resulted in its resolution into two plasmids (approx. 283 kb and 7 kb) in transconjugant MGIO. Comparative restriction analysis of the 7 kb plasmid, isolated from transconjugant MGIO, and pS50-7 from the strain S50 showed that they have the same restriction pattern. To distinguish between plasmid cotransfcr (plasmids pS50-7 and pS50-290) and the assumed resolution, PFGE experiments were performed with Smal-digested DNA of the strain S50 and transconjugant MGIO. These experiments gave results which are in favour of plasmid pS5()-290 resolution during conjugation, since pS50-290 has two Smal sites, whereas a plasmid of approx 283 kb in transconjugant MGIO has one. The other Smal site was detected in the 7 kb plasmid of this transconjugant.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
REGULATION OF THE EXPRESSION OF THE sgm GENE FROM Micromonospora zionensis
KOJIĆ, TOPISIROVIĆ, Branka VASILJEVIĆ
Institut za molekularnu genetiku i genetičko inženjerstvo, Beograd.
The strain m. zionensis, producer of antibiotic G-52, has the sgm gene which encodes 16S rRNA methylase responsible for resistance to aminoglycoside antibiotics. This gene possesses complex transcriptional regulation from two promoters, PI and P2. These promoters were subcloned into the promoter-probe vector and it was shown that the P2 promoter had four time stronger activity. The existence of two promoters enables differential gene expression. It was suggested that promoter PI was responsible for the constitutive expression of the sgm gene, while the promoter P2 had a role in the expression of downstream (biosynthetic) gene. Apart from the transcriptional regulation, this gene was regulated at the translational level. In order to prove this, sgm-lacZ gene fusions were used. The level of - galactosidase activity was determined and it was shown that an extra copy of the sgm gene decreased the activity either in cis or in irons position. These results suggested that the expression of the sgm gene is regulated by the translational autorcprcssion due to binding of the methylase to its own mRNA. It was shown by computer analysis that the same hexanucleotide is present 14 bp in front of RBS and in the C-I400 region of 16S rRNA, i.e. the region where most of the aminoglycoside resistance methylases act. This complex mode of regulation of the sgm gene provides enough molecules of methylase to protect the cell from the action of its own antibiotic. On the other hand, if all ribosomes are modified, sgm methylase binds to its own mRNA preventing any further translation.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
RECOMBINANT DNA TECHNOLOGY IN PLANT VARIETY PATENTING AND PROTECTION OF AUTHORS RIGHTS
Kosana KONSTANTINOV, Snežana MLADENOVIĆ, Snezana GOŠIĆ, G. SARATLIĆ, N. DELIĆ, R. PETROVIĆ
Institut za kukuruz, Zemun Polje, Beograd-Zemun
The visible advantage of recombinant DNA technology is its application in plant variety patenting and protection of breeders' rights. This technology enables basic genetic information on the existing genome organization and the identification of specific genome regions in a particular plant genome. Molecular genetic markers such as izoenzymes and restriction fragment length polymorphism (RELP) and their combinations are a powerful tool for plant genotype identification. Gene identification, location, expression and linkages of genes are crucial in plant variety protection. Several gene probes (rDNA, ZE-22, C1, wx-8, wx-9) were used to screen numerous maize genotypes. The results obtained indicated that visible differences could be identified between the investigated inbred lines and hybrids of maize. A combination of izoenzyme pattern and gene location will result in the "plant identity card". Besides existing polymorphism in the plant genome, new genes, originating either from the same plant species or from different plant species, bacteria or viruses could be integrated through gene technology, expressed and inherited through plant generations. These new genes are at the same time genetic markers in genotype identification. The new approach of integration of synthetic oligonucleotides as genetic markers in gene flanking sequences will be presented.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
TEMPERATURE - DEPENDENT ACTIVITIES OF HYBRID Escherichia coli PROMOTERS
KONSTANTINOVIĆ, Sanja IVKOVIĆ i GLIŠIN
Institut za molekularnu genetiku i genetičko inženjerstvo, Beograd
We have studied the effect of temperature on the activities of two hybrid E. coli promoters tac (De Boer, 1982) and PLtl (Konstantinović et al. 1991), which have the same nucleotide sequence of -35, -10 and the transcription start point region, but differ in upstream sequences. One of the promoters, tac carries the sequence for lac I, whilst PHI contains the lalcl and cl repressors binding sites. Our results show that, depending on the temperature, chemically regulated tac and, chemically and thermally regulated PLtl promoter exhibited different levels but similar profiles of activities when fused to the lacZ reporter gene.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
THE ACTIVATION OF ONCOGENES IN HUMAN MYELOID NEOPLASTA
Koviljka KRTOLICA, Nadežda UROŠEVIĆ, Dobrila NEŠIĆ, Ljiljana TUKIĆ, Z. MAGIĆ i B. DIMITRIJEVIĆ
Laboratorija za radiobilologiju i
molekularnu genetiku, Institut za nuklearne
nauke "Vinča", Beograd, Institut za medicinska istraživanja i klinika
za
hematologiju Vojno-medicinske akademije, Beograd.
One of the three borad classes of genes, involved in the transition from a normal cell to a malignant one, are oncogenes. Ras genes are frequently found to harbor a mutation in human mycloid neoplasia. Our aim was to indentify oncogene activation by point mutation or by amplification in genomic DNA, isolated from human peripheral white blood cells of mycloid neoplasia. The PCR amplification and slot-blot hybridization techniques were used for the detection of point mutation of codons 12 or 13, of the N-ras or K-ras genes. Slot-blot or Southern blotting analysis were used for the detection of any amplification of genes: N-ras, K-ras, c-myc and N-myc. The analysis of 4 MDS, 23 AML and 11 CML patients, revealed the prevalence of N-ras mutations (83%) over K-ras mutations (17%). A five to tenfold amplification of the c-myc oncogene was revealed in 24% of AML patients, where half of them had one of the ras mutations. All MDS patients were harboring one of the mutations: either the amplification of c-myc, K-ras and N-ras oncogene or the point mutation in the codon 12 of the N-ras gene. Two of them harboured double mutations. These results suggest that the collaboration between genes, such as ras and myc, might play a significant role in the pathogenesis of some AML and MDS patients.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
GENOTYPE-SPECIFIC ACCUMULATION OF BAR17mRNA IN MAIZE LEAVES DURING DROUGHT STRESS
Vesna LAZIĆ-JANČIĆ, D. KOVAČEVIĆ, A. STEED i S.A. QUARRIE
Institut za kukuruz "Zemun Polje", Beograd-Zemun,
Cambridge Laboratory,AFRC-IPSR, JI Centre, Colney Lane, Norwich, NR4
Plant respond to drought stress by accumulating abscisic acid (ABA). Increased concentrations of ABA, in general, help the plants to adapt to the stress. An increasing number of RAB (Responsive to ABA) genes are known to be induced by drought. Using maize genotypes known to vary in their capacity to accumulate ABA in response to a rapid dehydration-treatment we have shown that accumulation of RAB17mRNA is significantly correlated with leaf ABA content. The threshold for significant accumulation of the RABlVmRNA was between 50 and 140 ng AB/g fresh weight. At a given level of ABA, genotypes also differed in the quantity of this mRNA species.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
INVESTIGATION ON QTL FOR ABSCISIC ACID PRODUCTION USING RFLP MARKERS
Vesna LAZIĆ-JANČIĆ, C. LEBRETON, A. STEED i S.A. QUARRIE
Institut za kukuruz "Zemun Polje", Beograd-Zemun,
La Gourjonnierc, 35680 BAIS, France,
Cambridge Laboratory, AFRC-IPSR, JI Centre, Colney Lane, Norwich NR4
Identification of target molecules involved in beneficial adaptive responses at the whole plant level is a goal of many research groups working on the improvement of plant adaptation to environmental stresses. A major biochemical response to a wide spectrum of abiotic stresses and especially to drought is the increased production of the hormone abscisic acid (ABA). In general, increased tissue ABA concentrations make the plant better adapted to water shortage. The accumulation of ABA by detached and partially dehydrated maize leaves is known to be inherited in a quantitative manner. The location of the genes having a major effect on ABA concentrations in maize was determined using an F2 population of 81 individuals produced from parental lines that differed markedly in ABA content under different types of stress treatments (Polj17, high ABA and F-2, low ABA). Preliminary information on the likely chromosomal location of genes affecting ABA accumulation was obtained using MAPMARKER QTL. About 80 RFLP markers have been mapped coverings every chromosome. Significant QTL for leaf and xylem sap ABA content were located on every chromosome except chromosome 8. The biggest QTL effects on the ABA content of stressed leaves were on chromosomes 2 and 3 (2 loci). These did not coincide with any of the QTL for xylem ABA content and only the QTL on chromosome 2 with leaf ABA content under non-stressed conditions. Three of the QTL (on chromosomes 1, 4 and 5) were associated with more ABA in plants with the F-2 allele.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
RADIATION INDUCED EXPRESSION OF ACUTE PHASE PROTEIN GENES IN RAT LIVER
Z. MAGIĆ, Svetlana MATIĆ i G. POZNANOVIĆ
Institut za medicinska istraživanja, VMA, Beograd
Institut za biološka istraživanja "Siniša Stanković", Beograd
It is well established that ionizing radiation can induce DNA damage (strand breaks, mutation and chromosome aberrations). However, during the last few years increasing data show that ionizing radiation can induce the expression of different genes in eukaryotic cells. It was shown that there exists a kind of cascade in gene activation and that genes which induce the acute-phase protein gene expression are included in this cascade. Acute-phase proteins are a group of plasma proteins with an important role during the general reaction of an organism to different kinds of trauma. Taking these facts into consideration we have measured changes in the concentrations of albumin (Al), fibrinogen (Fb), haptoglobin (Hp), cysteine inhibitor protease (CPI) and i-acid glycoprotein (AGP) in the plasma of irradiated rats (inbred Albino Oxford_AO strain, male rats) after total body irradiation with 12 Gy of gamma rays (absolutely lethal dose). In the liver of irradiated rats the relative concentrations of their mRNA were measured after dot-blot hybridization with appropriate plasmid cDNA probes (nick labelled with 32P-dCTP). The obtained results showed that total body radiation caused a significant increase of plasma concentrations for Hp and Fb (2-3 fold compared tot he control values) and especially for CPI and AGP (4-5 fold), while the Al concentration was not significantly changed. Changes in the relative concentrations of the liver mRNA for Al, Hp, CPI and Fb were in correlation with the observed changes of their protein concentrations in the plasma of irradiated rats. In the case of AGP the increased concentration of protein was not accompanied with an appropriate change in the relative concentration of AGP mRNA, indicating that the increased concentration of AGP after irradiation was not preceded by a proportional increase of the relative transcriptional rate. In conclusion, these results showed that an absolutely lethal dose of ionizing radiation activated an acute-phase protein gene expression in rat liver.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
ANALYSIS OF mRNAs IN DEVELOPING BUCKWHEAT SEEDS
Vesna MAKSIMOVIĆ, Svetlana RADOVIĆ, Erika VARKONJI i Ana SAVIĆ
Institut za molekularnu genetiku i genetičko inženjerstvo, Beograd.
Tissue-specific and developmentally regulated seed storage protein gene expression is one of the events characterizing higher plant embryogenesis. Buckwheat embryogenesis, usually lasting 30 days, can be divided into several stages, clearly morphologically distinctive. PolyA RNAs have been isolated from different stages and translated in vitro using a wheat germ extract containing 35S-mcthionine. Analysis of the in vitro translation products from different developmental stages by SDS PAGE indicated that storage protein mRNAs are detectable after the 9th day after flowering and their synthesis continues throughout the whole seed development. The existence of individual mRNAs for different polypeptides of the storage protein complex excludes the existence of precursor mRNA which has been found in the gene expression of other "legumin-like" storage proteins.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
THE ANEMIC BELGRADE RAT 67kD ERYTHROCYTE MEMBRANE PROTEIN
Jelena MARJANOVIĆ, V. GLIŠIN i Zvezdana POPOVIĆ
Inslitut za molekularnu genetiku i genetičko inženjerstvo, Beograd.
The Belgrade laboratory rat (b/b) suffers from hereditary microcytic, hypochromic anemia inherited as an autosomal trait. The mutation affects the iron transport across the cell membrane. SDS-PAGE analysis of b/b red blood cell (RBC) membrane proteins revealed an extra protein band with a 67kD molecular mass. The Western blot analysis demonstrated that the 67kD protein is present in b/b RBC membranes, only. The major protein in an exosome fraction of both b/b and control rats comigrated in SDS polyacrylamide gels with the 67kD protein band from b/b RBC membranes. Polyclonal antibodies raised against this protein from control exosomes cross reacted with the b/b 67kD protein band. Incubation of the b/b erythrocyte membrane emulsion in the presence of ATP, resulted in the elution of the 67kD protein band and an 80kD protein, presumably Protein 4.1. No such dissociation was seen in control membranes. Further analysis should confirm both the connection of the 67kD protein band with Protein 4.1 in the b/b erythrocyte membrane and its possible ATPase activity.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
ANALYSIS OF THE REGULATOR DOMAIN OF THE prt GENE IN Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis BGIS29
N. MILADINOV, B. BOJOVIĆ, M. KOJIĆ, A. BANINA i Lj. TOPISIROVIĆ
Institut za molekularnu genetiku i genetičko inženjerstvo, Beograd.
Laciococcus lactis subsp. lactis BGIS29 was isolated from homemade cheese. It contains several cryptic plasmids. It appeared that some at the plasmids contained genes encoding resistance to the production of bacteriocin. In addition to bactericin, the strain BG1S29 produced an extracellular proteinase which proved to be a PI-lactococcal type of serine proteinase (hydrolyzed only -casein). This is an acid proteinase with an optimal temperature of 30C. Genetic analysis showed that the protcinase region, containing prlP and prtM genes, in the strain BGIS29 is located on a large plasmid of approx. 130 kb. It seems that the organization of genes within the proteinase region in the strain BGIS29 is very similar to that of L. lactis subsp. cremoris Wg2, since restriction maps of these regions are highly similar. The only apparent difference is that the regulator domain of proteinase genes in the strain BGIS29 contains no Clal sites, whereas the strain Wg2 contains two Clal sites, which flank the regulator domain. The regulator domain of the strain BGIS29 containing promoters of proteinase genes was enriched by PCR by using primers PO4C-P15 that originated from strain Wg2. The obtained PCR-enriched DNA fragment was cloned in vector pBV5030 and such a construct was used for the electroporetion of E. coli C600 and L. lactis 1L1403. Hybridization experiments confirmed that cloning was successful and that a low level of similarity exists between regulator domains of proteinase regions of strains BGIS29 and Wg2. This result is in agreement with the previously observed differences in restriction maps of these two strains. Testing of the minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) of resulting transformants showed that the cloned promoter fragment expressed an activity in both E. coli and L. lactis IL1403. However, the cloned DNA fragment proved to be very unstable in the E. coli recA strain, suggesting that this fragment had been subjected to deletions and/or other genetic rearrangements.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
A NEW cysB REGULATED GENE THAT MODIFIES NOVOBIOCIN REZISTANCE IN cysB MUTANATS OF Escherichia coli
Mirjana M. MILIĆ, M.Z. JOVIČIĆ, Radmila V. IVANIŠEVIĆ, Mila J. JANKOVIĆ i J. SAVIĆ
Institut za molekularnu genetiku i genetičko inženjerstvo, Beograd.
The CysB protein is a positive regulator of gene expression for the cysteine regulon, a system of 11 genes whose products are involved in the transport of sulphate, reduction to sulphide and biosynthesis of cysteine. In our laboratory we have discovered that cysB and cysE mutants of E. coli show an increased resistnace to novobiocin, a hydrophobic antibiotic whose target in the cell is the enzyme gyrase (Jasna Rakonjac, Mirjana Milić and Dragutin Savić; Mol. Gen. Genet. 1991, 228:307-311). In this report we have described the discovery of a new gene. This gene is CysLB regulated but it is not involved in the biosynthesis of cystcine. We used the system of AplacMu phage which allows the construction of random gene fusions. We selected a gene fusion which was activated in the absence of the CysB protein but it was repressed in the presence of the CysB protein. The examination of cysB mutants with this fusion on (LA) plates with novobiocin indicated that this fusion decreased the resistance to novobiocin. Mapping by PI transduction and Southern hybridisation revealed that this gene is located in the vicinity of the cysB gene. The gene was cloned and a comparison of the nucleotide sequence with known genes from a data base confirmed that it is really a new gene in E. coli.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
THE INFLUENCE OF BACTERIAL ON MULTIPLE ALLELE POLIMORPHISM IN MAIZE
Snežana MLADENOVIĆ, Kosana KONSTANTINOV, Bojana TADIĆ i G. SARATLIĆ
Institut za kukuruz Zemun Polje, Beograd - Zemun
The maize genome was transformed by integration of bacterial gene into the maize genome using different technologies. The introduced gene expression (NPTII - neomycinphosphotransferase activity), gene integration (Southern blot analysis) and gene transmission were confirmed in T3 and TS transgenic plants. Besides phenotypic changes, eliminated through cell cycles, plant height alteration and reduction of the period between planting and flowering are inheritable traits and no segregation was obtained in T3 and T4 plants. The genotype at 16 izozyme loci was analysed in coleoptile tissue to correlate foreign gene integration and host genome expression. The profiles were changed in transgenic plants at several analysed loci: Acpi, Acp4, Mdhl, Mdh2, Mdh5, betaGlu, Idhf and Pgm. No alteration of isozyme Mdh3 and Mdh4 forms was obtained in any transformed plant. Transgenic plants kept both good general and specific combining abilities of the original maize line. The results obtained showed that bacterial gene integration could induce stable useful mutations which enable the identification and localization of the genes controlling particular traits of maize.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
AN ANALYSIS OF THE DISTAL PROMOTER OF THE RAT bminy - GLOBIN GENE
Sonja PAVLOVIĆ, Tatjana MITROVIĆ, GLIŠIN i Zvezdana POPOVIĆ
Institut za molekularnu genetiku i genetičko inženjerstvo, Beograd
The distal promoter located from -100 to -900 bp upstream from the first ATAG codon of the rat bminy -globin gene was cloned into the pUC19 vector in both directions. The sequence of the cloned fragment was determined using Sanger's dideoxy sequencing method. The sequence determination of this regulatory region allowed a computer search and comparison with the cis-acting sequences in other types of globin promoters analysed up to now.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
INVESTIGATION THE REGULATION OF THE ACTIVITY OF THE Escherichia coli PENICILLIN G AMIDASE GENE BY FUSIONS WITH DIVERGENTE REPORTER GENES
S. RADOJA, M. KONSTANTINOVIĆ i V.
GLIŠIN
Institut za molekularnu genetiku i genetičko inženjerstvo, Beograd
An investigation of the primary structure and function of Escherichia coli penicillin G amidase (pac) gene has indicated the existence of complex regulation of the synthesis of this enzyme. The results which show that in the proximity of the promoter region of the gene there is antisense mRNA indicate a possible role in regulation of expression. The plasmid vector pCB267 (K. Schneider and F.C. Beck, 1986) with oppositely oriented genes, IacZ. (galactosidase) and phoA (Alkaline phosphatase) fused with various DNA fragments from the regulatory region of the pac gene has been used to investigate divergent promoter activity of certain DNA fragments. Under different physiological conditions of host cell growth the mutual activity of the defined DNA regions has been measured simultaneously.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
CHARACTERIZATION OF THE 13 S GLOBULIN OF BUCKWHEAT SEED
Svetlana RADOVIĆ, Vesna MAKSIMOVIĆ i Ana SAVIĆ
Institut za molekularnu genetiku i genetičko inženjerstvo
The major seed storage protein 13 S globulin of buckwheat was separated from a crude protein extract by sucrose density gradient centrifugation and gel filtration through Sephadex G-200. The obtained protein fraction was analyzed on SDS PAGE with and without 2-mcrcaptocthanol and different protein subfractions were identified. The same protein fraction was used to immunize rabbits and polyclonal antibodies were detected by immunodiffusion. It was shown that polyclonal antibodies crossreact with seed proteins of Polygonum aviculare and Avena sativa despite their different electrophoretical patterns. Analysis of the protein extracts from different developmental stages of buckwheat seed indicated the appearance of 13S globulin on the 14th day after flowering.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
DIALLELIC DNA POLYMORPHISM (SstI) OF Apo AI-CIII GENES AND SERUM LIPID LEVELS IN NORMOLIPIDAEMIC INDIVIDUALS
Ivana SAVIĆ, Sanja GLIŠIĆ, Nadežda RADOJA i D. ALAVANTIĆ
Institut za nuklearne nauke "Vinča", Laboratorija za radiobiologiju i
molekularnu genetiku, Beograd
Restriction fragment length polymorphism in the noncoding region (SstI) of the apolipoprotein AI-CIII gene was investigated to verify whether alleles of this polymorphism affect lipid levels. Blood samples were taken from normolipidaemic subjects from Belgrade. DNA was extracted using a standard procedure. The specific DNA region was amplified by a Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) in 183 samples, and restriction data were analyzed statistically. The frequency of the rare allele, S2, showed a linear dependence on serum lipid levels. Men non-smokers, with genotype S1S1, showed a significantly higher level of both total serum and LDL cholesterol than men smokers with the same genotype.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
DIALLELIC DNA POLYMORPHISM (Xbal) OF THE Apo B GENE AND SERUM LIPID LEVELS IN NORMOLIPIDAEMIC INDIVIDUALS
Ivana SAVIĆ, Sanja GLIŠIĆ, Nadežda RADOJA i D. ALAVANTIĆ
Institut za nuklearne nauke "Vinča", Laboratorija za radiobiologiju i molekularnu genetiku, Beograd
Restriction fragment length polymorphism at codon 2488 (Xbal) of the apolipoprotein B gene was investigated to verify whether alleles of this polymorphism affect lipid levels. Blood samples were taken from normolipidaemic subjects from the Belgrade area. DNA was extracted using standard procedure. The specific DNA region was amplified by a Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) in 230 samples and restriction data were statistically analyzed.
The frequency of rare alleles showed a linear dependence on serum lipid levels. Men with the rare allele, X2, showed a significantly lower level of HDL cholesterol than men with the XI allele. Women smokers, with genotype X1X1 showed a significantly lower level of HDL cholesterol, than women non-smokers with the same genotype.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
AN INVESTIGATION OF REPAIR MECHANISMS IN DIFFERENT Bacillus thuringiensis SUBSPECIES
S. STANKOVIĆ, J. KNEŽEVIĆ-VUKČEVIĆ, B. VUKOVIĆ-GAČIĆ i D. SIMIĆ
Katedra za mikrobiologiju, Instituta za botaniku i Botanička bašta, Biološki fakultet, Univerzitet u Beogradu, Beograd
B. thuringiensis is a Gram-positive soil bacterium which, during sporulation, forms parasporal crystalline inclusions that have insecticidal properties. This ability is used in the preparation of B. thuringiensis as a bioinsecticide. Mechanisms of DNA repair in B. thuringiensis have not been intensively studied, but they seem to be similar to E. coli repair mechanisms. In B. thuringiensis the existence of photo reactivation and excision repair has been reported. In addition, this bacterium responds to DNA-damaging agents (UV-irradiation, mitomycin-C, aflatoxin Bl) by eliciting several inducible SOB phenomena such as cell filamentation, prophage induction, Weigle-reactivation and Weigle-mutagenesis. A comparison of repair processes in different subspecies of B. thuringiensis can contribute to an understanding of repair mechanisms in B. thuringiensis. In this work we compared the effects of UV-irradiation which induced photoreactivation and cell filamentation, in the laboratory strains B. thuringiensis ssp. kurstaki, HD1 and CryB, as well as in the industrial strains B. thuringiensis ssp. tenebraionis (BTT), ssp. berliner (BTB) and ssp. israelensis (BTI). A similarity between HD1, BTT and BTI strains was observed, but the strain BTB was more sensitive to UV-irradiation. The most resistant strain was CryB. It is possible that the absence of plasmids increases the resistance ot UV-irradiation. Photo reactivation is more efficient in the strains (HD, BTI, BTT, BTB) which are more sensitive to UV-irradiation. The results concerning cell filamentation will be presented.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
CLONING AND CHARACTERISATION OF THE HUMAN SOX3 GENE
Milena STEVANOVIĆ 1 i P.N. GOODFELLOW 2
1 Institut za molekularnu genetiku i genetičko inženjerstvo, Beograd,
2 Department of Genetics, University of Cambridge, Downing Street, Cambridge, UK.
The recent cloning of the sex determining gene, SRY, has led to the identification of a large family of genes related to SRY. These genes have been named SOX genes. Southern analysis indicates that the SOX gene family is very large in man with as many as 20 members. Preliminary results suggest that many SOX genes are embryonically expressed and expression is restricted to neuronal and related tissues. Their spatial and temporal patterns of expression suggest a role in the regulation of the development of the nervous system. The human SOX3 gene was cloned by screening a cosmid library constructed with DNA from flow sorted human X chromosomes. Using a panel of somatic cell hybrids the SOX3 gene has been localised to the X chromosome in the region q26-27. The chromosomal location and phenotype in patients exhibiting deletion of the SOX3 gene suggest this gene is a candidate site for Borjenson-Forsman-Lehman syndrome, an X-linked mental retardation syndrome.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
A STUDY OF THE SEGREGATIONAL STABILITY OF PLASMID pAl FROM Lactobacillus plantarum A112
I. STOJANOVIĆ, M. VUJIČIĆ i Lj. TOPISIROVIĆ
Institut za molekularnu genetiku i genetičko inženjerstvo, Beograd
Plasmid pAl (2.8 kb) is the smallest of four plasmids in Lactobacillus plantarum All2. This plasmid replicates via the rolling circle mode of replication (RCR). Analysis of the pAl sequence revealed that it contained three open reading frames encoding proteins RepA, RepB and a truncated form of the Mob protein. To determine whether the RCR plasmid pAl can be replicated in a wide range of hosts, two plasmids have been constructed pAl-1 (4.7 kb) and pAl-6 (3.6 kb). Both vectors carry the erm gene coding for resistance to crythromycin, but pAl-6 docs not contain the RSA sequence. Successful transformation of other Lb. plantarum NCDO1193, as well as E. coli and Lactococcus lactis confirmed that plasmid pAl possesses the enpability of replicating in a wide range of hosts. The segregational stability of plasmids pAl-1 and pAl-6 was rather high in Lb. plantarum NCDO1193 and L. loctis 1L1403 (over 90% of cells growing under nonselective conditions retained plasmid after 60 generations). On the other hand, the segregational stability in E. coli rcaA+ was low (after 60 generations, 1% and 40% of cells retained plasmids pAl-1 and pAl-6, respectively). Since the recA genotype might have potentially caused plasmid instability due to the accumulation of single-strand DNA in this host, segregational stability was followed in an isogenic recA and recA pair of E. coli strains. Plasmid pAl-1 retained a high level of segregational instability in both the recA+ and recA derivatives, whereas plasmid pAl-6 did not show a significant difference in the segregational stability in both derivatives, suggesting that the RSA sequence could play a role in the replication stability of plasmids, yet to be defined.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
GENETIC AND BIOCHEMICAL CHARACTERIZATION OF THE BACTERIOCIN PRODUCED BY Laclobac Ulus casei subssp. pseudoplantarum BGUB9
J. SVIRČEVIĆ, M. KOJIĆ, A. BANINA i Lj. TOPISIROVIĆ
Institut za molekularnu genetiku i genetičko inženjerstvo, Beograd.
Bacteriocins are compounds of a proteinaccous nature with a bactericidal or bacteriostatic activity directed towards closely related species. A natural isolate of the lactic acid bacteria Lactobacillus casci subsp. pseudoplantarum BGUB9 produced the bacteriocin UB9 with a narrow range of actdivity (the bacteria Lactobacillkus casei BGHN14 was inhibited by bacteriocin UB9). Bacteriocini UB9 is thermostable (30 minutes at 100C) with actity in the pH range from 1-10. It was partially inactivated by chloroform and was completely inactivated by proteinases (pronase E, proteinase K, pepsin, trypsin and - chymotrypsin). Biosynthesis started after five hours of growth of the bacterial culture BGUB9 and the most intensive production was noticed between 12-16 hours. The molecular weight of the bacteriocin UB9 was determined by SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) and it was shown that the Mw is 6500-7000 Da. In order to determine the gene location for bacteriocin synthesis (chromosomal or extrachromosomal location) plasmid curing was used. The treatments with novobiocin (10g/ml) and elevated-temperature (42C) yielded Bac variants with a high frequency (35.5%). All Bacs derivatives were bacteriocin sensitive to bacteriocin UB9 (Bacs). The plasmid profile of the Bac+ strain BGUB9 and the cured Bac- strain BGUB9-16 was the same. For this reason, examination of these strains by PFGE is planned.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
GENE EXPRESSION OF ALBUMIN AND - FETOPROTEIN IN RAT LIVER AFTER HEPATECTOMY AND FRACTIONIZED RADIATION
Nataša TRUTIĆ, Koviljka KRTOLICA, M. ČOLIĆ i Z. MUGIĆ
Institut za hemiju, Medicinski fakultet, Niš,
Laboratorija za radiobiologiju i molekularnu genetiku, Institut za nuklearne nauke "Vinča", Beograd
Institut za medicinska istraživanja, VMA, Beograd.
Albumin is the protein most present in the plasma of higher organisms, with many functions that are necessary for homeostatic mechanisms. The appearance of fetoprotein in the plasma of an adult organism indicates the presence of malignancy, especially in the liver. This is the reason why the ratio of gene expression of these two proteins serves as a reliable indicator of liver function. Hepatectomy promotes an increase of liver metabolism and early DNA and hepataocyte proliferation, while high doses of ionizing radiation primarily damage the DNA molecule. Experiments were performed on male, inbred AO (Albino Oxford) rats which were hepatectomized (partial hepatectomy 30-40%), or were fractionally irradiated with 18 Gy of gamma rays in 5 daily doses. Total rat liver RNA was isolated 6, 12, 24, 48, 72 and 96 hours after the trauma. Relative concentrations of albumin and -fetoprotein mRNA were determined by slotblot hybridization of RNA and nick-tanslated plasmid cDNA probes labelled with 32P-dCTP. The results obtained showed that partial hepatectomy, especially 24-72 hours after the trauma caused a significant decrease (20-25%) of the relative concentration of albumin mRNA Albumin belongs to the group of so called "negative" acute-phase proteins the concentration of which decreases after trauma, and so decreased albumin gene expression in as a good an indicator of the acute-phase reaction as is the increased gene expression of "positive" acute-phase proteins. While the relative concentration of albumin mRNA was maximal in the adult intact rats, the relative concentration of -fetoprotein mRNA in the adult intact and traumatized rats was practically undetectable. A high expression of the -fetoprotein gene was found only in he fetal liver (several ten fold increases). These results showed that both kinds of trauma, during the examination period, caused only functional activation of rat liver cells.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
RESISTANCE TO HYGROMYCIN B IN Micromonospora STRAINS
Branka, M. KOJIĆ Lj. TOPISIROVIĆ
Institut za molekularnu genetiku i genetičko inženjerstvo, Beograd
Micromonospora strains which produce aminoglycoside antibiotics have a high level of resistance to 4,6- disubstituted dcoxystreptamine antibiotics that are structurally similar to their own products. On the other hand, these strains are sensitive to 4,5-disubstitutcd deoxystreptamines and streptomycin. It was surprising that all these strains showed the high level of resistance to hygromycin B, an antibiotic with a different chemical structure. M. melanosporae is a strain which does not produce any antibiotics and it is sensitive to all the antibiotics tested, including hygromycin B. Two genes responsible for resistance in Micromonospora producers were cloned so far. These are the grm gene from M. purpurea and the sgni gene from M. zionensis. Both genes were expressed in S. lividans, E. coli and M. melanosporae. Both genes conferred resistance in S. lividans and E. coli to all aminoglycosides as in their original hosts, but not to hygromycin B. Interestingly, the expression of these genes in M. melanosporae gave resistance even to hygromycin B. Since these genes encode specific 16S rRNA methylases, it was concluded that methylation of 16S rRNA only in M. melanosporae can lead to hygromycin B resistance. In this way it was confirmed that the high level of hygromycin B is indeed determined by the genes responsible for the aminoglycoside resistance (grm and sgm), but it is obvious that this resistance is strain dependent. This evidence suggests that there is some specificity in the 30S subunit structure in all tested Micromonospora strains. Further investigations included other genes from related genera, responsible for aminoglycoside resistance due to the methylation of 16S rRNA.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
EXTRACHROMOSOMAL REPLICATION OF PLASMIDS IN Drosophila EMBRYOS
Miloš VUJANAC, Vesna TODOROVIĆ, Snežana KOJIĆ, Ana SAVIĆ i Dragana STEFANOVIĆ
Numerous results emphasize the importance of scaffold attachment regions (SAR) in chromosomal nad extrachromosomal replication of DNA. We have assumed that AT-rich regions may serve as SARs and thus improve nuclear retention of plasmids and their ability to replicate extrachromosomally in Drosophila early embryos. To test this assumption, we have constructed a series of pGEM-derived vectors containing AT-rich inserts of different length. Along with an empty vector, each construct was introduced into Drosophila eggs by electroporation, left there during several embryonic cell cycles and DNA was isolated at the end of this period. DNA was separated into two portions and each portion was over digested with either Dpn I or Mbo I. These two enzymes recognized the same sequence on DNA, but Dpn I cuts only methylated DNA (replicated in bacteria) while Mbo I cuts only unmethylated DNA (replicated in eggs). Restricted DNA was introduce back to bacteria, and the proportion of blue (empty vector) and white (AT-region containing the construct) colonies was determined in each sample. Our results confirm the importance of SARs in DNA replication.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
ANALYSIS OF THE pMZl PLASMID FROM Micromonospora zionensis
Nataša VUKOV, Snežana KOJIĆ, Lj. TOPISIROVIĆ i Branka VASILJEVIĆ
Institut za molekularnu genetiku i genetičko inženjerstvo, Beograd
Plasmid pMZl (size 9.9 kb) was isolated from M. zionensis. A restriction map of this plasmid was determined and the different restriction sites were used fort the insertion of a selectable marker. The thiostreptone resistance gene from plasmid pIJ702 was used as the selectable marker. In order to analyze as many sites as possible appropriate for the integration of this gene, Sau3AI digestion was used as well. It was shown that out of 15 possible Sau3AI sites it is feasible to incorporate the thiostreptone resistance gene only into two sites. This result demonstrated that all other sites are located in regions essential for the replication of the pMZl plasmid. Similar results were achieved during the construction of himeric plasmids between pMZl and pIJ702. Chimeric plasmids were obtained only when part of the pIJ702 plasmid was incorporated into the unique BamHI site (plasmid pMSl/2) or into one of the two Bell sites (plasmid pMS3/l). In order to analyze possible ORF regions on the pMZl plasmid, promoter fragments were cloned into the pIJ487 promoter-probe vector. The fragments which showed promoter activity were used as probes in hybridization analysis. These analyses demonstrated that all promoters were located into three different regions. Further analysis of these regions was done by subcloning them into pUC19 which enabled their nucleotide sequences to be determined.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
SELECTION POSSIBILITIES FOR A
HIGH CONTENT OF ACTIVE SUBSTANCES IN Digitalis lanala Ehrh. AND Datura
innoxia Mill
D. S. ADAMOVIĆ, B. PEKIĆ i Z. LEPOJEVIĆ
Institut za ratarstvo i povrtarstvo, Tehnološki fakultet, Poljoprivredni fakultet, Novi Sad
The Woolly Foxglove (Digitalis lanata Ehrh.) is still the most important source for the isolation of glycosides used in heart therapy. Earlier investigations showed that this plant may be cultivated successfully in Yugoslavia. Since the content of the dominant glycoside (lanatoside C) was relatively low, selection was found to be necessary. The results obtained show that after two cycles of individual selection the lanatoside C content may be increased to 0.31% (on average) when compared with the initial 0.2%. In certain selected plants the lanatoside C content in dry leaves was over 0.4%. Future investigations will show whether it is possible to increase further the content of lanatoside C and whether it is stable in this biennial medicinal plant. Indian Thornapple (Datura innoxia Mill.) is an important raw material for scopolamine isolation which is widely used in the pharmaceutical industry. Preliminary investigations showed that D. innoxia may be successfully grown in Yugoslavia. In order to increase the economic efficiency of the isolation of scopolamine, selection was performed to increase its content in the dry aboveground mass (herb). The scopolamine content was increased to 0.32% (on average) from the initial 0.17% by using three cycles of individual selection. In certain plants the scopolamine content was even over 0.5%. It should be emphasized that in the promising progenies selected scopolamine was present almost exclusively, whereas other alkaloids were present in very low amounts or only in traces.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
MODE OF INHERITANCE AND GENE EFFECT OF THE HARVEST INDEX AND GRAIN YIELD PER PLANT IN MAIZE (Zea mays L.)
J. BOĆANSKI, M. STOJAKOVIĆ
Institut za ratarstvo i povrtarstvo, Novi Sad
Six different inbred lines were inluded in this study. The inbred lines were diallelly crossed and 15 F1 hybrids were produced. The mode of inheritance was evaluated by applying the test of significant means values of generations in reltion to the parental mean (Borojević, 1965). The gene effect was calculated according to the method of Jinks (1954) and Hayman (1954). Superdominance was present in most hybrids for the inheritance of the harvest index, while in three combinations, full dominance was present. For the harvest index, the dominant component of genetic variance is higher than the additive one which means that the majority of genetic variance belongs to the dominant component for the inheritance of this character. As the F value is positive, it can be concluded that he dominant gene effect prevails over recessive genes. The average dominance degree is higher than 1, which demonstrates that superdominance is present in the inheritance of the harvest index. Superdominance for the inheritance of grain yield per plant was present in all crossing combinations. Analysis of genetic variance components shows that the dominant variance component was higher then the additive one, i.e. that interaction of the genes for mass of grains per plant is present. The F value is negative which means that recessive genes prevail over dominant alleles. Since the average value of the degree of dominance is higher then one, superdominance for the inheritance of the grain mass per plant is present.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
METHODS FOR EVALUATING ADDITIVE GENETIC EFFECTS
V. BOGDANOVIĆ 1, D. RADOJKOVIĆ 1, Radica VIDIĆ-DEDOVIĆ l i P. STOJIĆ 2
1 Poljoprivredni fakultet, Beograd – Zemun
2 Zavod za stočarstvo i veterinarstvo, Agroekonomik, Beograd
Additive genetic effects represent those effects of genes that are manifested independently from other effects of genes in the genotype. They are the only effects surely inherited by the offspring and therefore their precise estimation and evaluation is possible. These effects have great importance for contemporary livestock production, because they show the best breeding value estimate of the observed animals. There are different methods for evaluating additive genetic effects: the average, comparison daughter - mother, CC - method, MCC - method, selection index, the least squares method, the best linear unbiased prediction and the animal model.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
THE INFLUENCE OF ENVIRONMENTAL
CONDITIONS ON WHEAT HYBRIDS RESISTANT TO PUCCINIA RECONDITA TRITICI IN
MODELING THE GENE-FOR-GENE RELATIONSHIP
Jelena BOŠKOVIĆ i M. BOŠKOVIĆ
Poljoprivredni
fakultet, Institut za zaštitu bilja, Novi Sad
Two hybrid wheat lines with three pairs of resistant genes to Puccinia recondita tritici where modelled according to the system of gene-for-gene relationships in constant (definite) and different (nondefinite) environments. Several different characteristics of the parasite : host : environmental system have been discussed. The application of the gene-for-gene model with a Boolean algebraic approach has shown many advantages compared with conventional methods, since the slightest increase in either V or N results in a very large number of possibilities of the genetic differentiation of sources of resistance. The definitive acgricorpus genotypes that produce small differences in one environment may produce much larger differences in phenotypes if functioning in another, defined environment. This partial function of definitive acgricorpus genotypes in a nondefined environment is a likely basis of "horizontal resistance" and "slow-rusting resistance". If this is the case, many reported horizontal resistances are also controlled by genc-for-gene relationships in varying environments.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
A STUDY OF MICROGAMETOGENESIS IN VITRO IN SOUR CHERRIES
R. CEROVIĆ
Institut za istraživanja u poljoprivredi "Srbija", Centar za voćarstvo i vinogradarstvo Čačak, Čačak
An epifluorescence microscope was used for observing the process of male gametogenesis in vitro in two sour cherry cultivars by applying fluorochromes specific for DNK, ethidium bromide (EB) and Hoechst 33258. Both fluorochromes when used as vital stains or applied after fixation, allowed clear visual discrimination between vegetative and generative or sperm nuclei in the pollen grain or the pollen tube. Both fluorochromes when used in staining reactions were superior when used as vital stains, Hoechst 33258 showing a more brightly visible straining reaction. When finalizing the process of gametogenesis in the pollen tube, the dynamic functional structure known as the "male germ unit" (MGU) was created, consisting of the vegetative nucleus and two sperm cells. In both sour cherry cultivars, MGU mobility in the pollen tube differed, which was directly associated with the different germination dynamics and the pollen tube length of the cultivar studied. In the field of fruit reproductive biology, the process of microgametogenesis in vitro, i.e. the behaviour and migration of pollen nuclei during pollen tube growth, represents the necessary prerequisite, the regularity determines the course of the double fertilization process.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
COMBINING ABILITIES FOR THE LEAF AREA INDEX OF SUGAR BEET (Beta vulgaris L.)
N. ČAČIĆ, L. KOVAČEV i Snežana
MEZEI
Institut za ratarstvo i povrtarstvo, Poljoprivredni fakultet, Univerzitet u Novom Sadu, Novi Sad
The objective of this investigation was to study the effect of genes and combining abilities of six sugar beet genotypes on the leaf area index (LAI). Diallel crossing of six different genotypes of sugar beet was performed. Parents and fi without reciprocal crosses were included in the study. Highly significant values of general combining ability (GCA) and specific combining ability (SCA) obtained in this study, indicate that additive and non-additive gene action (dominance and epistasis) contribute to the inheritance of this trait. The relationship GCA/SCA shows the higher effect of the additive gene on the total genetic variability of LAI. Two genotypes (A-0900 and B-200) had negative GCA values for LAI while the other four genotypes (SC-950, C-300, MS-504 and F-489) had positive GCA values for this trait. Only the cross A-0900 x C-300 had significantly positive SCA values while the other seven crosses had positive SCA values for LAI. The results of this study showed that the best specific combining abilities were found in the crosses in which one of the parents had negative and the other positive GCA values for LAI.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
ANALYSIS OF THE GENE EFFECT IN THE INHERITANCE OF THE NUMBER OF KERNELS PER SPIKE IN WHEAT
M. DIMITRIJEVIĆ, Sofija PETROVIĆ i Marija KRALJEVIĆ-BALALIĆ
Poljoprivredni fakultet, Institut za ratarstvo i povrtarstvo, Novi Sad
The gene effect in the inheritance of the number of kernels per spike was evaluated by using regression analysis of variance and covariance in diallel crosses of five wheat genotypes (Triticum aestivum ssp. vulgare), namely: NS Rana 2, Bankut 1205, NS 732, Atlas 66 and Siete Cerros 66. There was no indication of a non-allelic interaction, so the chosen model was sufficient to analyze the data. Regression analysis showed a dominant gene effect for the examined character, as well as an unequal arrangement of dominant and recessive genes between varieties. The results obtained indicated an association of higher number of kernels per spike with the increase in the number of dominant genes.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
RECURRENT PHENOTYPE SELECTION OF PROTEIN SUNFLOWER (Helianthus annum L. var. macrocarpus Ckll.)
B. DOZET, R. MARINKOVIĆ
Institut za ratarstvo i povrtarstvo, Novi Sad
After two cycles of recurrent selection eight synthetic populations were analyzed. Hybrid NS-Dclija was used as the standard. Two synthetic populations had a significantly higher proportion of the big fraction (>4.5 mm), and three populations had a significantly higher proportion of the big and medium fractions (>2.5 mm) than the standard. None of the analysed populations had a significantly higher proportion of kernel, compared to the standard. The proportion of kernel was between 65.85% and 72.94%. Five populations had significantly higher protein content and seven populations had significantly lower oil content than the standard. A strong negative correlation (r = -0.57) between the protein and oil content was found. Two populations and hybrid NS-Dalija were resistant to rust. The percentage of plants infected with a root and stem form of Sclerorinia sclerotiorum was between 0.77% and 15.27%. One population was significantly more resistant to this disease than the standard. It was observed that two synthetic populations had accumulation of good traits and these populations can be used for the creation of inbred lines of protein sunflower.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
GENETIC GAIN FROM SELECTION BASED ON HS PROGENIES IN TWO SYNTHETIC POPULATIONS OF MAIZE
G. DRINIĆ, M. IVANOVIĆ i Jelena VANČETOVIĆ
Institut za kukuruz "Zemun Polje", Beograd - Zemun
On the basis of parameters obtained by analysis of variance according to the Nested design - Random model, the estimation of genetic gain from selection by applying HS recurrent selection (Sprague and Eberhart, 1977) was done in four top-cross combinations of maize (BS12C8C1 x L82, BS12C8C1 x L15, ZPEP x L82 and ZPEP x L15). The trials were set up in 1991 in Zemun Polje, Indjija and Velika Plana according to the Nested design. The highest value of genetic gain for grain yield (t∙ha-1) was calculated for the combination ZPEP x L82 (5.31% and 7.8% cyle-1 for selection intensities of 20% and 5%, respectively), while the lowest value was obtained for the combination BS12C8C1 x L82 (4.47% and 6.59% cycle-1 for selection intensities of 20% and 5%, respectively). The values obtained were to a certain extent higher than expected, as genetic gain was calculated not according to additive variance but to total genetic variance. The results obtained point to the possibility of a successful application of HS recurrent selection in the investigated combinations.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
GENOTYPE SPECIFICITIES OF THE EFFECTS OF SEED WEIGHT AND CONCENTRATION AND QUANTITY OF NITROGEN IN THE SEEDS ON SEEDLING VIGOUR IN WHEAT (Triticum aestivum) I. ACCUMULATION, PARTITIONING AND CONCENTRATION OF NITROGEN IN THE PLANT
D. ĐOKIĆ, S. LOMOVIĆ, M. MILOVANOVIĆ i R. OGNjANOVIĆ
Institut za istraživanja u poljoprivredi "SRBIJA" – Beograd, Centar za strna žita, Kragujevac
The nitrogen uptake of seeds during germination and early stages of plant growth of twenty four winter wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) varieties in an experiment with pots containing a sand culture, was studied. For this research seeds with two nitrogen concentration levels for each genotype (the smaller one 1,3-1,6 and the higher one 1,8-2,6%) was produced. Both groups were divided in a larger >3,0 for varieties with larger seed weight and smaller <2,8 for genotypes with smaller seed weight. Fifty seeds per pot and were planted. Plants were washed from sand, divided into the root and top part, oven dried. They were then weighed and the nitrogen content was analyzed. Nitrogen accumulation in the plant and plant nitrogen utilization in the formation of dry matter in the plant (physiological efficiency of nitrogen) were analyzed. Nitrogen accumulation in the plant was higher in the variants with a higher seed weight and seed nitrogen concentration. There were considerable differences among the studied genotypes in plant nitrogen quantities. Nitrogen utilization from seeds was higher in variants with a smaller seed size and lower seed nitrogen concentration. In these variants were higher nitrogen quantities were found in the plant compared to the seed. This increased content of nitrogen was obtained as a result of water uptake or by taking into account root nitrogen fixation. There was a great difference among the studied genotypes in view of this. The efficiency of plant nitrogen utilization in the formation of dry matter was higher in plants that were obtained from seeds with a small size and low nitrogen accumulation. Considerable differences among varieties in the value of this parameter were found. Nitrogen efficiency in the plant was negatively correlated to accumulation. Genotypes with a higher nitrogen concentration and quantity positively affected plant nitrogen accumulation but negatively influenced nitrogen utilization.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
GENOTYPE SPECIFICIES OF THE EFFECTS OF SEED WEIGHT AND CONCENTRATION AND QUANTITY OF NITROGEN IN THE SEEDS ON SEEDLING VIGOUR IN WHEAT (Triticum aestivum) II. EFFICIENCY OF SEED NITROGEN AND SIZE
D. ĐOKIĆ, S. LOMOVIĆ, M. MILOVANOVIĆ i R. OGNJANOVIĆ
Institut za istraživanja u poljoprivredi "SRBIJA" – Beograd, Centar za strna žita, Kragujevac
The influence of seed size, seed nitrogen content and concentration on the dry matter yield of seedlings in the third leaf stage was studied under greenhouse conditions. For each genotype seeds with a lower content (LCN) and a higher contend of nitrogen (HCN), 1,3-1,6% N and 1,9-2,1% N, respectively were produced. Each seed group was subdivided further into two groups: a larger (>2,8 mm) and a smaller fraction (<2,8 mm) for varieties with a smaller seed size and a larger (>3,0 mm) and smaller fraction (<3,0 mm) for cultivars with a larger seed size. The efficiency of grain weight (plant dry matter yield/grain weight) and efficiency of grain nitrogen (plant dry matter yield/grain nitrogen) utilisation were analyzed. The efficiency of grain nitrogen utilisation for all variants ranged from 48 to 63 mg d.m./mg grain nitrogen. The highest values were obtained in NS Rana 2, Logan and Francuska genotypes. Grain nitrogen efficiency was considerably higher in plants from grain with lower nitrogen content. There were no differences in grain nitrogen efficiency between larger and smaller seed fractions with the same nitrogen concentration. The efficiency of grain weight varied less compared to grain nitrogen efficiency. It ranged from 0,87-1,08. The highest values of this parameter were found in Rumska crvenka, Logan, Nizija, Obrij and Super Zlatna varieties. Seedlings from smaller seeds had a higher efficiency of grain weight utilisation. In a repeated trial with a longer day and higher light intensity conditions higher seed grain and nitrogen efficiency were obtained in plants from seeds with a higher seed nitrogen concentration.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
GENOTYPE SPECIFICITIES OF THE EFFECTS OF SEED WEIGHT AND CONCENTRATION AND QUANTITY OF NITROGEN IN THE SEEDS ON SEEDLING VIGOUR IN WHEAT (Triticum aestivum) III. THE UPTAKE OF GRAIN NITROGEN, ITS ACCUMULATION AND UTILIZATION IN PLANTS
D. ĐOKIĆ, S. LOMOVIĆ, M.
MILOVANOVIĆ i R. OGNJANOVIĆ
Institut za istraživanje u poljoprivredi "SRBIJA" – Beograd, Centar za strna žita, Kragujevac
The influence of seed size and seed nitrogen concentration of the yield and partitioning of seedling dry matter and seedling nitrogen concentration was studied in twenty four winter wheat genotypes (Triticum aestivum L.) in a pot experiment. Two seed sixes, above and under 2,8 mm, for varieties with smaller seeds (SS) and two seed sixes above and under 3,0 mm, for genotypes with larger seeds (LS) were investigated. Each seed size had two nitrogen concentrations. It ranged from 1,31-1,66% for SS and 1,81-2,58% for LS depending on the variety. Dry matter yield of the root and top for all variants ranged in average from 1,66-2,09 g/50 plants per plot. The highest yield of dry matter was obtained in Rumska crvenka, Skopljanka, Obrij, KG - 56 and Logan genotypes. The seedling dry matter yield was higher for plants with smaller seeds for all genotypes and with the same seed nitrogen concentration. Different seed nitrogen concentrations had no influence on the seedling dry matter yield. In a repeated trial with longer day and higher light intensity conditions, a higher seedling dry matter yield from LS and higher seed nitrogen concentration was obtained. The seedling nitrogen concentration was higher in varieties with higher grain protein content.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
SOME PARAMETERS OF MINERAL NUTRITION EFFICIENCY AS AN INDICATOR IN WHEAT SELECTION
D. ĐOKIĆ, M. KOSTIĆ, S. LOMOVIĆ i M. JELIĆ
Institut za istraživanja u poljoprivredi "SRBIJA", Beograd, Centar za strna žita, Kragujevac
Some parameters which affect the efficiency of mineral nutrition in wheat and their application in plant breeding are described. The efficiency of mineral nutrition was measured by determining amounts of dry matter per unit of used or available nutrients in the soil. The efficiency of mineral nutrition on grain yields is achieved through the uptake and accumulation of nutrients and their utilization in plants. Accumulation efficiency represents the activity of the root system into incorporate mineral nutrients. The efficiency utilization represents plant top activity to include these nutrients in plant synthetic processes. The accumulation and utilization of nutrients in plants are often in negative correlation, which makes plant breeding of wheat for increased fertilization efficiency more complex. Grain yield as the product of these two parameters may be the resultant of high values for one parameter and low values for the other or average values of both. Only, by obtaining high values of both parameters in a new genotype, can the efficiency of fertilization and productivity be increased. Also, some other parameters such as measurements of the efficiency of wheat plant nutrition (concentration of nutrients in the plant, nutrient harvest index and development and activity of the root system) were analyzed. It is recommended that mineral nutrition efficiency of parents and their hybrids is studied under conditions with insufficient nutrients. Deficiency of the studied nutrient should be the main limiting factor of growth and productivity under such conditions. The genotype shows its resistance or susceptibility to nutrient deficiency best under such conditions.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
THE EFFICIENCY NITROGEN NUTRITION AS A GENOTYPE CHARACTERISTIC OF WHEAT
D. ĐOKIĆ, M. KOSTIĆ, S. LOMOVIĆ i M. MILOVANOVIĆ
Institut za istraživanje u poljoprivredi "SRBIJA", Beograd, Centar za strna žita, Kragujevac
The efficiency of nitrogen nutrition of different winter wheat varieties was studied in three field and three pot experiments with different soils (Chernozem, alluvium, podzol). The efficiency of nitrogen nutrition (accumulation x utilization of nitrogen), grain nitrogen content and nitrogen harvest index was analyzed. The accumulation of nitrogen in the plant top ranged from 315-392 mg N/2,5 dm planting area. Florida, Bezostaja, Studenica and Francuska had the highest values of nitrogen accumulation. The efficiency of nitrogen utilization ranged from 39-48 g grain/g plant nitrogen on average for all treatments. The highest values of this parameter were obtained for cv. Francuska, Srbijanka, Florida and Dynasty. Plant nitrogen accumulation was higher in the pot experiment and plant nitrogen utilization was higher in the field trial. The efficiency of nitrogen nutrition ranged from 13,1-18,8 g/2,5 dm and it was the highest in cv. Dynasty, Francuska, Florida, Srbijanka and Studenica. The same or similar grain yields can be expected with different values of plant nitrogen accumulation and utilization. By incorporating the highest values of the studied parameters in a new genotype, a high protein content can be obtained without decreasing the grain yield of the parent with a higher yield. The existence of a negative correlation between accumulation and nitrogen utilization was discussed in this study as a great problem in breeding wheat plants for more efficient nitrogen nutrition.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
THE PHYSIOLOGICAL BASIS FOR GENOTYPE IMPROVEMENT OF WINTER WHEAT (Triticum aestivum L.) GRAIN PROTEIN CONTENT
D. ĐOKIĆ, M. KOSTIĆ, S. LOMOVIĆ i M. MILOVANOVIĆ
Institut za istraživanje u poljoprivredi "SRBIJA", Beograd, Centar za strna žita, Kragujevac
The object of this study was to determine some physiological parameters which affect genotype differences in winter wheat grain protein content. These studies were conducted under greenhouse conditions. Two winter wheat varieties with a higher grain protein (HP) content (Tamiš and El Gaucho) and two winter wheat cultivars (Srbijanka and Skopljanka) with a lower grain protein (LP) content were experimentally grown in pots. Parameters of accumulation and distribution of dry matter and parameters of the concentration, accumulation, distribution and utilization of plant nitrogen were analyzed. No differences in plant dry matter accumulation and the distribution between HP and LP varieties was noticed. Grain yield and (he grain harvest index were considerably lower and the biological yield was similar in El Gaucho compared to LP cv. Between Tamiš and cv. LP there were no differences in these parameters. HP cv. had higher total and productive tillering. The differences in the nitrogen content between HP and LP cultivars were more obvious at the lower nitrogen nutrition level. HP had a more favourable ratio of nitrogen concentration in grain: straw. The variety Tamiš had a greater nitrogen accumulation in the plant lop. No significant differences in the accumulation of nitrogen in the plant top existed. The nitrogen harvest index was similar between HP cultivars nad LP varieties. The physiological efficiency was lower in HP varieties. The accumulation of dry matter and grain nitrogen yield in plants was considerably higher in HP varieties. An increased grain protein content in Tamiš was obtained mainly as a result of an increased plant nitrogen content, and in the variety El Gaucho it was obtained mainly through the reduction of the grain yield. Increased plant nitrogen accumulation! is an important conditions for overcoming the negative correlation between the grain yield and grain protein content in plant breeding programmes. This is a basis for increasing the protein content without decreasing high productivity.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
PHENOTYPE CORRELATIONS FOR STALK LODGING RESISTANCE IN (B14 x K134)F2 SYNTHETIC POPULATIONS OF MAIZE (Zea mays L.)
J. ĐORĐEVIĆ i M. IVANOVIĆ
Institut za kukuruz, "Zemun Polje", Beograd - Zemun
For this investigation Ssub1 progenies from the (B14 x K134)F2 maize synthetic populations were used. A multiple phenotype correlation of nine stalk traits on the grain yield and stalk lodging resistance was determined. This analysis showed that the stalk water content and stalk mechanical rind content has the greatest impact on of the lodging resistance stalk. No significant relationship was found between the grain yield and the percent of stalk lodged plants. This means that breeding for better stalk quality will have affect future progress in yield potential.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
THE INFLUENCE OF "AFILA" GENES ON THE FORMING OF PODS IN Pisum sativum L.
R. ĐORĐEVIĆ 1, Z. MARKOVIĆ 1, V. PEŠIĆ 2 i I. ĐINOVIĆ 3
1 Institut za istraživanja u poljoprivredi "Srbija", Beograd, Centar za povrtarstvo, Smederevska Palanka
2 Poljoprivredni fakultet, Beograd - Zemun
3 Visa poljoprivredna škola, Prokuplje
The gene af in a recessive homozygotc state in peas causes plant modification, so that plants form only tendrils with offshoots, instead of normal leaves. A Cultivar, Filligreen, of the afila genotype has been crossed with 12 cultivars of normal leaves with the aim of investigating the influence of the afila genotype on the forming of pods. Genetic analysis of F1 and F2 generations (separation ration 3:1, normal 16 af:afila type) confirmed a monohybrid model of inheritance and recessive characteristics of the afila genotype. The number of pods per plant in the F1 generation was higher than the one in both parental types. In the F2 generation afila genotypes reduced the number of pods per plant by 13% in relation of the F1 generation, also 1% compared to a normal plant, and so about 30% more than the afila parent. The reduction of the number of pods per plant in the F2 generation was influenced by the reduction of the assimilation surface.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
GENETIC SPECIFICITY OF MORPHOLOGICAL CHARACTERS OF HYBRID PLANE HALF-SIB PROGENY
Matilda ĐUKIĆ i Dragica OBRATOV
Šumarski fakultet, Beograd
The study of Platanus x acerifolia Ait./Willd, morphological variability by the analysis of progeny of 45 parent trees i'n the region of Belgrade, is aimed at enabling a wider utilization of this species in our conditions. The basis for this is its properties such as quick growth, longevity, resistance to adverse effects of the environment, visual suitability, etc. The analysis of progeny morphological parameters (height, diameter, and mass of the seedling, size, mass and specific area of the leaves) show very expressed inter and intra familiar variability. As the progeny was raised in more or less homogeneous ecological conditions (which is shown by the analysis of variance), the variability of the analyzed characters is the result of genetic specificity. Based on the obtained data, the individuals with distinguished characters were singled out, such as: quick or slow growth, marked diameter increment, formation of strong root system, leaves with large assimilation area or with marked mesophyll, etc. The most important trees are those with several economically significant properties. The implementation of the studied morphological criteria can accelerate and develop the process of seed three selection and improvement of plane trees intended for nursery production for forestry and landscape architecture. The research points to a high genetic potential and adaptability of hybrid plane, which is proved by good phenotype characters of the selected parent trees, as well as the vitality and of its progeny.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
THE EFFICIENCY OF WITHIN LINE AND RECIPROCAL RECURRENT SELECTION FOR INCREASING BODY WEIGHT AND LITTER SIZE IN MICE
Ž. GAJIĆ i A.E. BELL
Poljoprivredni fakultet, Beograd -
Zemun
Purdue University, Lafayette, Indiana, USA
The main objectives of selection are systematic genetic improvement in the over-all merit of existing populations of domesticated animal and plant species. Nowadays, for the further improvement of populations, various methods of selection have been proposed, such as purebred selection which depend on additive genetic variance and recurrent or reciprocal recurrent selection which could use both additive and non-additive genetic variance for the improvement of the performance in the final cross. In order to improve of 60. day body weight in mice a comparative investigation of the efficiency of within line selection based on purebred performance and reciprocal recurrent selection based on crossbred performance was made. The basic genetic material for this study consisted of two lines of mice, the Goodalc Large White and Falconer Nutrition Full line. Appropriate control populations, were also maintained. The selection was conducted over nine generations. The average genetic gain per generation was estimated by linear (b) and quadratic regressions (y) which signifies whether the gains per generation area increasing or decreasing. The results obtained showed that the average genetic change in the 60. clay body weight per generation was 0.270 ± 0.072 for within line selection, and somewhat lower (0.249 ± 0.107 for reciprocal recurrent selection. The observed results showed that there was no significant difference between the within line and reciprocal recurrent selection methods for improving the 60. day body weight in mice. In selection studies it is important to know how the improvements of the selected character will cause simultaneous changes in other characters, the so-called correlated responses. When correlated responses were estimated as regressions of deviations on the generation number the estimates for total no. born, no born alive and no. weaned were 0.105 ± 0.054; 0,132 ± 0.050 and 0.132 ± 0.055 with the within line selection and 0.125 ± 0.072; 0.158 ± 0.073 and 0.129 ± 0.053, respectively with the reciprocal recurrent selection. Slightly lower values were obtained for the weaning weight (0.169 ± 0.096 and 0.156 ±0.096) and the largest were for the 42. day weight (0.310 ± 0.081 and 0.254 ± 0.057) with the within line selection and reciprocal recurrent selection, respectively. The average regression coefficients for weaning weight were significant and the 42. day weight highly significant. The regression was positive for all traits and similar with both methods of selection. From these comparative investigations of the efficiency of two methods of selection it may be concluded that there are no significant weight and litter size in mice between within line selection and reciprocal recurrent selection for increasing the body weight and litter size in mice.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
GROWTH CHARACTERISTSICS OF SIBERIAN ELM (Ulmus pumula L.) ROOTED CUTTINGS FROM DWARF PARENT TREES
M. GRBIĆ
Šumarski fakultet, Beograd
A seedling with typical "yatsubusa" characteristics was produced out of freely pollinated seed of a Siberian elm tree. After the first vegetation, its above-ground height was 5 cm, and its leaves were 1 cm. The same half-sib progeny was used to raise an individual in which the above-ground height after the first vegetation was 54 cm, which is above the average of the family. The characteristic of growth of this individual did not point to a predisposition to nanism. In the following five years, the first, dwarf, individual was grown in a large container whose walls did not restrict root growth. The second plant was transplanted to a shallow container and it was pruned by a standard Bonsai technique. After five years, the habit of the second individual was very similar to the first one. Ten root cuttings and ten green cuttings were then taken from each plant. Rooting was carried out by the usual procedure, and comparative measurements were taken after the first vegetation. The results of the experiment prove the starting hypothesis that the origin of nanism in the first individual is in its inheritance factors, as shoot growth of its cuttings was significantly less than that of the second individual. The method of vegetative reproduction of the individual with dwarf growth induced by external factors affects the speed of character change to the original form if the conditions in which nanism occurs are changed. In practice, yatsubusa characteristics can be obtained under the effect of genetic, but also under the effect of external factors, under the conditions that the norm of the individual reaction is wide enough, so that intensive pruning of root and shoot is not lethal.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
DIFFERENCES BETWEEN 6 VARIETIES OF MULBERRY (Morus alba, L.) PROPAGATED IN VITRO
Branislava GRBOVIĆ i Biljana NIKOLIĆ
Institut za šumarstvo, Beograd
The primary culture was obtained from auxiliary buds that originated from 1-year-old seedlings of the cultivars: Kurimelto I1N2, Murasaki-Vase I1N2, Ošima I1N2, Taškent-Saniš 15, No-106 and Kumrin. The culture was established on MS-medium (Murashisge and Skoog, 1962) containing BAP and IBA. Measured characteristics were: number of new explants, length of main shoot, length of main root and number of root branches. In multiplication experiments using several concentrations of BAP (0,0-2,0 mg-1) significant differences were found between the Japanese Variety Murasaki-Vase I1N2, and the Bulgarian Variety Kumrin, using the t-Test. In experiments of rooting containing 0,5 mg-1 IBA all cultivars developed roots and differences among them were significant. All investigation of the interaction Variety concentration of 1BA (0,0-1,5 mg-1) in experiments containing activated charcoal (0,1%) was achieved through analysis of variance. Results of the F-test showed that the interaction was significant only for characteristics of roots since differences between Varieties were significant in all measured characteristics of explants.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
COMPONENTS OF GENETIC VARIANCE FOR THE LENGTH AND WIDTH OF PEPPER FRUITS (Capsicum annuum L.)
Đ. GVOZDENOVIĆ, Marija KRALJEVIĆ-BALALIĆ, I. MIHALJEV i A. TAKAČ
Poljoprivredni fakultet, Institut za ratarstvo i povrtarstvo, Novi Sad
The pepper is one of the most important vegetable crops. In our country, the pepper is grown on acreage of 25,000 ha and is used in human diets cither fresh, or conserved, processed or frozen. As it contains sugars, protein, vitamins, especially vitamin C, mineral matter, fat and aromatic components, pepper fruit is highly valuable. Several studies have shown the existence of heterosis for yield. However, the expensive production of hybrid seeds hampers the extension of hybrids in large-scale production. The objective of this paper was to study genetic variance, additive and dominant as well as general and specific combining abilities for the length and width of hybrid pepper fruits. Seven female parents (varieties or lines) (L-l/2, Viktorija, Feherozon sinteticus, Albaregija, Herab, Corno Di Toro Rosso and Buketna 1) and three male parents (testers) (Kalifornijsko čudo, Šorokšari and Matica) were used in this study. Trials were set up according to a standard method in the experiment fields of the Institute of Field and Vegetable Crops at Rimski Šančevi. It is evident from the results that the non-additive component for fruit length was greater than the additive one, but the additive one was also significant. On the other hand, the additive component of genetic variance had a higher effect on the fruit width. The best general combiners for the fruit length and width were the varieties Corno Di Toro Rosa and L-l/2, respectively. These two varieties had highest mean values for the studied traits as well. The combinations Hebar x Kalifornijsko čudo and Buketna 1 x Matica had the highest SCA values for fruit length and Albaregija x Kalifornijsko čudo for the fruit width. It can be concluded that the genotype’s investigated differed significantly regarding the studied traits.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
AN ASSESSMENT OF THE POSSIBILITY OF UTILIZING SOME CHARACTERISTICS OF BLACK POPLAR LEAVES (Section aigeiros) IN THE IDENTIFICATION OF VARIETIES
V. GUZINA, S. ORLOVIĆ i G. ABRAMOVIĆ
Naučni institut za topolarstvo, Novi Sad
The registration of new varieties of poplars at national and international levels requires reliable scientific criteria for their identification. The Proceedings of the latest session of the International Poplar Commission held in Saragosa (ed. Padro, 1992) present a register of the clones accepted in the member countries of IPC, which also includes Yugoslav clones. Recommendations regarding phenotype characteristics of seedlings and trees suitable for the identification of varieties are also given. These recommendations are largely in accordance with the regulations by OECDE and UPOV. However, reliable experimental data on the degree of genetic identification of genotypes is still insufficient, so further research in this respect is necessary. This paper is an attempt, based on measurements and observations of the leaves of one and two -year - old poplar cuttings, to obtain information on intra - and inter - clonal variability of several properties. This should result in the selection of the most suitable properties for the identification of clones, i.e. varieties. The morphological parameters were leaf blade sizes (length, width, position of the largest width, length of main vein), then the number of lateral veins, the angle between the two lower veins, length of petiole, as well as the coefficients of interrelations of some magnitudes. The examined elements of anatomic structure were the number and size of stomata and the variability of elements of the leaf blade cross section. The biochemical parameters included are phenotype appearance of isoenzymes, as well as the degree of sensitivity to rust (Melampsora sp.) and brown leaf blight (Marssonina bruneca). To summarize, the most reliable parameters were the phenotype expressions of isoenzyme variability, the coefficients of interrelationships of some values of leaf sizes and the degree of sensitivity to leaf diseases. However, it should be taken into account that the degree of disease attack varies from year to year, and that changes of genotype sensitivity are possible as the result of new strains of pathogens, consequently continuous research of the relationships between varieties and pathogens is necessary.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
DEVELOPMENTS IN THE IMPROVEMENT OF AUSTRIAN PINE (Pinus nigra Arn.) IN SERBIA
V. ISAJEV, A. TUCOVIĆ i Mirjana ŠIJAČIĆ
Šumarski fakultet, Beograd
The Austrian pine has a discontinuous range, its isolated populations are characterised by a specific gene pool and the spontaneous phenomenon of a greater number of intra species taxa. The variability and taxonomy of Austrian pine in Serbia has been insufficiently studied, although pure or mixed populations, as well as plantations, are growing successfully in different sites. By mass and individual selection, work on the improvement of Austrian pine has been intensified in Serbia by a detailed study of: a) the nature of the character of variability (discontinuous, continuous), b) the relation between juvenile an adult stages of some important physiological properties, c) seed sources which are most favourable for specific sites. By the analysis of group and individual phenotype variability, stationary monitoring and the analysis of seeds from free population, several populations have been separated in West Serbia as well as forty test trees whose seeds were used in the production of half-sib families. The results of the comparative morphological physiological investigations, at the levels of populations, individuals, seeds, and half sibs, have confirmed the significant individual and group variability. By testing the resistance of half sibs to water stress, physiological parameters have been identified which are significant in the production of nursery stock with an increased resistance to transplantation stress. In the area of 3 ha, 6,500 half-sib seedlings from 40 families have been planted to establish a seed orchard of metapopulation structure, composed of 6 repeated sib structures, which ensures better preservation of the gene pool in them, the dynamics of gene exchange and the vitality of both the plantation and the seed.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
RECURRENT SOYBEAN SELECTION: INTERDEPENDENCE AND HERITABILITY OF PROTEIN CONTENT AND YIELD COMPONENTS IN THE 'PRO' SOYBEAN POPULATION
Đ. JOCKOVIĆ 1, J.R. VILCOX 2, H.J. XU 2, Milica HRUSTIĆ 1 i M. STOJAKOVIĆ 1
1 Institut za ratarstvo i povrtarstvo, Poljoprivredni fakultet, Novi Sad
2 Purdue University, Department of Agronomy, W. Lafayette, Indiana, USA
The objective of this paper was to study the interdependence of the protein content in grain, yield components and grain yield per plant in the 'PRO' population of soybean recurrent selection. Additionally, our aim was to specify the variability level and heritability of the studied traits after the third cycle of recurrent selection. The research material for this study was provided by Prof. J.R. Wilcox, Purdue University, W. Lafayette, Indiana, USA. The method of Brim and Burton (1981) was applied. Three cycles of recurrent selection were performed. Bees were used as pollen vectors. Identical correlations were found regarding the studied traits in the PRO' population and in 20% selected plants from the population. Significant negative correlations between the protein and oil content in grain were found in the two populations. The protein content in grain and grain yield per plant were in negative correlation, but not in COSO and C1SO in the 'PRO' population. In both studied populations, highly significant positive correlations between the number of pods per plant, 1000-seed mass, plant height and grain yield per plant were found in C3SO. The genotypes with more grains per pod had lower protein content in grain in both populations. The variability of the studied traits did not decrease after the three cycles of recurrent selection. The highest heritability (over 0.81%) was found for vegetation period. The results indicate that sufficient variability of the studied traits exists in the PRO' population of soybean and that recurrent selection should be continued.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
COMBINING ABILITY FOR YIELD COMPONENTS OF F1 HYBRIDS OF SUNFLOWER (Helianthus annuus L.)
J. JOKSIMOVIĆ, R. MARINKOVIĆ i M. MIHALJČEVIĆ
Institut za ratarstvo i povrtarstvo, Novi Sad
The aim of this study of basic quantitative and genetic parameters for yield components of F1 sunflower hybrids was to evaluate combining abilities of inbred lines and F1 hybrids and the interrelationship of the studied traits. The experimental material, selected at the Institute of Field and Vegetable Crops in Novi Sad consisted of 8 genetically divergent inbred lines and 15 F1 hybrids. The two-year study included the analysis of the following traits: seed yield, seed number, and 1000-sced mass. An analysis of combining abilities according to the method of line x tester (Singh and Choudhary, 1976) gave information on general combining abilities (GCA) of inbred lines, speciF1c combining abilities (SCA) of F1 hybrids, components of genetic variance, average contribution (%) of lines, tcstcir, and their interaction in expressing the given trait. SigniF1cant differences were found between the studied sunflower genotypes with respect to average values of all studied traits. Heterosis occurred in the inheritance of seed yield and the number of seeds per plant. The nonadditive component of genetic variance had the main role in inheritance. Inbred lines with a positive and negative GCA effect for the traits were deF1ned. Only a small number of F1 sunflower hybrids had significant SCA values. Correlation analysis helped to determine interdependence of the studied traits. The basic assessments are considered to be average phenotypic values, the model of the F1 hybrid with respect to seed yield, good GCA of inbred lines and SCA of F1 hybrids and their stability, lines HA-BCPL and RHA-178 are the best parent components.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
THE INFLUENCE OF DIVERSE CAYENNE GERMPLASM ON THE INHERITANCE OF FRUIT CHARACTERS IN THE F1 GENERATION
B. JOVANOVIĆ 1, S. PRODANOVIĆ l i D. STEVANOVIĆ 2
1 Poljoprivredni fakultet, Beograd - Zemun
2 Centar za povrtarstvo, Smederevska Palanka
The objects of investigation in this study were found parental cultivars originating from two cayenne subspecies: Capsicum annuum L. ssp macrocarpum (with varieties grossum and longum) and Capsicum annuum L. ssp microcarpum (with varieties acuminatum and longum). The effects of genes in the parental varieties, on the values of five characters in F1 diallel hybrids were calculated, using VrWr regression analysis (Mather and Jinks, 1971). This is the first use of this method in our country, for estimating the genetic diversity of cayenne germplasm. For all characters studied, partial-dominance models of inheritance were found. In addition, these results indicated that the macrocarpum varieties of cayenne have mostly dominant genes for the number of fruits per plant. Microcarpum varieties carry mostly dominant allcles for fruit width. A source of dominant alleles for fruit length is the variety longum in ssp microcarpum. In the inheritance of pericarp thickness, the variety grossum has the biggest number of recessive alleles, while the other varieties carry mostly dominant genes. Dominant genes for fruit weight are mostly contained by microcarpum varieties. Such a genetic structure of parental varieties for the fruit characters studied shows the complexity of cayenne breeding. Actually, parents which had a smaller number of fruits, and also had narrow and short fruit with a fine pericarp partially dominated in the F1 generation.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
IDENTIFICATION OF WHEAT VARIETIES BY Gli- ALLELE COMPOSITION
D. KNEŽEVIĆ
Institut za istraživanja u poljoprivredi "Srbija", Centar za strna žita "Kragujevac", Kragujevac
The gliadin allele composition of 10 winter wheat varieties was analysed by acid PAG electrophoresis. These wheat varieties were created in the Institute for Small Grains. The genetic formulae of gliadin alleles were determined on the basis of identified gliadin blocks which were encoded by genes located on the short arm of 1A, IB, ID, 6A, 6B and 6D chromosomes. Seventeen different alleles at the six Gli- loci were identified. A different number of alleles at each Gli- locus was determined, namely: 3 alleles at the Gli-Al, Gli-Bl, Gli-Dl and GH-D2, 4 at the GH-A2 and 1 at the GH-B2 locus. Each variety was characterized by a specific genetic formula of the gliadin allele composition. Alleles were designated according to the nomenclature of Metakovsky el al. (1991). The Gli- alleles were found to have widely differing frequencies in the wheat varieties analysed. The highest frequencies were established for Gli-Alb, Gli-Blb, Gli-Dlb, Gli-A2b, Gli-B2b and Gli-D2b.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
ALLELIC VARIATION AT Gli- LOCI IN SOME MACEDONIAN WHEAT CULTIVARS
D. KNEŽEVIĆ 1, Mirjana MENKOVSKA 2 i Dragica ZORIĆ 2
1 Institut za istraživanja u poljoprivredi "Srbija", centar za strna žita "Kragujevac", Kragujevac
2 Žito Skopje, Skopje, Makedonija
3 Poljoprivredni fakultet, Beograd - Zemun
Sub units of gliadin extracted from a single kernel of 8 Macedonian winter wheat varieties were separated by PAG electrophoresis to identify their alleles, and the frequency of each allele was calculated. Gliadin allelcs were determined on the basis of identified gliadin blocks which were encoded by genes located on the chromosomes comprising homologues groups 1. and 6. Nineteen alleles from six Gli- locio were identified, three at the Gli-Al locus, three at the Gli-Bl, two at the Gli-Dl, three at the GH-A2, five at the GH-B2 adn 3 at the GH-D2 locus. The most frequent alleles were Gli-Alb (62,5%), Gli-Bll (37,5%), Gli-Dlb (62,5%), and Gli-D2b (62.5%).
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
GENETIC ANALYSIS OF THE AREA OF THE FLAG LEAF IN WHEAT (Triticum aestivum L.)
D. KNEŽEVIĆ, M. PAVLOVIĆ, Marija KRALJEVIĆ-BALALIĆ l i Veselinka ZEČEVIĆ
Institut za istraživanja u poljoprivredi "Srbija", Centar za strna žita "Kragujevac", Kragujevac
1 Poljoprivredni fakultet Novi Sad, Novi Sad
Diallel crosses of
four diverse wheat genotypes (Jugoslavia, Žitnica, Novosadska Rana 2 and Osiječanka)
were studied to evaluate the mode of inheritance, gene effects and arrays of
dominant and recessive alleles for the area of the flag leaf in the F1 and F2
generations and parents of wheat cultivars. Analysis of the variance of genetic
components was done according to the methods of Hayman (1954), Jinks(1954). The
Vr/Wr, graphical analysis was done by the method suggested by Mather
and Jinks (1971). The results obtained indicate that the mode of inheritance of
the leaf flag area in wheat was different. The inheritance of this trait in the
fi generation was over-dominance
with the occurrence of heterosis and in F2 it was intermediate partial
dominance and over-dominance. The additive (D) component of variance was lower
than the dominance component (HI, H2) which indicated that dominance components
had the main impact in the inheritance of the leaf flag area. The values of F,
Kd/Kr, H2/4H1 showed the preponderance of dominant over recessive genes for the
area of the flag leaf. The frequency of dominant alleles (u) was higher than
that of recessive ones (v) which was in complete agreement with F, Kd/Kr,
H2/4H1 for the area of the flag leaf. The degree of dominance measured by ![]() indicated over-dominance in F1
and partial dominance in F2 in the inheritance of flag leaf area. The
regression line cut the Wr axis below the point of origin in F1 indicating
over-dominance, and above the point of origin in F2 indicating partial
dominance which is in agreement with the degree of dominance. The expected
regression line in both analyzed generations was distant from the limiting
parabola which indicated that dominance effects prevail in the inheritance of
flag leaf area, the scatter of the array along the regression line indicated
the presence of genetic diversity in the parents. The Jugoslavia cultivars had
more dominant genes and Novosadska Rana 2 cultivars more recessive genes for
the area of the flag leaf.
indicated over-dominance in F1
and partial dominance in F2 in the inheritance of flag leaf area. The
regression line cut the Wr axis below the point of origin in F1 indicating
over-dominance, and above the point of origin in F2 indicating partial
dominance which is in agreement with the degree of dominance. The expected
regression line in both analyzed generations was distant from the limiting
parabola which indicated that dominance effects prevail in the inheritance of
flag leaf area, the scatter of the array along the regression line indicated
the presence of genetic diversity in the parents. The Jugoslavia cultivars had
more dominant genes and Novosadska Rana 2 cultivars more recessive genes for
the area of the flag leaf.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
POLYMORPHISM OF Gli-Dl AND GH-D2 LOCI IN WHEAT (Triticum aestivum L.)
D. KNEŽEVIĆ, Ljiljana VAPA l i Aleksandra YURIEVNA NOVOSELSKAYA 2
Inslitut za istraživanja u poljoprivredi "Srbija", Centar za strna žita, Kragujevac, Kragujevac
1 Prirodno matematički fakultet, Novi Sad
2 Institut za opštu genetiku i molekularnu biologiju, Moskva
Genes encoding for protein synthesis in wheat are located in the short chromosome arms of group I and VI of the ABD genome. Earlier investigations have revealed great allelic variability of all six gliadin loci, some of which represent markers of certain agronomically and technologically important wheat characteristics. In the present work, therefore, we discuss the allclic variability of the gliadin loci (Gli-Dl and GH-D2) in 61 wheat cultivars. Gliadins were extracted in 70% ethanol and separated on 8,3% polyacrylamide gel at pH 3,1. Gliadin blocks were identified by comparing the examined wheat cultivar electrophoregrams with standard cultivars. Genetic analysis showed that gliadin blocks controlled by Gli-Dl and GH-D2 alleles possessed 3-6 gliadin components. Five different gliadin blocks encoded by Gli-Dl and seven by GH-D2 locio were identified. Gli-Dlb and Gli-D2b were among the most frequent alleles.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
HALF-SIB TESTS CROSS RECURRENT SELECTION OF MULTIGERM TETRAPLOID POLLINATORS OF SUGAR BEET
L. KOVAČEV, N. ČAČIĆ i Snežana MEZEI
Institut za ratarstvo i povrtarstvo, Novi Sad
Further improvement of the genetic potential for yield and other agronomic characters of sugar beet depends on several factors: the creation of new genetic variability; the proportion of superior genotypes in the original population; the efficiency of breeding methods which will increase the frequency and accumulation of desirable genes, the identification and fixation of superior genotypes. As multigerm tetraploid populations are used as pollinators, i.e. donors of two genomes in the triploid hybrid in sugar beet, their role is important in the formation of the final characteristics of the hybrid. It can be concluded from the results, even though only one cycle was included, that half-sib test cross recurrent selection can be an efficient method to increase desirable genes, improve the population per se and its combining abilities.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
CALLUSOGENESIS IN SUGAR BEET (Beta vulgaris L.)
B. KOVAČEVIĆ, Snežana MEZEI i Marija KRALJEVIĆ-BALALIĆ
Institut za ratarstvo i povrtarstvo, Poljoprivredni fakultet, Novi Sad
Sugar beet (Beta vulgaris L.) is a dicotyl, biennial cultivar from the family, Chenopodiaceae. Examination of callusogenesis in sugar beet is an important task in the process of improving sugar beet breeding. Three diploid, monogerm, autofertile, synthetic populations 112 A, 115 and 116 Z were examined. Explants of cotyledon, hypocotyl and leaf, taken from 3-week old seedlings were used. A percentage of callus initiation was transformed and used for the calculation of statistical tests by the STATGRAPHICS program. The rate of change was calculated as the relative value of callus growth. Differences between variants were tested by the t-test. Initiation and growth of calli were examined according to the genotype source of explants and the medium. Calli differed according to the medium content and consistency. It was found that on liquid media, the initiation of callus was significantly influences by the medium content and the source of explants, but on solid media only by the medium content. There was no significant difference in callus growth between the first four and the second four weeks of growth, as well as between the calli from cotyledon and hypocotyl of population 112 A. A significant influence of the medium content on callus growth was noticed.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
COMBINING ABILITY ANALYSIS FOR GRAIN NUMBER IN WHEAT
Mirjana KRALJEVIĆ-BALALIĆ, M. DIMITRIJEVIĆ i Sofija PETROVIĆ
Poljoprivredni fakultet, Institut za ratarstvo i povrtarstvo, Novi Sad
A 5x5 diallel analysis, excluding reciprocals, was done in the F1 generation to obtain data on gene action, namely, general (GCA) and specific (SCA) combining ability in wheat. Five genetically divergent wheat genotypes, possessing different major genes for plant height (NS Rana 2, Bankut 1205, NS 732, Atlas 66 and Siete Cerros 66) were crossed. The ten F1 hybrids and their parents were tested under field conditions in a randomized, complete block design with three replications. The combining ability analysis was made according to Grilling (1956), method 2, model I. The results obtained showed that the parents, used in the crosses, significantly differed in the studied character. Both additive and non-additive gene actions controlled the expression of grain number per spike. The highest positive GCA values were shown by Siete Cerros 66. The crosses NS Rana 2xNS 732 and Bankut 1205 x Siete Cerros 66 were the combinations with the highest positive SCA values, so they may provide potential breeding material.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
COMBINING ABILITY AND GENE EFFECTS FOR ROOT VOLUME IN WHEAT
M. KUBUROVIĆ, M. PAVLOVIĆ i D. KNEŽEVIĆ
Institut za istraživanja u poljoprivredi "Srbija", Centar za strna žita "Kragujevac", Kragujevac
Considering the importance and role of the root system in plant life, roots are the subject of many investigations. In this work the root volume as an important element of the development of the root system was studied. Three divergent wheat genotypes (Sava, Libellula and Kruševačka 9083), were used for diallel crosses (without reciprocals). The mode of inheritance, gene effects and combining ability for the root volume in wheat was studied in the F1 and F2 generations. Analysis of variance for combining ability was made using method 2, model I (Griffing, 1956), and regression analysis was done by the method used by Mather and Jinks (1971). The results of this investigation showed that partial dominance prevails in the inheritance of root volume. Analysis of variance for combining ability showed that the general combining ability was highly significant, which indicated that additive components have the main impact in the inheritance of this trait. The best general combiner was the Sava cultivar for stable root volume in wheat. The variance for the specific combining ability was not significant indicating the absence of differences for root volume. The regression line was nearly on the limiting parabola, which indicated, that genes with additive effects prevail in the inheritance of root volume. The regression line cuts the Wr axis above the point of origin indicating partial dominance in the inheritance of this trait. Libellula and Kruševačka 9083 had more dominant genes and the Sava cultivar more recessive genes for root volume. The scatter of array points and values of the regression coefficient indicated the absence of an interallelic interaction for root volume.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
INDUCTION OF HAPLOID CALLUS IN SUGAR BEET
Nevenka KUPREŠANIN i Snežana MEZEI
Institut za ratarstvo i povrtarstvo, Poljoprivredni fakultet, Novi Sad
In these experiments the influence of two media Cr (4,5 ηM, 2,4 D, 9,3ηM kin. and 0,5ηM GA3) and XII (4,5ηM, 2,4 D and 4,6ηM kin.) on callusogenesis of eight different genotypes of sugar beet was studied. The terminals of immature inflorescences were removed and sterilized. Ovules were excised from flower buds and after four weeks haploid plants regenerated. Callus was obtained on leaf explants that originated from haploids. Explains were grown in sterile conditions and inoculated on the tested media which contained Gamborg bs macro and micro elements with the addition of 3% sucrose, 0,7% agar and plant growth substances. A large variability in callus cultures was observed concerning pigmentation, texture and consistency of tissue. Analysis of variance for callus proliferation showed highly significant differences in callus growth between the genotypes and an interaction genotype/media. Genotype 1 showed the highest proliferation of callus cells on both tested media.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
POSSIBILITIES OF THE APPLICATION OF RESTRICTED SELECTION INDEXES IN DAIRY CATTLE POPULATIONS
D. LATINOVIĆ 1, LJ. LAZAREVIĆ 1, P. STOJIĆ 2, G. TRIFUNOVIĆ 1 i M. KATIĆ 2
1 Poljoprivredni fakultet, Beograd - Zemun
2 Agroekonomik, Beograd
For an illustration of the construction of restricted selection indexes, random sampled black and white bulls and cows with a different proportion of Holstein Friesian genes were used. Basic indexes, variances and covariances were calculated using the program "selind" (Cunningham, 1989) and the least squares method (Harvey, 1990). The indexes of bulls and cows are shown by the following general equations:
IB = b1χ1 + b2χ2
IB = b1χ1 + b2χ2 + b3χ3
b1b2b3 = Regression coefficients
χ1 = Milk yield in the standard lactation (kg)
χ2 = Milk fat yield in the standard lactation (kg)
χ3= Service period (days).
Restriction is imposed on the milk fat yield. It means that this trait is treated as a constant (Dummy trait). According to the results, the following indexes are constructed:
Ibulls = 0,0157 χ1 + (-0,3441) χ2;
Icows = 0,0152 χ1 + (-(),3302) χ2+ (-0,0085) χ3
Further investigations need to include more traits of economical importance.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
THE PHENOTYPE - PHYSIOLOGICAL VARIABILITLY OF 29 DOUGLAS FIR PROVENANCES IN TEST PLANTATIONS
Vera LAVADINOVIĆ, V. ISAJEV
Institut za šumarstvo i šumarski fakultet, Beograd
The Douglas fir is one of the most important species for forestry in Serbia. In this aim, provenance tests of the introduction for exotic species have been carried out for the improvement of allochthonous conifers. In order to study the genetic potential of Douglas fir provenances for their directed utilization, an experiment was set up with 29 provenances of this species, at two localities (Juhor and Tanda) using seeds collected throughout Western U.S. from Mexico up to the State of Washington. The choice of experimental fields was made on the basis of the climate, soil characteristics, altitudes and the existing vegetation. The objective of this investigation was to study a series of phenotype - physiological characteristics in order to select the most favourable provenances for the corresponding sites in Serbia in which this fast-growing species will be successful. The research of the phenotype-physiological variability was carried out with the aim of obtaining more reliable selection of provenances for sites in Serbia. Based on the results obtained it can be concluded that test - trees should be identified for long - term analyses, cloning and hybridization.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
POSSIBILITIES AND LIMITS IN THE GENETIC IMPROVEMENT OF MILK CHARACTERISTICS IN CATTLE
LJ. LAZAREVIĆ
Poljoprivredni fakultet, Beograd-Zemun
Genetic improvement of milk characteristics is of substantial economic importance and is a subject of interest of both scientists and breeders. With reproduction by insemination genetic improvement is mainly achieved through bulls. When considering the possibilities for genetic improvement attention is given to the genetic variation, the methods of breeding value estimation, and the selection intensity, while the limits discussed are test conditions, size of active population, and inbreeding. Possible contributions of new methods of embryo manipulation and genetic engineering are also presented.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
THE INFLUENCE OF THE LEVEL OF MILK
PRODUCTION ON THE GENETIC VARIATION
LJ. LAZAREVIĆ, D. LATINOVIĆ, G.
TRIFUNOVIĆ, M. KATIĆ i P. STOJIĆ
Poljoprivredni fakultet, Beograd-Zemun
The expression of additive gene effects for quantitative traits is essentially dependent on environmental influences. Related to that the additive genetic variation was investigated at three levels of milk production. A sample with 5143 cows, daughters of 21 sires from a black and white cattcl population was the subject of this investigation. All cows were divided into three groups or levels of milk production. The estimation of the components of variance was performed by mixed models with sires, farms, years, seasons, service period and age at calving included. Heritability (h2 ) which are indicators of the additive genetic variation increased with higher level of milk production. For the milk yield h2 was 0.02 (low level) and 0.17 (high level), and for FCM 0.04 (low) and 0.19 (high level). Based on the results obtained the conclusion is that better environmental conditions yielded higher additive gene effects and that makes more efficient selection possible.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
INHERITANCE OF STEM HEIGHT IN BARLEY HYBRIDS (Hordeum vulgare L.)
Milomirka MADIĆ 1 i M. PAVLOVIĆ 2
Agronomski fakultet - Čačak
Institut za istraživanja u poljoprivredi "Srbija", Centar za strna žita "Kragujevac", Kragujevac
In diallel crosses of four diverse barley genotypes, F1 and F2 hybrids were obtained. These cultivars and hybrids were used to investigate the mode of inheritance, gene effects and heritability for stem height. Statistical analysis was done according to Hayman (1954), Jinks (1954), and Mather and Jinks (1971). The results indicate that the mode of inheritance of stem height in barley was different (partial dominance, dominant inheritance and overdominance). The stem height in barley was mostly inherited as an overdominance character. The presence of an excess of dominant genes in all parents included in the diallel existed. The degree of dominance indicated superdominance in the inheritance of stem height. The regression line cut the Wr axis below the point of origin indicating overdominance. The array near to Vr, Wr indicated a genetic divergence of the parents which differed in the possession of dominant and recessive genes for stem height. Heritability was 42%, indicating the influence of the environment on the expression of stem height.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
CORRELATIONS AND PATH ANALYSIS IN CASTOR BEANS (Ricinus communis L.)
R. MARINKOVIĆ,
D. ŠKORIĆ, J. CRNOBARAC i N. DUŠANIĆ
Institut za ratarstvo i povrtarstvo, Novi Sad
We have studied correlation between some plant and seed traits (plant height, raceme height, number of leaves per plant, number of seeds per plant, 1000-seed mass, kernel content) and their correlation with seed yield per plant. A positive, highly significant correlation was found only between the seed yield per plant and 1000-seed mass. All other traits were in negative and plant height and number of leaves per plant in a significantly negative correlation with seed yield. Path-coefficient analysis showed that plant height had the highest direct positive effect on seed yield. The number of seed per plant had also a positive, but not so high direct effect on seed yield. All other studied traits had negative effects on seed yield.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
THE INTERRELATIONSHIP BETWEEN MORPHO-ANATOMICAL CHARACTERISTICS OF THE FLAG LEAF AND CEERTAIN COMPONENTS OF WHEAT YIELD
Ljiljana MERKULOV 1, Jadranka IVEZIĆ l i Marija KRALJEVIĆ-BALALIĆ
2
Inslitut za biologiju, PMF, Novi Sad
2 Institut za ratarstvo i povrtarstvo, Poljoprivredni fakultet, Novi Sad
Selection of high-yielding genotypes also demands an appropriate amount of knowledge of the leaf structure and physiology if it’s role in organic matter synthesis and therefore in yield formation is taken into account. In this respect the role of the flag leaf is important owing to its position, i.e. immediate vicinity to the spike supping it directly with assimilation products. In our present work, therefore, we investigated the morpho-anatomical characteristics of the flag leaf in different wheat genotypes to establish the degree of interrelationship between these characteristics and certain yield components. Ten wheat genotypes of different geographical origin grown on the experimental field at Rimski Šančevi (Institute of field and Vegetable Crops) in the period 1991/92 were used. Plant material was collected in July. The leaf area was measured by the Parable Areameter Li 3000 (USA). Transversal sections of the median lamina portion were made by using a freezing microtome and microscopic measurements were clone to analyze leaf anatomy. Features of the stomatal apparatus were analyzed on epidermal prints after Wolf. The results obtained show remarkable genetic differences in the leaf area, size of stomata, their number per mm, their total number, mesophyll thickness, and finally bundle sheath size. A significant genetive correlation between the number of stomata per unit area and yield was established. A negative correlation was obtained between the mesophyll thickness and yield while a positive but not statistically significant correlation was found between leaf and bundle sheath areas and the yield.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
GENETIC VARIABILITY OF WHEAT IN MAKING NATURAL ASSOCIATIONS WITH FREE-LIVING DIAZOTROPHS
Danica MIĆANOVIĆ 1, Zora SARIĆ 2, M. SARIĆ 3 i V. MITROVIĆ 4
1 Institut za istraživanja u poljoprivredi "Srbija" - Centar za strna žita "Kragujevac", Kragujevac
2 Poljoprivredni fakultet u Novom Sadu, Novi Sad
3 Srpska Akademija nauka i umetnosti, Beograd
4 Institut za istraživanja u poljoprivredi "Srbija", Centar za voćarstvo, Čačak
The ability of Triticum aestivum L. to develop in a natural association with free-living diazotrophs makes possible the selection of the best association of genotype strain for most important trails for nitrogen fixation and nitrogenase activity. Ten wheat cultivars: KG-56, Srbijanka, Skopjanka, Studenica, Tamiš, Sana, Jugoslavia, Evropa, NS-Rana, and Partizanka were studied. Plants were grown in vitro in aqueous media with a Reid-York nitrogen solution set. In two successive experiments diazotrophs were transferred from a wheat root grown in vivo to the wheat roots grown in vitro. Nitrogenase activity was determined on a gas chromatograph by the acetylene-ethylene association method (Hardy, 1968). Nitrogenase activity varied between the investigated genotype-strains in both experimetns. The highest nitrogenase activity in the first experiment was 62,5 amol Cz//4gr, of root. In the second experiment the highest nitrogenase activity was 420 amol C2//4gr of root. Based on the obtained results it was possible to conclude that the examined genotypes are able to select and stimulate the multiplication of some diazotrophs within the root rhizhosphere.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
ATROPHY OPOVULES IN FLOWERS WITH AN INTERRUPTED DEVELOPMENT IN THE PLUM (P. domestica L.)
N. MIŠIĆ R. CEROVIĆ i Gordana ĐURIĆ
Inslitut za istraživanja u poljoprivredi "Srbija", Centar za voćarstvo i vinogradarstvo, Čačak
While studying the flower development of different plum cultivars, interruption in flower development was observed in cvs. Požegača and Čačanska Rodna, occurring from the beginning of the baloom stage to full flowering. As a result of the interruption in the development of petals, sepals and filaments, atypical flowers were formed, which fell immediately after flowering. Histological analyses of the atypical flowers compared to the normal ones showed the occurrence of ovule atrophy. The first atrophy symptoms were observed when the flowers were in the baloon stage. Histological analyses of the flowers showed normally developed male and female gametophytes, atrophy of the ovules being observed in the chalaza region of the nucellus. As the flowering stage began, the atrophy of the nucellus continued to spread to the integuments as well, spreading over the embryo sac in the full flowering stage. On the basis of the development of the embryo sac structure in the atypical flowers, it may be concluded that the described phenomenon of ovule atrophy did not appear due to disorders in embryo sac development, or under its influence.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
OVARY DEFORMITIES IN PLUMS DUE TO IRREGULAR CARPEL FUSION
N. MIĆIĆ, R. CEROVIĆ i Gordana ĐURIĆ
Institut za istraživanja u poljoprivredi "Srbija", Centar za voćarstvo i vinogradarstvo, Čačak
Fruits formed with various degrees of deformity in the suture region, and partially open or cracked fruits were observed in some plum cultivars. This phenomenon clearly indicates that deformities occur due to a disorder of the fusion of carpel margins. Histological analyses showed various irregularities during the fusion process of the carpel, which is carried out simultaneously with the differentiation of the ovule primordia, as well as with the full flowering process. Disorders observed during the carpel fusion may be grouped as follows: (1) complete fusion of different contact regions of carpel margins; (2) partial fusion of carpel margins; (3) carpel not fused along the whole ovary length (from the obturator region to the ovary base). All three groups have normally developed ovules with embryo sacs. Besides the effect on the fruit morphology, disorders of carpel fusion may cause development of various numbers of ovules, as well as a different position of ovules in the loculus of the ovary.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
YELLOW SPOTS ON SUNFLOWER LEAVES (H. annum L.) ARE CAUSED BY NUCLEAR AND EXTRANUCLEAR FACTORS
M. MIHALJČEVIĆ
Institut za ratarstvo i povrtarstvo, Novi Sad
Albinism and chlorotic changes on the leaves of sunflower inbred lines occur spontaneously with continual self pollination of cross pollinating plants. The occurrence of yellow sectors or spots on sunflower leaves may be caused by parasites, chemical agents or can be induced by nuclear or extranuclear factors. Direct and reciprocal crossing of the genotype RHA-CD-YLW (yellow spotted leaf) with a standard (green leaf) produced plants with green leaves in the F1 generation. The segregation ratios of 13:3 in the F2 generation (P = 90-95% for direct and P = 50-70% for reciprocal crosses) and 1:1 in the test crosses (P = 50-70%), indicate inhibitory gene action. Crossing of the genotype XMAC-27 with a standard produced significant differences between direct and reciprocal crosses in the F1. Self-pollinated plants with chlorotic sectors give progenies which had a similar phonotype and also plants with albino and green leaves in different and non-stable ratios. The results obtained confirmed the hypothesis of the influence of cytoplasmic particles on the expression of the changes studied. Plastid variegation indicated a strict maternal determination of the progenies. The effect of somatic segregation was inducted by the higher number of lethal albino plants. The highest number of albino plants originated from seeds of the albino head sector (>90%) and from mixed sectors (>40%).
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
FUTURE NEEDS FOR CCHANGES OF CONCEPTIONS AND METHODS IN PLANT BREEDING
I. MIHALJEV, Marija KRALJEVIĆ-BALALIĆ, P. DORIĆ i S. PETROVIĆ
Poljoprivredni fakultet, Institut za ratarstvo i povrtarstvo, Novi Sad
In this century excellent progress in plant breeding has been achieved. A great number of varieties and hybrids with good agronomic characteristics were created, and the potential for yields in many species was increased by the rate of 1% yearly. In the next decade plant breeding faces new tasks. Because of this it is necessary to plan changes of conceptions and methods of creating new cultivars. Regarding conceptions to requirements which are the result of changes which have arisen in the modern world need to be satisfied and they can be expressed in a few main statements: to adapt to global climatic changes, to protect from environmental pollution, to increase hygienic security and the nutritive quality of food, to increase the level and stability of yields, and to increase the profitability of crop production. Regarding methods and techniques of plant breeding, thanks to new knowledge from "in vitro" cultures, cytogenetics, molecular genetics and genetic engineering, it will be possible to improve conventional methods of plant breeding and introduce new methods and techniques. Having this in mind, in this paper several possibilities to meet future needs in plant breeding: breeding disease and insect resistant cultivars, biological control of pathogens, breeding low input cultivars, fixation of atmospheric nitrogen, breeding hybrid cultivars by utilization of genetic mechanisms, breeding cultivars suitable for mechanisation, breeding for improving nutritive food quality, and the introduction of new plant species are identified.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
THE VARIABILITY OF GRAPE YIELD AND CHLOROPLAST PIGMENT CONTENTS IN HYBRID DESCENDANTS OF THE GRAPE VINE (Vitis sp.)
M. MILUTINOVIĆ, Ružica DŽAMIĆ, L.
AVRAMOV, D. NIKOLIĆ i M. NIKOLIĆ
Poljoprivredni fakultet, Beograd – Zemun
In the grape vine breeding program, interspecies hybridization is applied for creating new cultivars, which are resistant to diseases and inviolable ecological factors, and also with an expressed yield and quality of grape. This work shows the results of an investigation regarding variability in yield, chlorophyll and carotenoid contents, as well as chl.a/b i chl.a+b/carot ratio variability in interspecies hybrids of the F1 generation, obtained by crossing S.V.18315 x Black Muscat. The yeild of the grape vine was measured at full ripeness, and the dynamics of the photosynthetic pigment contents was observed in two phenological phases (gloss owing and growth of berries). Their content were expressed through average values. The contents of chlorophyll and carotenoid were determined spectrophotometrically, after extraction with acetone (Wetsttein, 1957). The grape yield varied between 0,86 and 6,80 kg, and per parental partners, between 3.18 and 4.37 kg. The chlorophyl content was highest m Black Muscat leaves (5.51 mg/g), and in most seedlings, it varied within the boundaries of the other parent (S.V.18315) (4.74 mg/g). The chlorophyll a/b ratio did not change significantly in relation to parental parents. A similar relation was established for the carotenoid content. On the basis of the calculated coefficient of variation, it can be stated that the greatest variability was in the grape yield (CV = 62,91%), and the least was in the carotenoid content (CV = 3,72%). The coefficient of correlation between the yield and chl.a/b ratio (r = 0,41) showed a moderate correlation, whilst coefficients of correlation between the grape yield and chlorophyll content (r = 0,261 and between the yield and carotenoid content (r = 0,09), showed no significant correlation between the mentioned polygenically determined characteristics.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
MULTIVARIATE ANALYSIS IN DIFFERENT POPULATIONS OF WILD SWEET CHERRY (Prunus avium L.)
M. MILUTINOVIĆ, Gordana
ŠURLAN-MOMIROVIĆ, N. RALEVIĆ, Ivana RALEVIĆ i Vera RAKONJAC
Poljoprivredni fakultet, Beograd - Zemun
Several autochthonous populations of wild sweet cherry (P. avium L.) have been collected from Serbia. Morphological variability in these populations was analyzed. The discrimination effect of the eight characters was examined. It using methods of multivariate analysis. The results of the classification obtained according to the linear discriminant functions expressed a very slight difference between the real and evaluated groups. Similar populations were clusted according ot the results of Euclidean distance analysis. The results obtained indicate precise separation into clusters by the numerical method, as well as evaluation of the collection of wild chery germplasm.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
SELECTION OF PERSIAN WALLNUT, Juglans regia L. IN SERBIA
A.M. MIRKOVIĆ, R.R. TODOROVIĆ, P.D. MIŠIĆ, Z.V. PAVLOVIĆ i N.G. ZEC
Zavod za voćarstvo i vinogradarstvo, Institut "Agroekonomik", Beograd
Persian walnut is a fruit tree with a long phylogenemis its Walnut kernel has a high nutritive value. Its production in Yugoslavia is insufficient. The aim of walnut selection from the polymorphic-native population in Serbia was: vitality, late leafing, heavy cropping and high kernel content. Twenty vital walnut selections have been chosen from 1983 to 1991. The most promising selections are: 37/MP/83 (from Mali Popović), Z/206/87 (Zlot), V/204/87 (Vlasotince) and S901 and S902 (Stubal, Aleksandrovac). Selection Z/206/87 is laic leafing (early May), S901 is a heavy cropper (250 kg/tree) and V/204/87 has a high edible kernel content (64%).
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
ECONOMIC AND BIOLOGICAL PROPERTIES OF SOME WALNUT SELECTION
M. MITROVIĆ
Centar za voćarstvo i vinogradarstvo - Čačak, Čačak
There is an abundant walnut population in Yugoslavia, developed spontaneously from seeds. Over the last 15 years, there has been an increasing interest in walnuts, which necessitated the selection of this nut crop, and it is being conducted in several Yugoslav scientific-research institutions. Clonal selection resulted in hundreds of walnut types with interesting economic and biological properties. About 110 of them have been studied thoroughly. From amony them, 6 were released as the first Yugoslav walnut cultivars. The fruit and Viticulture Research Institute in Čačak has been engaged in work on clonal selection of walnuts and in more recent years planned hybridization has also been employed. Of the types selected, a more detailed account will be given for 5 of them that were distinguished by their characteristics, as follows: Type 5/79 - Vrba, late, productive; Type 7/88 - Ljubić, productive, recemose type; Type 11/89 - Milićevci, exceptionally productive; Type 12/90 - Jczdina, exceptionally productive, recemose type; Type 1/90 - Kablar, late, exceptionally productive.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
COMPATIBILITY BETWEEN SUGAR BEET HYBRIDS AND Azotobacter STRAINS
Nastasija MAKOVAČKI, Snežana MEZEI i L. KOVAČEV
Institut za ratarstvo i povrtarstvo, Novi Sad
For their normal development sugar beet plants use the ammonium or nitrate form of nitrogen which is added as a mineral fertilizer. The practical importance of nitrogen in metabolic processes in sugar beet is, as in other species, in the synthesis of aminoacids. An increase of nitrogen uptake by the application of inoculations of nitrogen fixing bacteria has been demonstrated by several authors. The selection of sugar beet should include the identification of genotypes which are able to replace part of the mineral nitrogen indispensable for their nutrition with elementary nitrogen from the air. Such an associative nitrogen fixation would enable the production of hybrids which would produce a high and stable yield after applying low amounts of mineral nutrients. The objective of this study was to isolate strains of Azotobacter sp. from the rhizosphere of two studied sugar beet hybrids and test their compatibility. We studied the specific relationship between 7 Azotobacter strains (1,2, 3, 5, 8, 12 and 13) isolated from the rhizosphere of two sugar beet hybrid varieties NS-Hy 11 and Dana. We observed the relocation of Azotobacter strains towards the root of differently aged plants (2 and 4 weeks old seedlings). The assay of nitrogenase activity was done in pure cultures. Strain 3 had the highest nitrogenase activity in pure culture followed by strains 13, 8 and 1 in that order. When observing the colonization of roots of the hybrids, strains 3 and 8 colonized the hybrid NS-Hy 11 best, (14 and 28 days after inoculation) which correlates with the activity of nitrogenase in the pure culture. The hybrid Dana had similar root colonization with all strains except 13, which showed no colonization. It can be concluded that the hybrid Dana is more compatible with all strains of Azotobacter studied than NS-Hy 11.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
AN ASSESSMENT OF THE POSSIBILITY OF UTILIZATION OF LEAF-BLADE ANATOMIC STRUCTURE IN POPLAR SELECTION
S. ORLOVIĆ, V. GUZINA
Naučni institut za topolarstvo, Novi Sad
This paper presents the results of research on the variability of epidermal, palisade, spongy and hypodermal tissue thickness, percentage of photosynthetically active tissue, number, stoma length and width, diameters and heights of one-year-old seedlings, as well as the produced biomass of six poplar clones, i.e.: cl.53/86, cl.54/86, (P. nigra), cl.M1 and cv. green robusta (P. x euramericana) and cl.PE 19/66 and S1-8 (P. deltoides). Differences were observed between the clones regarding the examined parameters of the leaf-blade anatomic structure, stomata and biomass of one-year-old seedlings, as well as the relations between them. It was concluded that the greatest number of stomata per mm2 on the adaxial side of the leaf is present in the clones P. deltoides, then P. x euramericana and P. nigra, whereas there is no regularity in this respect on the abaxial side. Stoma length and width were greatest in the clones off nigra and smallest in P. deltoides. The clones of P. x euramericana were mainly intermediary in this respect. The greatest percentage of photosynthctically active tissues, as well as the greatest biomass dry-weight produced was found in the clones of P. deltoides. Cluster analysis showed clone grouping of P. nigra, P. x euramericana nad P. deltoides which points to the expressed specificities of the researched species. The results suggest the possible utilization of leaf-blade and stoma anatomic characteristics in the selection of poplar genotypes for desired properties. Only based on the results of experimental research, we shall be able to define more precisely the elements of the leaf-blade anatomic structure which are narrowly related to the desired properties in poplar selection.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
POPCORN HYBRIDS - DEVELOPMENT AND UTILIZATION
Zorica PAJIĆ i M. BABIĆ
Institut za kukuruz "Zemun Polje", Beograd-Zemun
Popcorn is a special type of flint maize. It differs from standard maize in a way that in response to heating kernels pop forming large flakes. Popcorn hybrids have higher yields and a high popping volume, and therefore, production based on there hybrids are economically justified. To attain the maximum popping volume, it is necessary to harvest popcorn when kernel moisture is below 20%, not to damage the kernel pericarp and to assure that kernel moisture at popping is 13-14%.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
GENETIC EFFECTS AND INHERITANCE OF THE SIZE OF THE SCLERENCHYMOUS LAYER IN THE WHEAT STEM
M. PAVLOVIĆ, M. KUBUROVIĆ, D. KNEŽEVIĆ i Veselinka ZEČEVIĆ
Institut za istraživanja u poljoprivredi "Srbija", Centar za strna žita, "Kragujevac", Kragujevac
Lodging resistance represents a complex trial which is determined by a group of morpho-anatomical stem traits. This trait is genetically controlled and its expression depends on environmental factors. The sclerenchymous layer in the wheat stem is close to the epidermis and consists of cells with thick lignified walls in several rows. Considering the absence of protoplasm, these cells contribute to the firmness and mechanical support of the stem. Diallel crosses of four diverse wheat genotypes (KG-75, Jugoslavia, Baranjka, NS-322) were studied to evaluate the mode of inheritance, gene effects and combining ability for the size of the sclerenchime layer in the F2 generation. The combining ability was analyzed according to Griffing (1956) method 2, model I, and regression analysis was done by the method Hayman and Jinks (1971). The testing of the mean value in progenies in relation to parents showed that the most frequent mode of inheritance was the over-dominance of the parent with a smaller sclerenchymous layer. The regression line was substantially distant from the limiting parabola which indicated that dominance effects prevail in the inheritance of this trait. The regression line cut the Wr axis below the point of origin indicating over-dominance in the inheritance of the size of the sclerenchymous layer. The distribution of array points was within the limiting parabola that indicated genetic divergence of parent cultivars. The KG-75 cultivars had more dominant genes and Baranika had more recessive genes for the studied traits. The scatter of array points in the Wr-W’ graph and the value of the regression coefficient showed the presence of an interallelic interaction for the size of the sclerenchymous layer. Analysis of variance of the combining ability showed that the specific combining ability (SCA) was highly significant indicating the preponderance of non additive gene action in the inheritance of the size of the sclerenchymous layer. The Yugoslavia cultivar and the highest value of GCA. The SCA values were mainly negative, which indicated that variance in these crosses was non additive.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
INHERITANCE OF STEM HEIGHT IN WHEAT HYBRIDS OF THE F3 AND F4 GENERATIONS
V. PEŠIĆ i Dragica ZORIĆ
Poljoprivredni fakultet, Beograd-Zemun
This paper discusses the involvement of inheritance, genes and heritability in affecting stem height in wheat in 15 crosses combinations. The following types of crosses were studied: a) four cross combinations with two varieties (Beogradjanka, Agrounija, Rana niska, KG-56); eight cross combinations with three varieties (Zemunka, Rana niska, Marija, Agrounija, Zadruga, Partizanka, Skopljanka, Panorama, Nizija); c) four cross combinations with four varieties - complex crosses (Zadruga, Lasta, Rana niska, Nizija, Parlizanka, Agrounija, Marija, Zemunka 1). In 1991 and 1992 the pedigree selection method was used by which a RECORD was made of the lines selected. A frequency distribution was done for all cross combinations involving the inheritance of wheat stem height in the F3 generation and some lines in the F4 generation. Significant differences between mean parent values were assessed. Mean values in the F3 generation were reported to be with in the scope of those of parent plants and with a greater variability of the traits in the generation. On the basis of the results obtained, stem height was shown to be mostly partially dominantly and intermediary inherited. In some combinations the occurrence of transgressive partition was reported. Both the additive and non-additive components were involved in the inheritance of stem height although at varying rates. A relatively high heritability value was assessed proving thereby that the inheritance of this trait is genetically influenced.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
AN ESTIMATION OF THE DIVERGENCE OF DONORS CONTAINING FAVOURABLE ALLELES FOR THE IMPROVEMENT OF GRAIN YIELDS OF SOME ZP MAIZIE HYBRIDS (Zea mays L.)
R. PETROVIĆ, N. DELIĆ i M. VIDAKOVIĆ
Institut za kukuruz "Zemun Polje", Beograd-Zemun
For the purpose of evaluating and improving three ZP hybrids, several genotypes were crossed with parent ZP hybrids. Relative values of favourable (dominant) and unfavourable (recessive) genes (alleles) were estimated for several genotypes as potential donors of favourable genes. On the bases of an average grain yield analysis (Dudley, J.W. 1987b) we selected some genotypes that contain favourable alleles at loci where both parents of the elite crosses to be improved, contained unfavourable alleles. In this way it is possible to shorten the breeding procedure.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
THE INHERITANCE AND PHENOTYPIC VARIABILITY FOR THE NUMBER OF KERNELS PER SPIKE IN WHEAT
Sofija PETROVIĆ, Marija KRALJEVIĆ-BALALIĆ i M. DIMITRIJEVIĆ
Poljoprivredni fakultet, Institut za ratarstvo i povrtarstvo, Novi Sad
Five divergent wheat varieties (NS Rana, Bankut 1205, NS 732, Atlas 66 and Siete Cerros) were diallely crossed in order to examine the mode of inheritance and the components of phenotypic variability for the number of kernels per spike. Dominance was observed in F1 progenies of most of the crosses, the rest showed superdominance. Analysis of phenotypic variability components revealed that dominant genes prevailed over recessive, as well as that the main part of genetic variation belonged to the dominant gene effect. The positive and negative alleles at dominant loci were not in equal proportions in the parents. The value of the mean dominance degree indicated that, an average, superdominance occurred in the crosses examined.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
GENETICAL PARAMETERS OF TRAITS OF BODY DEVELOPMENT IN YOUNG FEMALE CATTLE
M.M. PETROVIĆ, R. LAZAREVIĆ, LJ. LAZAREVIĆ 1 S. VASOVIĆ, B. MIŠČEVIĆ, S. ALEKSIĆ, D. RADOSAVLJEVIĆ
Naučni institut za stočarstvo, Beograd-Zemun
1 Poljoprivredni fakultet, Beograd-Zemun
The effect of direct and indirect selection for quantitative traits of body development in young cattle depends on the level of heritability and the genetic connection of the properties. The level of the heritability coefficient influences the choice of breeding method with an objective to increase certain economically important traits of cattle. This investigation of genetical parameters, which implies additive genetical variance in the total phenotypic and genetic correlation, was carried out on a herd of Black and White cattle. The investigation included 200 head of cattle, the daughters of 8 bull - sires, at the ages of 4, 9, 4 and 24 months. In included several traits of body development, body mass, height to withers, shoulders and shellbone, length of carcass, chest and shcllbone width, as well as chest depth and girth. Genetical parameters were evaluated from variance components of sires through model 1 (fixed), method of least squares (Haravey, 1987). The contribution of the additive genetical parameter in the total phenotypic variability was different for different ages. Thus, heritability coefficients changed for certain traits and were from 0,13 to 0,60. Genetical correlations between mass and certain body dimensions, as well as among exterior measurements, were positive and mainly varied from a weak to a strong and complete correlative link (rg = 0,294 to rg= 0,929), depending on the age.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
APPLICATION OF GENETIC MALE STERILITY TO THE SOYBEAN BREEDING PROGRAM
LJ. PRIJIĆ 1, Mirjana JOVANOVIĆ 1 i M. MLADENOVIĆ 2
1 Institut za kukuruz "Zemun Polje", Beograd-Zemun
2 Poljoprivredni fakultet, Beograd-Zemun
It is difficult to manage a high number of crosses in soybeans, because even experienced workers obtained only a few hybrid seeds. Specht et al. (1985, Crop. Sci 25: 717-718) registered an SG1 population with the mS2 gene for genetic male sterility. The initial synthesis of the SG1 population was accomplished by making two-was crosses between 39 female parental lines and four male parental lines, later as mS2 gene donors. In this investigation, the F2 seed from male fertile plants, obtained after four random matings was used. The seed was planted in an isolated nursery, in order to examine pollination efficiency. Plants were grown in an open plot and in a caged plot, both with honey bee (Apis mellifera L.) hives. Male fertile plants were harvested individually. Pedigree selection was applied for obtaining F5 homozygous male fertile lines. The population showed its advantage in the breeding program. More F1 seeds were produced by natural crossing and the selected lines showed superior performance in the yield test.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
VARIJABILITY AND HERITABILITY COMPONENTS OF SOME SWEET CHERRY FRUIT CHARACTERISTICS
Vera RAKONJAC, T. ŽIVANOVIĆ i D. NIKOLIĆ
Poljoprivredni fakultet, Beograd-Zemun
Inheritance parameters of five characteristics (fruit stalk length, fruit length, fruit width, fruit weight, stone weight) in 20 sweet cherry genotypes were calculated from the results af a 2-ycar trial. Using analysis of variance, a significant influence of genetic factors on the variability of all the characteristics studied was detected. The fruit length, fruit width, fruit weight and stone weight were significantly affected by environmental factors. The highest genetic and phenotypic variability (CVS = 19,5%; CVf = 22,0%) was assessed for fruit weight. The lowest variability (CVS = 5,6%; CVf = 7,3%) was estimated for fruit width. Heritability ranged from 58,0% (fruit width) to 84,7% (fruit stalk length) showing thereby that the sweet cherry genotype is of crucial importance to the expression of the characteristics investigated. Very significant and positive genetic and phenotypic correlations between fruit width and fruit weight (rg = 0.96**; rf = 0.93**); fruit length and fruit weight (rg = 0.92**; rf = 0.90**); fruit width and stone weight (rg = 0.98**; rf = 0.60**); fruit length and stone weight (rg = 0.81**; rf = 0.66**) and fruit length and fruit width (rg = 0.89**; rf = 0.83**) were found. The correlation coefficients obtained show that fruit weight is affected by direct selection for increasing fruit dimensions. Based on the results obtained sweet cherry breeders may successfully observe the genotype base of the characteristics investigated and accomplish better the breeding program planned.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
GENETIC CONTROL OF THE OIL QUALITY IN THE MAIZE KERNEL
G. SARATLIĆ 1, K. KONSTANTINOV 2, I. VEREŠBARANJI 1, Snežana MLADENOVIĆ1, J. DUMANOVIĆ 1, B. KEREČKI 1
1 Institut za kukuruz "Zemun Polje",
Beograd-Zemun
2 Institut za ratarstvo i povrtarstvo, Novi Sad
Oil is stored in maize kernels in the form of triglycerides accumulated in the embryo tissue. The unsaturation level is determined from the participation of unsaturated fatty acids in the triglyceride molecules. The fatty acid chain length, level of unsaturation and fatty acid position in the triglyceride molecule are genetically determined. In this report the results of the effect of recurrent selection of two high-oil synthetic maize populations of faly acid content and composition will be discussed. An increase of the oil content is associated with changes in the ratio between saturated and unsaturated fatty acids both in embryo and endosperm tissue. The oleic (C181)/linoleic (C181) fatty acid ratio decreased but the palmitic (C160)/stearic (180) ratio increased. Differences in the fatty acid content and composition between embryo and endosperm tissue were found in both populations. These results were obtained in maize plants belonging to different selection cycles per se. Results concerning the effect of two population crosses and the inbreeding depression effect on the lipid unsaturation level will be presented as well. The relationship between oil quality and protein content in the maize kernel will be discussed.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
THE MODE OF INHERITANCE OF LEAF AREA IN MAIZE (Zea mays L.)
P. SKLENAR, J. BOĆANSKI i Marija KRALJEVIĆ-BALALIĆ
Institut za ratarstvo i povrtarstvo, Poljoprivredni fakultet, Novi Sad
The objective of this study was to determine the mode of inheritance of the leaf area in the F1 maize hybrid. Thirteen inbred lines, CM109, HI20, PLS61B, Mo17HtR, Kapio, W729C, A641, P165, F2, 250A, CM 105, LH-74, Mo17-23 and two lines (CM109 x A6342Ht) and (Mo17Ht x Mo17-23) were used as research material. The crossings were performed in 1990. The plot was established according to the randomized block design in three replications in experimental fields of the Institute of field and Vegetable Crops at the location of Rimski Šančevi in 1991. The highest mean value of this trait was observed in the line (CM 109 x A632Ht) x = 554,01 cm2, the lowest in the inbred line F2 x = 264,24 cm2. Considering the hybrid combinations, the highest mean value of this trait was observed in the combination LH74 x Mo17-23 x = 709,40 cm2 and the lowest int he combination CM109 x PLS61B x = 541,94 cm2. In all hybrid combinations, superdominance (positive heterosis) was the mode of inheritance of this character.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
ČARNA - A NEW CHERRY CULTIVAR
A. STANČEVIĆ i M. NIKOLIĆ
Institut "Srbija", Centar za voćarstvo i vinogradarstvo, Čačak
The work on breeding new cherry (Prunus avium L.) cultivars has been conducted in the Fruit and Grape Research Center in Čačak over the last 35 years. Over 4.500 cherry hybrids have been developed. Out of them, 47 (only 1,04%) have been selected for thorough studies. One of the selected, elite hybrids (V/32) has recently been released as a cultivar and named "Čarna" after its fruit colour and the town it originates from. Čarna cherry was created by aimed hybridization in 1975. It was derived from a cross of Majova Rana x Schrecen Bigarreau, using the required stamen emasculation. Čarna is a mid-earyl cherry cultivar. It ripens in the middle of June, at the same time as cv. Van. The fruit is flat-round, with no prominent suture; the skin is thin, flexible, smooth and glossy, the ground colour being dark red. The flesh is firm, crispy and juicy, dark red, with an excellent aroma. The fruit juice is also dark red, very suitable for colouring juices of other fruit species and for the candy industry. The fruit is suitable both for fresh use and for all kinds of processing. Čarna cherry is high yielding and resistant to fruit cracking.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
IN VITRO GERMINATION AND STORAGE OF BLACKBERRY POLLEN
M. STANISAVLJEVIĆ
Institut za istraživanja u poljoprivredi "Srbija" Beograd, Centar za voćarstvo i vinogradarstvo, Čačak
In breeding new blackberry (Rubus fruticosus L.) cultivars by hybridization a problem may arise that the flowering times of some parent cultivars do not coincide. This is most markedly expressed between the thorny and thornless cultivars. There is a need, therefore, to study the possibility of pollen preservation in blackberry cultivars by deep freezing so that it can be used the following year. The thorny blackberry cv. DARROW and THORNLESS cvs BLACK SATIN, DIRKSEN'S THORNLESS, 74126-RA8, SMOOTHSTEM and THORNFREE were used to test the possibility of pollen preservation. Flowers were collected in the field, just before the petals unfold. The anthers were removed by means of a scalpel and placed in poetri dishes to dry at room temperature for 36 hours. Testing of germination % of fresh pollen was done by germinating it in hanging drops of 12% and 16% sucrose. After 3 hours, the number of germinated pollen grains was assessed under a microscope. Pollen was preserved in stoppered glass vials at -18 to -20°C. Part of the pollen sample was concurrently held at room temperature. After one year pollen germination was carried out again, as already described. Pollen germination immediately after anther removal and drying ranged from 20.91% (DIRKSEN) to 49.20% (SMOOTHSTEM) in 12% sucrose, whereas the values in 16% sucrose ranged from 18.51% to 32.04%, respectively. The germination average in all cultivars was higher in the 12% sucrose solution (34.10%) compared to that of 16% (30.05%). Pollen germination after storage in the 12% sucrose solution ranged from 5.01% in D ARROW to 41.0% in SMOOTHSTEM, whereas in the 16% solution the values varied from 4.03% to 42.30%, respectively. The average pollen germination was slightly higher in the 16% sucrose solution (26.56%) compared to that of 12% (25.90%). If germination of fresh pollen from the blackberry cultivars tested is compared to that stored for one year in a deep freeze, it may be observed that germination declined by 8.20% and 3.49% in the 12% and 16% sucrose solution, respectively. It may be concluded therefore, that pollen may be successfully stored in the given conditions without substantial loss of germination ability, so that it can be used in hybridization in the next growing season.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
A INSIGHT INTO GENETIC SIMILARITIES OF GEOGRAPHICALLY ISOLATED SERBINA SPRUCE POPULATION BASED ON THE TERPENOID COMPOSITION OF VOLATILE NEEDLE OILS
Tatjana STEVANOVIĆ JANEŽIĆ i V. ISAJEV
Šumarski fakultet Univerziteta u Beogradu, Beograd
Secondary conifer metabolites, such as polyphenols, alkaloids or terpentines, with a limited distribution in nature, were analyzed in order to determine the genetic similarity of isolated populations and in hemotaxonomic studies. The concept of using a chemical plant constituent as an independent biochemical property is based on the fact hat biosynthesis of a majority of secondary metabolites is genetically controlled in the same way as morphological and cytological characteristics. By analysis of the terpene composition of volatile needle oils of test Serbian spruce trees from several populations in Europe the degree of genetic control of the synthesis of these secondary metabolites was determined. The trees from which the needles were collected were from a wide range of habitat from the Arboretum of the Faculty of Forestry in Belgrade and from the Arboretum of the Institute for Forest Genetics of BFH in Hamburg. Ether solutions of volatile, needle oils were analyzed by gas-liquid chromatography GLC using a Perkin-Elmer Sigma 2B gas-chromatograph with a Shimadzu C-RIB data system. The identification of single peaks was done with authentic compounds. On the basis of hydrocarbon monoterpenes and their oxygenated derivatives (alcohols, essters and ketones), the same terpene pattern was determined for Serbian spruce volatile needle oils from all examined localities: bornylacetate as a major component, and, in order of decreasing concentrations a-terpineol, limonene/β-phelandrene, camphene, ά-pinene, myrcene, citronellol, santene and tricyclene. On the basis of the high degree of similarity found for terpene patterns of Serbian spruce volatile needle oils from several geographically distant localities it can be concluded that the biosynthesis of these secondary metabolites is significantly genetically controlled.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
A STUDY OF COMBINING ABILITIES FOR GRAIN YIELD IN MAIZE (Zea mays L.)
M. STOJAKOVIĆ, D. JOCKOVIĆ, J. BOĆANSKI, G. BEKAVAC i R. POPOV
Institut za ratarstvo i povrtarstvo, Poljoprivredni fakultet, Novi Sad
Combining abilities of maize lines and hybrids were studied with the aim of producing high-yielding hybrids of the FAO maturity group 600, suitable for growing in plain regions of Yugoslavia. The lines obtained from crossing the line B-84 with similar lines from the BSS population were used as maternal components. Three lines (one from the Lancaster population, two obtained from crossing between domestic plasm and Lancaster plasm) were used as testers. The plots were established according to the randomized block design in Srbobran and Novi Sad, in 1993. The method of line x tester was used for the study of the combining abilities. At both locations, the best general combiner for the grain yield was the line NS L-8, followed by NS L-5 and NS L-4. The worst general combiners were lines NS L-l and NS L-2. In Srbobran, the tester NS L-9 had highly significant positive GCA values for grain yield, while testers NS L-10 and NS L-ll had negative GCA values. In Novi Sad, tester NS L-10 was the best combiner. Significant differences were found between the studied hybrids with respect to the SCA for grain yield of maize. Lines NS L-9 x NS L-11 and NS L-3 x NS L-9 were the best combiners in Srbobran and Novi Sad, respectively. Hybrids NS L-l x NS L-11 and NS L-4 x NS L-10 had the worst SCA values. The dominant component of genotypic variance of grain yield of maize was more significant than the additive component of genotypic variance.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
MODE OF INHERITANCE FOR PLANT HEIGHT IN ORNAMENTAL SUNFLOWERS
Vidosava ŠEĆEROV-FIŠER
Poljoprivredni fakultet, Beograd-Zemun
Plant height is a very important character of ornamental sunflowers. Diallel crosses of five inbred lines of ornamental sunflowers were evaluated for the mode of inheritance, combining ability and components of genetic variability for the plant height in F1 and F2 generations. Significant differences were found among the inbred lines for the examined character. Plant height in F1 and F2 generations was inherited superdominantly or dominantly dependent on the combination. The results of combining ability showed that in the inheritance of plant height, genes with non-additive effects were included.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
EVALLUATION OF GERMPLASM COLLECTION OF Agrostis stolonifera L. THROUGH MULTIVARIATE ANALYSIS
Gordana ŠURLAN-MOMIROVIĆ, Zorica TOMIĆ 1, Ivana RALEVIĆ i N. RALEVIĆ
Poljoprivredni fakultet,
Univerzitet u Beogradu, Beograd-Zemun
1 Institut za istraživanja u poljoprivredi "Srbija" -
Beograd, Centar za krmno bilje, Kruševac
Thirty-five autochthonous populations of the species Agrostis stolonifera L. collected from a narrow Serbian region were analyzed using both univariate and multivariate analysis. The plants were collected from various habitats: valley meadows - 22 populations, hilly meadows - 7 populations and mountain meadows and pastures -6 populations. Fifty seeds of each population were germinated in Petri dishes in the autumn 1991 and seedlings were planted in fields. Populations of the species A. stolonifera L. exhibit three levels of polyploidness: diploid, tetraploid and hexaploid. The effect of the eleven most important quantitative characters was examined on thirty-five populations. The characters monitored were recorded during 1992 and 1993 on a single plant basis. The results of the classification obtained according to the linear discriminant functions expressed very slight differences between the real and evaluated groups. The objective of this study was to classify our collection of Agrostis stolonifera L. by means of multivariate analysis applied to a set of quantitative traits describing morpho-physiological and agronomical characteristics of the population with the practical purpose of orientating a breeding programme.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
IMPROVEMENT OF ITALIAN RYEGRASS (Lolium multiflorum Lam.) BY CHROMOSOME DUPLICATION
Zorica TOMIĆ
Institut za istraživanja u poljoprivredi "Srbija" - Beograd, Centar za krmno bilje,
Kruševac
Italian ryegrass (Lolium miultiflorum Lam.) is a major grass species known for its high productivity and fodder quality. The selection of new varieties offers favourable possibilities for its improvement. This report describes the creation of a new tetraploid variety with better quality and higher hay yield than the variety K-13. The results obtained for the isolation of homozygote tetraploid families by chromosome duplication that are constituent parts of the newly registered tetraploid variety are given. In 1980 trials were conducted by inducing tetraploids. From two hundred germinated diploids tolaked in 0,2% colchicine for two hours. The seedling was planted in a trial field. During the growing season some morphological properties were assessed and the dry matter production determined. The seeds were harvested. Plants were selected for further improvement on the basis of a cytogenetic analysis. Tetraploid plants 2n=2x=28 were used only. The next six generations of C6 families were homozygotes whereby seven, three and two families originated from varieties B-9, Jabeljska and K-13, respectively. By maternal line selection and using the polycross type of crossing a new variety was created. In 1990-1992 small plot trials were conducted in Ljubljana, Banja Luka, Novi Sad and Kruševac using the new variety and the control K-13 variety. The hay yield (15.501 kg/ha) and protein content (2.328 kg/ha) of the new tetraploid was significantly higher in comparison with the control K-13.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
THE VARIABILITY AND HEREDITY OF LEAF MORPHOLOGICAL PARAMETERS IN POPLAR CLONES, SECTION LEUCE
Z. TOMOVIĆ i S. ORLOVIĆ
I.R.C. Javno preduzeće "SRBIJAŠUME", Beograd; Naučni institut za topolarstvo, Novi Sad
Research on the variability and heredity of leaf morphological parameters in poplar section LEUCE included ten clones as follows: Populus alba, P. alba, f. boleana, P. tomentosa, P. Alba x P. grandidentala and P. tremula cv. Astria. The number and sizes of the following parameters were measured on leaf samples from a nursery experiment: leaf length along the midrib (XI), greatest width of leaf (X2), length from leaf tip to the place of greatest width (X3), length of leaf petiole (X4), number of veins (X5), angle between the lower pair of lateral veins (X6), deviation of the leaf base from the imagined flat base of the leaf (X7), the greatest depth of incision on the leaf margin (X8), and the number of incisions (X9). In addition to the above parameters, the following rations of the parameters were determined:
X2 X3 X4
X1 X1 X1
The results showed that there were statistically very significant differences between the clones (genotypes) regarding the size and number of the researched leaf parameters. In addition, very high values of heredity coefficients in the broad sense (h/bs) were obtained. The total results showed clearly that these parameters of leaf size and form can be utilized as reliable indicators in the macroscopis determination of clones both in experimental and in regular nursery production.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
THE INFLUENCE OF THE LEVEL OF HOLSTEIN FRIESIAN GENES ON MILK ABILITY AND FERTILITY OF BLACK AND WHITE COWS
G. TRIFUNOVIĆ 1. LJ. LAZAREVIĆ 1, D. LATINOVIĆ 1, P. STOJIĆ 2 i M.
KATIĆ 2
1 Poljoprivredni fakultet, Beograd-Zemun
2 Agroekonomik, Beograd
The influence of the level of Holstein Friesian genes, including the first three whole and standard lactations, on the milk production and reproductive traits was investigated. Results were obtained from a population of black and white cows which were born and raised on the farms at the Agriculture Combinate "Belgrade". An analysis was carried out of a total of 730 lactations - calvings, as follows: first lactation -309, second lactation - 236 and third lactation - 185 individuals. Three groups of cows were formed according to the level of Holstein Friesian genes (first - 0-24%, second -24-39% and third - 39-100%). Data were processed using the least squares method (Harvey, 1990). The duration of lactation was on average 324.3 days, milk yield 5932 kg (first group), 5960.9 kg (second group), and 6291.6 kg (third group). In the same order, the milk fat yield was from 220.3 kg to 232.2 kg, and 4% fat corrected milk 5677.7 kg, 5693.0 kg, and 6000.00 kg. Differences between the groups, were highly significant (P <0.01) except for the milk fat content (P >0.05). Differences between groups for reproductive traits (index of insemination, interval from calving to first insemination, interval between calvings and body weight of calves) were statistically non-significant (P >0.05).
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
SELECTION PROGRESS AND DIVERGENCE IN LOCAL SYNTHETIC POPULATIONS OF MAIZE (Zea mays L.)
B. TRIFUNOVIĆ, V. TRIFUNOVIĆ, Gordana RADOVIĆ i D. JELOVAC
Institut za kukuruz "Zemun Polje", Beograd-Zemun
The purpose of this study was to determine selection progress for yield and other agronomic traits as well as to provide divergence of maize breeding material synthesized from inbreds of a) local origin (IVu, IRu, IVuRU, MRIZP) and b) local origin x exotic germplasm (MRI/USA). The significant yield increase, as a result of the accumulation of favourable alleles, was determined in local synthetic populations and their test crosses. The incorporation of exotic germplasm significantly positively affected the level of these changes, especially for the moisture content and stability of the maize plant. The analysis of primary components (PCA) indicates that synthetics, their combinations and checks are spatially distributed into two differentiated groups. The first primary component is defined by yield and, based on that, it could be concluded that the highest heterotic effect occurs in the combination of synthetics or their combinations with Lancaster plasm (except in the case of the synthetic IVu/USA). The combination with SSS plasm results in a lower level of heterosis, except in the synthetic MRI/USA. This synthetic has good combining ability with both Lancaster and SSS plasms. The MRIZP synthetic was derived by recombination of inbreds built into the synthetics IVu and IRu, while the synthetic MRI/US was developed by recombination of inbreds from MRIZP with the inbred B37. This leads to the conclusion that recombination of the initial material results in a broader genetic base of htis synthetic than in individual synthetics IVu or IRu or their combination IVuIRu. A high combining ability in both synthesized germplasms with world-renowned testers (Lancaster and SSS) points to the fact that this breeding material has kept its divergence. The obtained results indicate that new maize germplasm recourses are convenient for the development of improved hybrid combinations by choosing an appropriate selection procedure.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
POLYPLOID COMPLEXES, DIPLOIDIZATION AND IMPROVEMENT OF TREES AND SHRUBS
A. TUCAKOVIĆ i V. ISAJEV
Šumarski fakultet, Beograd
The evolutionary potential of polyploid complexes has a significant role in the process of tree and shrub improvement. This paper deals with the range of chromosome numbers of trees and shrubs, the level of polyploidy, the distribution of polyploidy, basic number of chromosomes and the process of diploidization of tree and shrub polyploids. The significance of polyploidy in the reconstruction of woody species has been illustrated by the example of rose breeding, and the general methodical approach has been based on the following: a) a significant number of species (15.1%) of trees and shrubs are polyploids, b) individual tree species reach a high degree of polyploidy, c) polyploidy stabilizes heterozygosis and reduces the ability of transition from the potential to free variability, and d) nonuniform distribution of polyploidy depends on chromosome structure, method of reproduction, climate and other factors. The distribution of trend shrub polyploidy in different taxonomic groups is not uniform, as illustrated by the examples of ten families of trees and shrubs: Belulaceae, Budleiaceae, Caprifoliacea, Fabaceae, Hippocastanaceae, Magnoliacceae, Moraceae, Rosaceae, Tiliaceae, Agavaceae. By adopting n=6 to 9 for the most probable value of the number of chromosomes, trees and shrubs with n=10 up to n=21 belong to a group of secondary - ancient diploids. By diploidization, ancient polyploids acquire the properties of primary diploids, which make the basis for further improvement. Some polyploids in nature belong to alloploids, which enable the barriers of hybrid sterility to be surpassed, enable hybrid reproduction in pure forms, ensure the stability of highly heterozygous genotypes, as well as the properties of heterosis and physiological homeostasis in hybrid combinations.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
SEX VARIABILITY AND ITS SIGNIFICANCE IN THE IMPROVEMENT OF THE BLACK POPLAR (Populus nigra L.)
A. TUCOVIĆ, V. ISAJEV i Mirjana ŠIJAČIĆ
Šumarski fakultet, Beograd
Several types of sex variability have been observed in the black poplar, which is a dioecious species: the clone Populus nigra var. thevestina has dioecious flowers, while the trees of the black poplar in the Poibarje region exhibit monoecism and polygamy on one tree with branched basically male inflorescences. The nature of the observed extreme sex variability has ben analysed, for the monoecious tree by field experiments and by growing self-fertilized progeny, and for trees with dioecious flowers and branched polygamous inflorescences with stationary monitoring. Autofecundation and self-fertilized progeny raising has been carried out by the method of ablactation of fertile branches of the monoecious tree by means of a container with water on two-year-old generative media grown in pots. The results of the analysis of parent trees and grafts of a monoecious tree, prove that the analysed abnormalities in the structure of black poplar reproductive organs are genetically controlled. Autofecundation and the progeny raised supplement the existing methods of black poplar reproduction, in addition to the exclusive xenogamy and frequent autovegetalive reproduction, which enrich the ontogenetic and phylogenetic adaptation of the species, as well as its further improvement.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
MASS AND INDIVIDUAL SELECTION OF THE WHITE BARK PINE (Pinus heldreichii Chrisst.) IN SERBIA
A. TUCOVIĆ, V. ISAJEV i Mirjana ŠIJAČIĆ
Šumarski fakultet, Beograd
Whitebark pine is a tertiary relic and an endemic species characterized by a great genetic potential. The improvement of this species in Serbia started by mass and individual selection. The objects of this research are large and small populations within the range, and several plantations. The analysis of group and individual phenotype variability has been carried out by comparative morphological -physiological investigations, stationary phenological and other monitoring, by free and assortment pollinations, absence of pollination, self-pollination and inter-species hybridization of experimental Austrian pines. The above investigations included: 1. A study of the nature of phenotype variability of large and small populations, 2. The effect of the pollination type on the internal seed characteristics, 3. A quantification of the possibility of Austrian pine and white bark pine hybridization, and 4. The development of methods of mass and individual selection. The results indicate great individual and group variability of the analyzed properties, as well as incompatibility in interspecies hybridization of white bark pine and Austrian pine. The occurrence of viviparity directs the future supplementary cytological, histological and embryological research. As white bark pine is a tree species with modest requirements regarding the site, the results confirm that whitebark pine is a species suitable for the afforestation of very poor sites. Further investigations should be directed mainly to the utilization of whitebark pine seed stands in the belt between 1,400 and 1,800 m asl., smaller groups of 600 to 1,000 m asl., and the establishment whitebark plantations outside its natural range.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
RFLP AT THE Glu-1 LOCI AND THE BREAD-MAKING QUALITY OF WHEAT CULTIVARS
Ljiljana VAPA, S. DENČIĆ 1, Erika RAKK-ŠOLTES 2 i S. KEVREŠAN
Prirodnomatematički fakultet, Novi Sad
1 Poljoprivredni fakullet, Novi Sad
2 Department of Botany, University of Toronto,Canada
It is now well recognized that the HMW glutenin subunits, coded by genes at the Glu-1 loci, are associated with significant differences in bread-making quality. The aim of this paper was to relate the RFLP pattern at the Glu-1 loci to the bread-making quality of different wheat cultivars. Genomic DNAs were isolated, digested with BamHI, Southern transferred, labelled and probed with an insert pTag1290, encoding a HMW glutenin polypeptide. Bread-making quality was determined by standard methods. The 10 kb fragment was derived from the Glu-Al-1 locus, 3 kb from Glu-Bl-1; 2.7 kb, 2.8 kb and 2.9 kb from Glu-Bl-2; 11.5 kb rom Glu-D-1; while the 2.5 kb and 2.5 kb fragments arose from Glu-D-1-2. The origin of the 2.3 kb fragment remained unknown. Significant differences in sedimentation value, water absorption, flour yield, farinological number, loaf volume and loaf quality were found between cultivars possessing the 2.3 kb fragment compared with those lacking this fragment.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
GENETIC ANALYSIS OF THE NUMBER OF SEEDS PER PLANT IN WHITE BEAN CROSSES
MirjanaVASIĆ
Poljoprivredni fakultet, Institut za ratarstvo i povrtarstvo, Novi Sad
The number of seeds per plants one of the traits used for bean plant description. This characteristic is a direct product of the number of pods per plant and the number of seeds per pod. Most scientists use these three traits as criteria in plant selection. All three traits were studied in crosses of lines of the populations Gradištanac and Tetovac with the varieties Medijana, Biser and Oplenac. The lines from these populations have indeterminate while the varieties have determinate stems and both have white seeds. The five parent populations, six F1 populations and six F2 populations were analysed. Regarding the parents, the highest number of seeds and pods per plant was found in Tetovac, followed by Gradištanac while Oplenac had the lowest. The studied varieties had a higher number of seeds per pod than the lines from the populations. The variability of the number of seeds and the number of pods per plant ranged from medium to high both in parents and hybrids. Low variability was found for the number of seeds per pod. The heterotic effect or the dominance of parents with a higher mean value occurred as the mode of inheritance in the F1 generation. The intermediary mode of inheritance occurred for the number of seeds per pod. Heterosis was highest with respect to the number of seeds per plant. In the F2 generation mean values of populations decreased. The mode of inheritance of the number of seeds and pods per plant was intermediary or showed dominance of the parent with the higher mean value. The number of seeds per pod was inherited in the F2 dominance of the parent with the lower mean value. One negative heterosis occurred. Heritability of the number of the number of seeds and pods per plant and the number of seeds per pod was high in most of the combinations. Plants with transgressive characteristics occurred in the crosses with Gradištanac. In crosses with Tetovac, transgression occurred only for the number of seeds per pod.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
"IN VITRO" SELECTION OF SUNFLOWER (Helianthus annuus L.) PLANTLETS FOR RESISTANCE TO Diaporthe (Phomopsis) helianthi Munt.-Cvet. et al.
Dragana VASIĆ, Ana MARJANOVIĆ i B. DOZET
Poljoprivredni fakultet, Institut za ratarstvo i povrtarstvo, Zavod za uljne kulture, Novi Sad
Seeds of the sunflower inbreds CMS-V-8931-3-4 and Ha-74 were sterilized and placed on B5 medium. Plantlets with well developed cotyledons were transferred on to B5 medium supplemented with different concentrations of Phomopsis culture filtrate (0%, 25%, 50% and 75%). After seven days, nine characteristic of the plantlets were determined: height, growth, hypocotyl colour, number of leaves formed, root development, fresh weight, dry weight, proportion of dry and fresh weight and stem anatomic structure. Statistic analysis showed that the growth and number of leaves formed can be used as indicators of resistance to Phomopsis because there were significant differences between the two tested genotypes for these characteristics. The more resistant genotype, Ha-74, had better growth and a bigger number of formed leaves. The culture filtrate concentration of 50% was optimal for determination of resistance.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
THE VARIABILITY OF MACROSCOPIC AND MICROSCOPIC CHARACTERISTICS OF TWO-YEAR-OLD SEEDLINGS OF HALF-SIB FAMILIES OF THE BLAKAN MAPLE (Acer heldreichii Orph.)
Dragica VILOTIĆ, Mirjana ŠIJAČIĆ i V. ISAJEV
Šumarski fakultet, Beograd
The Balkan maple, as most endemic relic species, is distinguished by a high genetic potential, thanks to which it is significant m the establishment of cultural populations in high mountain sites. The seeds from 26 test trees from natural populations of Golija were used and in the Ivanjica Nursery, using standard methods, half sib families were raised by a block system. Several macroscopic characteristics were measured on two-year-old seedlings: the height and diameter at the root collar and microscopic characteristics: width of vessels, lignum ray height and width, number of vessels and lignum rays per unit area. The above characters were chosen as they are considered very significant for plant growth dynamics in the juvenile stage. The results of morphometric analyses on the sample of 15 seedlings per family showed a significant interfamiliar variability of mean values and other statistical parameters of all the analyzed properties: the height 37,9 to 97,7 cm, diameter at the root collar 0,73 - 1,01 cm, vessel diameter 18,6 - 47,7 micrometers, lignum ray height to 32 cells, lignum ray width 1-4 cells. The results of linear correlations showed great degrees of dependence in most characteristics. The growth dynamics of one-year-old and two-year-old seedlings, as well as their resistance to transplantation stress largely result from the character of the analyzed properties. For this reason the degree of inheritance of the desired macro- and microscopic properties of seed from trees belonging to extreme families should be determined in subsequent years, after which they should be used to mass produce saplings with the desired characteristics.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
INHERITANCE OF STOUTNESS OF THE PERICARP IN TOMATO FRUITS (Lycopersicon escukntum Mill.)
Jasmina ZDRAVKOVIĆ, Z. MARKOVIĆ, M. DAMJANOVIĆ i M. ZDRAVKOVIĆ
In diallel analysis 6 parent genotypes of tomato, significantly different for stoutness of the pericarp, were examined for the inheritance of this characteristic in 15 hybrids of F1 and F2 generations. In the F1 generation, stoutness of the pericarp was inherited dominantly (with the phenomenon of superdominance). In the F1 generation heterosis, occurred in five hybrids, in two hybrids domination of parents with the stouter pericarp and in two combinations intermediary inheritance occurred. In the F2 generation in two hybrids heterosis was found, in three hybrids domination of parents with the stouter pericarp and in four combinations intermediary inheritance occurred. The results for combining ability in the F1 and F2 generations showed that genes with nonadditive and additive effects take part in the inheritance of this characteristic. In the F1 generation nonadditive genes (SCA >GCA) predominate and in the F2 generation additive genes (GCA >SCA) predominate.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
GENETIC ANALYSES OF PRODUCTIVE TILLERING IN WHEAT
Veselinka ZEČEVIĆ, M. PAVLOVIĆ, D. KNEŽEVIĆ i B. VULIĆ
Institut za istraživanja u poljoprivredi "Srbija", Centar za strna žita "Kragujevac", Kragujevac
The inheritance, gene effect and combining ability for productive tillering in 4 divergent cultivars (Srbijanka, Partizanka, KG-56 and PKB-111) in diallel crosses (without reciprocal) were studied. Plants at the F 2 generation were analyzed. Analysis of genetic components of variance was done according to the methods used by Hayman (1954) and Jinks (1954), and regression analyses by the Mather and Jinks (1971) method. The combining ability analysis was made following method 2, model I by Griffing (1956). The results obtained showed that inheritance of productive tillering was different (partial dominance, dominance and over-dominance). Analysis of genetic components of variance showed that dominance played a more important role in the inheritance of productive tillering than additive components. The frequency of dominant alleles was higher than recessive. The degree of dominance was higher than unity which indicated over-dominance for all crossing combinations. Regression analysis showed a dominant mode of inheritance. Parent cultivars showed the presence of genetic diversity in the arrangement of dominant and recessive genes for productive tillering. Analysis of variance for combining ability showed that non additive gene effects had a higher impact on the inheritance of productive tillering. Also the GCA/SCA ratio was lower than unity indicating the preponderance of non-additive gene action. The best general combiner was the Partizanka cultivar, but the Srbijanka xPKB-111 combination had the highest value of specific combining ability.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
ISOZYME VARIATION AMONG MAIZE COLLECTIONS FROM YUGOSLAVIA
Marija ZLOKOLICA i I. GERIĆ
Institut za ratarstvo i povrtarstvo, Novi Sad
Isozymic variability of enzymic systems has been analyzed in populations from the Yugoslav maize collection. Isozymes are used as molecular markers for studying variability between populations. The isozymic variability was analyzed for 12 enzymic systems controlled by 21 genetic loci. The analyzed populations differed both within an among the classification groups. The genetical distance between analyzed populations was different. The relationships between variability and the genetical distance were determined: most populations with high intrapopulational variability were, genetically distant, but populations with a low intrapopulational variability were genetically close. These investigations of maize collections are important for breeding.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
NUMERICAL TAXONOMY OF ZPSIN POPULATIONS OF MAIZE BASED ON QUANTITATIVE TRAITS
T. ŽIVANOVIĆ, Gordana ŠURLAN-MOMIROVIĆ, Ivana RALEVIĆ i N. RALEVIĆ
Poljoprivredni fakultet, Beograd-Zemun
A classification of 28 maize populations taken from the Zemun Polje germplasm collection, according to 16 morphological criteria and three environments, is reported. The populations were created by recurrent selection. Dimensional traits of the ear, morphological-vegetative of the plant and physiological-adaptive characteristics were considered. Data of individual plants were analyzed through multivariate statistical methods (Canonical Analysis). Similar populations were clustered in four groups according to the results of Euclidean distance analysis. A good representation of the variability and a synthetic description of the main quantitative characteristics were obtained. The results are considered according to the accuracy of the clusters obtained through numerical methods and the importance of the evaluation of germplasm collections. The use of numerous quantitative traits is of great importance in the description of the germplasm source, because it makes it possible to obtain a summary of the most relevant characters, to assess the relative contribution of different characters to the total divergence and to group together similar populations on the basis of information that can be directly used in maize breeding program.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
POPULATION GENETICS AND TWO GREAT SYNTHESES OF MODERN BIOLOGY
N. TUCIĆ
Biološki fakultet i Laboratorija za evolucionu biologiju, Institut za biološka istraživanja "Siniša Stanković", Beograd
The main task of contemporary population genetics is the description and prediction of changes is the genetic and phenotypic structure of populations responding to different evolutionary mechanisms such as mating system, selection, genetic drift, mutation, gene flow and recombination. The modern version of Darwin's evolutionary theory, best known as "the synthetic" theory of evolution, has population genetics at its core. Certain elements of modern evolutionary synthesis have recently been sharply challenged by palaeontologists and molecular biologists. In this plenary address I shall discuss contemporary topics of the evolutionary theory such as mechanisms of speciation, transposable elements and chromosome rearrangements and evolution, regulatory genes and evolutionary novelties from the perspective of population genetics and provide evidence to refute claims that "the synthetic theory" is no longer valid. Another great synthesis in the biology of this century is sociobiology. Again, population genetics is an important constituent of this new synthesis. Starting with Wilson, modern sociobiologists offer a genetical explanation of such human cultural manifestations as ethics, religion, tribalism, patriotism, warfare, genocide, conformity, indoctrinability etc. Although little of what sociobiology offers as an "explanation" of "human nature" is new and different from classical biological determinism, it seems appropriate at this time to analyze carefully the ideas that are being presented in sociobiology, particularly as those ideas have recently received widespread and uncritical attention in our society.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
GENETIC COMPONENTS OF VARIATION IN SIZE AND SHAPE DURING ONTOGENY IN THE LIZARD Lacerta oxycephala
I. ALEKSIĆ
Laboratorija za evolucionu biologiju, Institut za biološka istraživanja "Siniša Stanković", Beograd
Lizards have been employed very often in tests of various hypotheses concerning the mechanisms of adaptation and speciation at the morphometric level. However, despite the fact that knowledge of the genetic variation of morphometric size and shape are essential for complete evolutionary analyses, information on the extent of quantitative genetic variation of these traits is almost completely absent for lizard populations. In this study we provide estimates of the components 01 phenotypic variance and covariance among seven metric traits using full-sib analyses of newborn lizards of the species Lacerta oxycepahla. In addition, we have also attempted to detect changes of these components over the first 90 days of growth under laboratory conditions.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
QUANTITATIVE GENETICS OF THE JUVENILE TRAITS IN Iris Pumila: THE STRUCTURE OF PHENOTYPIC VARIATION
S. AVRAMOV i Branka TUCIĆ
Institut za biološka istraživanja "Siniša Stanković", Beograd
Due to considerable mortality occurring during germination and seedling establishment, these periods of juvenile growth are thought to be the most critical phases in the life cycle of many plant species. It is also frequently mentioned that strong phenotypic selection might operate during the seedling stage of the plant life cycle. If natural selection of juvenile plants is indeed a strong evolutionary force, one would expect to find relatively low levels of additive genetic variance of traits that are strongly correlated with fitness and are undergoing directional selection. In order to test this hypothesis we assessed the structure of phenotypic variation in seed size, life history and several fitness components in a population of Iris pumila to determine the causes of differential juvenile performance. A paternal half-sib crossing design allowed us to partition the phenotypic variance in 16 quantitative seedling traits into genetic and environmental effects. We found no evidence of additive genetic variance of any of the examined traits. The non-additive and maternal component of variance, however, was significant for most traits, particularly those expressed during the first 10 days of the I. pumila life cycle. These results support theoretical predictions of reduced additive genetic variance in traits associated with fitness and suggest little or no progress for the selection of these early juvenile traits even if differential fitness is observed.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
PRESENCE OF FOSSA MENTALIS AND DIMPLES IN SAMPLES, FROM THE AREA SURROUNDING SUBOTICA
C. CEKUŠ
F. Kluza 23, Subotica
As part of an anthropological and genetical observation of schoolchildren from the area surrounding Subotica, an anthroposcopical research of fossa mentalis and dimples was done. Fossa mentalis is present cither as central of longitudinal, while a dimple (which appears when smiling) can be one-sided or bilateral, present either like a small hollow or in the shape of a line. Our aim was to establish the frequency of the presence of both fossa mentalis and dimples in one person, as well as the mutual combination of the observed small hollows. Out of the number of 1266 examined pupils - 653 boys and 613 girls - 342 (27,01 per cent) had cither fossa mentalis or a dimple. From these 342 cases only 27 (7.89 per cent), and from the whole sample 2.13 per cent, had both small hollows: 11 boys and 16 girls. The most frequent combination was a line-shape one-sided dimple and a longitudinal fossa mentalis. This was noticed in 7 boys (25.93 per cent) and 5 girls (18.52 per cent). A bilateral dimple and a vertical fossa mentalis also appeared quite often, in 2 cases for each sex. The combinations of a bilateral hollow dimple and a central fossa mentalis, a bilateral line-shaped dimple and a central fossa mentalis as well as a one-sided line-shaped dimple and a central fossa mentalis were only present in girls. In conclusion, we can say that both fossa mentalis and dimples seldom appear simultaneously, although these features are dominant. There is no significant difference between the sexes (χ2 =0.92). The most frequent combination is a one-sided line-shaped dimple and a longitudinal fossa mentalis.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
VARIATIONS OF HAIR LIMITS ON THE FOREHEAD IN SAMPLES FROM NORTHERN SERBIA
G. CEKUŠ
R. Kluza, Subotica
This study is a result of anthroposcopical observations of schoolchildren in Northern Serbia. The main aim of this research was to determine the variations of hair limits on the forehead in four samples from the area surrounding Subotica (Bački Vinogradi, Hajdukovo, Horgoš and Male Pijace). This fracture is important for anthropogenetics. During the research all pupils from all settlements were examined, a total number of 1266 (652 boys and 614 girls). A modified somatoscopical method according to Lorencova was used. In accordance with this method, there are four types of hair limits on the forehead: horizontal, convex, concave and heart-shaped. The heart-shaped type is the dominant type. The convex hair limit is most frequently noticed, which relates to boys (33.55 per cent) as well as girls (36.16 per cent). The heart-shaped type seldom appears, in 25.90 per cent of the girls and m a little less, namely 24.08 per cent, of the boys. The convex shape is also most frequently noticed in the settlements, from 31.97 per cent (in Hajdukovo) to 38.98 per cent (in B. Vinogradi). The frequency of this shape in age groups varies, from 21.55 per cent (14-year-olds) to 45.36 per cent (7-year-olds). There was an appreciable dissimilarity (χ2 = 131.500) between the individual types. There is no significant sexual difference χ2 = 2.700. In the boys the frequency of some types are significantly different, χ2 = 62.453 but that is not the case in the girls, χ2 = 33.930. In conclusion, we can say that htc most represented type in this sample is the convex type of hair limit on the forehead, although the frequency of this shape varies between settlements as well as between age groups. The heard-shaped type is more frequent in Hajdukovo (27.50 per cent) in comparison to the other settlements.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
POPULATION GENETIC STRUCTURING IN THREE LACERTID LIZARD SPECIES (Sauria: Lacertidae) INHABITING THE LAKE SKADAR REGION
Jelka CRNOBRNJA-ISAILOVIĆ i I. ALEKSIĆ
Laboratorija za evolucionu biologiju, Institut za biološka istraživanja "Siniša Stanković", Beograd
Among six members of the family Lacertidae whose species-area includes the territory of Lake Skadar, Podarcis nmralis, Lacerta oxycephala and Podards melisellensis appeared to be the most abundant. Besides the coastal area, they also inhabit a number of small karstic islands (more than 27) known as "the south-western Lake Skadar archipelago". As part of complex evolutionary biological and biogeographical investigations, we performed a starch-gel electrophoretic study on island and mainland population samples of all three species. The main goal of this study was to estimate and then explain the degrees of genetic differentiating among populations within each species, taking into consideration the possible influence of isolation effects. The results showed that the species differ in the extent of genetic structuring of their populations, reflecting known facts about their microtaxonomy and biogeographical impacts. In this particular case, the alloxymic data failed to explain precise colonization routes of the islands by the analyzed species or apparent phenotypic variability noticed in the analyzed populations. However, by using already known parameters (average heterozygosity per locus, degree of polymorphic loci, gene flow rate, and distribution of rare and unique alleles in populations) we tried to recognize the processes which would have a predominant influence on the distribution patterns of allelic frequencies obtained.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
THE QUANTITATIVE GENETIC BASIS OF INCREASED LONGEVITY IN THE BEAN WEEVIL (Acenlhoscelides obtectus)
Ivana GLIKSMAN
Laboratorija za evolucionu biologiju, Instituta za bioloska istraživanja "Siniša
Stanković, Beograd
In the present study quantitative genetic transmission patterns of long- and short- lived lines obtained by selection for early and late reproduction in the bean weevil have been analyzed. This study used four lines with postponed ageing ("old" lines), two "control" lines and two "young" lines, all created from the same founding base population. In a series of diallelic analyses all possible crosses were performed to test for heterogeneity among the lines of a given treatment. A series of crosses between treatment lines (i.e. control x young: control x old and young x old) was also performed to test for patterns of dominance and maternal effects. The following traits were studied: early fecundity, first and last day off egg laying, late fecundity, total fecundity and female and male longevities. There was little evidence for maternal effects in the inheritance of the studied traits in the "control x young" and control x old" crosses. In the "young x old" cross maternal effects were present for the last day of egg lying and female and male longevities. Dominance effects, however, were more pronounced in the “control x young" cross (for the first and last day of egg laying, total fecundity and female and male longevities) than in the other two types of crosses.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
SEXUAL SELECTION AND BODY SIZE IN Drosophila melanogaster
V. KEKIĆ, Sofija PAVKOVIĆ-LUČIĆ, Aleksandra ČVORO i N. MILOŠEVIĆ
Biološki fakultet PMF-a i Inslitut za biološka istraživanja "Siniša Stanković", Beograd
In most animal species the act of copulation is preceded with a series of behavioural acts, probably the most complex in the species' repertoire. It is the courtship phenomenon. Its biological meaning is complex, and the basic one is to enable recognition between specimens of the same species, and in some animals it synchronizes different cycles that lead the specimen of the opposite sex to a proper physiological state necessary for successful copulation. During this process, another extremely important phenomenon occurs, noticed by Darwin (1859, 1871), and theoretically discussed by fisher (1930, 1958). This is the phenomenon of sexual selection. Darwin and fisher like most contemporary theoreticians, recognized sexual and natural selection. The first one is present when there is a variance in copulation success, and the second one when there is a variance in other fitness components (like in viability or fertility in individuals that copulate). Several possible ways in promoting sexual selection through succeeding generations are suggested by theoretical analyses of the genetic basis of these mechanisms. Usually, differences are made between processes based on competition between males and female choice. In practice, in experiments investigating mechanisms of sexual selection, the first step is to detect characters correlated with the reproductive success of each sex. This character would make one male more successful then the other one, either in competition for a female or/and as a result of a females choice. In the present experiment we concentrated on the body size in both sexes. The aim of this paper was to determine: 1) If there is non-random mating in Drosophila melanogaster, i.e. is the mating success a size-dependent character, 2) If this phenomenon is frequency-dependent, i.e. does the effect of body size change as a function of the number and proportion of males and females, and 3) If there si size-dependent assortative mating, i.e. is there a correlation between body sizes of males and females in copulation.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
A POPULATION GENETIC STUDY OF LEFT-HANDEDNESS IN CITIZENS OF PROKUPLJE
D. KNEŽEVIĆ, D. MARINKOVIĆ 1, LJ. AGRAMOVIĆ 2
Institut za istraživanja
u poljoprivredi "Srbija", Centar za strna žita "Kragujevac",
Kragujevac
1 Prirodno-matematički fakultet, Univerzitet u Beogradu, Beograd;
2 Prirodno-matematički fakultet, Univerzitet u Podgorici, Podgorica
A population study of handedness has shown variability in two common types of this trait: left-handedness and right handedness. The frequency of left-handedness as a rare phenotype in the observed sample (810 individuals) was 13.8%, q = 0.37. A total of 180 families (360 parents and 324 children) and 810 pupils were observed. The total number of examined persons was 1494. An inheritance study of left-handedness in 180 families showed differences in the percentage of the recessive phenotype between parents and offspring as well as between males and females within the whole sample but they were not significant.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
QUANTITATIVE GENETIC ANALYSIS OF FITNESS COMPONENTS IN TWO LABORATORY POPULATIONS OF BEAN WEEVILS (Acanthoscelides obtectus)
Stanislava MIKULJANAC i O. STOJKOVIĆ
Laboratorija za evolucionu biologiju, Institut za biološka istraživanja "Siniša Stanković", Beograd
This study was undertaken to determine the pattern of genetic variation and co-variation among fitness components in two populations of bean weevil (Acanthoscelides obtectus) cultured in the laboratory for 60 generations on bean and chickpea seeds. In order to determine the extent of genotype-by-environment interaction within each population a split-family, two environments (bean vs. chickpea seeds) experiment was used. By assessing the environment-depending expression of genetic variation in different fitness components (preadult viability, duration of preadult development, female fecundity and longevity) it is possible to estimate the extent of population genetic trade -offs among fitness components. By using half-sib analyses the genetic variance in female oviposition preference (which is defined here as % oviposition on chickpea = (No of eggs of chickpea)/(total No of eggs) x 100) was also estimated, and then it was examined whether this variation was genetically correlated to some the fitness components.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
SUBSTRATE-RELATED VARIABILITY OF SOME FITNESS COMPONENTS IN DIFFERENT GENOTYPES OF THE Amy LOCUS IN Drosophila subobscura
Mirjana MILANOVIĆ i M. ANĐELKOVIĆ
Institut za biološka istraživanja "Siniša Stanković", Odeljenje za genetiku, Beograd
Alpha-amylase was found to be a polymorphic enzyme in D. subobscura individuals. Variability of some fitness components under specific environmental conditions was studied in the lines homozygous for "slow" and "fast" amylase alleles, which were obtained by selection. The results obtained throughout these studies revealed amylase allele-related differences between the selected lines in the rate of preadult development, survival rate, longevity of the adults, as well as in amylase activity, no matter which substrate (standard, starch or maltose) were applied. Individuals of the SS genotype were characterized by faster preadult development, better viability and shorter longevity comparing to individuals of the FF genotype almost on all three substrate types. Amylase activity was about the same in individuals kept on starch and standard substrates, while it was significantly decreased in both selected lines when the maltose substrate was used. Limiting feeding conditions when starch or maltose were the only carbohydrate sources probably led to physiological stress which influenced some of the fitness components.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
MECHANISMS OF MAINTENANCE OF GENETIC VARIATION FOR HOST CHOICE IN BEAN WEEVILS (Acanthoscelides obteclus)
Dragana MILANOVIĆ i Sofija KARAULIĆ
Laboratorija za evolucionu biologiju, Institut za biološka istraživanja "Siniša Stanković", Beograd
There are two explanations how genetic variation for host choice is maintained within phytophagous insect populations. First, the genetic variation for host choice could be maintained because of a genetic correlation between preference and performance. A second major explanation rests on the assumption that when survivorship is density-dependent, genetic variability of host choice will be maintained due to natural selection favouring genotypes which ensure an equal viability of offspring on different hosts. Our experiments with Acanthoscelides obteclus suggest that long-term rearing of this weevil species on two hosts (Cicer arietinum and Phaseolus vulgaris) could result in a different sensitivity of host choice to adult density. In the Cicer population we have not detected density-dependent effects on host choice, while in the Phaseolus population these effects have been observed. These results suggests that on the primary host (bean seeds) density-dependent selection could maintain genetic variation for host choice, whereas on the new host (chickpea seeds) it could be genetic correlation between (maternal) host choice and some of the offspring fitness components.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
LEARNING IN Drosophila melanogaster IMPLICATIONS ON THE GENETIC STRUCTURE
N. MILOŠEVIĆ, V. KEKIĆ, Sofija PAVKOVIĆ-LUČIĆ i Aleksandra ČVORO
Institut za biološka istraživanja "Siniša Stanković" i Biološki fakultet MPF-a, Beograd
Behavioural aspects were not present in population genetics theory considerations, until recently, and they were then the assumption that all individuals have uniform behaviour (e.g. they mate randomly, they migrate following the same principal, they are dispersed uniformly, etc.) was followed. Behaviour, as well as behavioural characteristics, is a fitness character par excellence, for an individual's entire life presents a continuity of various behavioural forms. The role of behaviour in evolutionary processes is clearly obvious if it is genetically correlated with some of the standard fitness components (Variability, fertility, etc.). Regarding new theoretical models on the individual's choice of "micro" habitat (which presents a behavioural act) in ecological heterogeneous and variable habitats resulting in an increase of its fitness, together with already known mechanisms (and some recent ones, like frequency-dependent and density-dependent), a more successful explanation of an "old" theoretical problem, high genetic polymorphism in the natural population, was possible. On the other hand, there is minimal knowledge of the genetic basis of habitat preference and its genetic correlation to other fitness components. Even less is known about the role of learning, and of behavioural activities changed by experience which are of importance in viability, reproduction, and in habitat choice. The aim of this work was to determine whether fruit flies in laboratory conditions and in a complexly designed experiment, can use previous experience positive or negative), memorize it and react adequately in the repeated situation. Fruit flies were conditioned with various visual, olfactory and gustative stimuli for choosing a specific space. For example, are they going to prefer a yellow coloured surface in the test procedure, if they were fed on a yellow substrate during the training procedure? The purpose at the next series of experiments was to determine if development on a certain substrate, or residing of an adult in the first hours after eclosion, has an effect on the later choice of substrate (for feeding, egg laying, etc.). Also, we tried to establish if the choice of individual has an effect on their fitness, as well as on their progeny.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
THE EFFECT OF TRAUMA ON CHANGES OF CONCENTRATIONS OF HAPTOGLOBIN AND a2-MACROGLOBULIN IN AO AND DA INBRED RATS
Milica MILOŠEVIĆ 1, Z. MAGIĆ 1, Č. RADOJIČIĆ 1, i D. MARINKOVIĆ 2
1 Institut za medicinska istraživanja VMA, Beograd;
2 Biološki fakultet PMF, Beograd
The response of an organism to trauma is polygenic and probably some genes, or a group of genes, are more responsible than others for increased resistance of an organism to trauma. The most prominent event during the metabolic reaction of an organism to trauma is an increased synthesis of acute-phase proteins (APP). This is a heterogeneous group of plasma proteins which helps an injured organism to restore the homeostatic balance disturbed by traumatic agents. Haptoglobin (Hp) and especially a2-macroglobulin (a2-MG) are among the most important acute-phase proteins rats. It was shown that rats of the AO (Albiono Oxford) and DA (Dark Augustin) strain have different resistance to trauma and we supposed that these two strains might have different scrum concentrations of Hp and a2-MG. The aim of this study was to determine scrum concentrations of Ph and a2-MG (by rocket immunoelekctrophoresis) before and after trauma (24 hours after tourniquet trauma) in a parental generation and their hybrid progeny. The results obtained showed that basal values of Hp and a2-MG were different in AO and DA rats. Higher basal concentrations of both proteins were found in the AO rats which are more resistant to trauma. These results suggested a positive role of these proteins in the resistance of an organism to trauma. After the infliction of trauma, concentrations of Hp and a2-MG were significantly higher in parental and all hybrid (F1, F2, backcross) generations. These values were similar for both strains meaning that regulatory mechanisms of DA rats overwhelmed differences which existed at the basal level. Individual variability which was present in both strains was also lower after the infliction of trauma. This decrease of individual variability and the fact that mean values of Hp and a2-MG after trauma were similar, draw us to the conclusion that there are optimal concentrations of these two proteins which organisms try to achieve.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
POPULATION-GENETIC INVESTIGATIONS OF RECESSIVE PROPERTIES IN ISOLATED HUMAN POPULATIONS IN MONTENEGRO
V. NOVOSEL
Medicinski institut, Univerzitet Crne Gore, Podgorica
The objective of this paper was to determine the genetic burden of some human populations - isolated in small and limited living areas. The need for these investigations originated from the frequency of the occurrence of psychopathic diseases in a number of families. These examinations were performed on 154 persons of various ages. With the objective of comparing the data, a sample comprising 100 people from Podgorica, was also examined as a control group. Twenty typical phonotype properties were examined for recessive inheritance. Since these are naturally isolated human populations, objective conditions existed for the occurrence of "genetic drift" which resulted in changes of the genetic structure of the examined populations. On the basis of the application of adequate statistical methods some significant differences have been recorded between the studied and control group, concerning the frequency of homozygote recessive inheritance of properties whose values ranged from p = 0.05 to p = 0.001.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
CALCULATING THE RISK FACTOR FOR TRANSFUSION-ASSOCIATED GRAFT-VERSUS-HOST DISEASE
D. PAUNOVIĆ, R. SIMONOVIĆ, I. STOLIĆ i M. DOKIĆ
Zavod za transfuziju krvi Srbije, Beograd
Considering all cases of transfusion - associated graft-versus-host disease (TA-GVHD) described until now it seems that donor homozygosity for an HLA haplotype, for which the recipient is haploidentical could be a particular risk. Because of the high mortality associated with this disease, irradiation of all units of blood for immunocompromised patients was recommended. In this work we have shown that, using some mathematical formulas derived from the frequency of some haplotypes in the population it was possible to estimate the probability for developing TA-GVHD. Our results implied that the potential risk is much higher for first-degree relatives than for random donors, and it is in correlation with the frequency of the particular hyplotype.
RELATIVE RISK
.
|
srodstvo |
roditelji deca |
baba, deda ujaci...
|
braća sestre |
prvi rođaci |
drugi rođaci |
nesrodni |
|
haplotip IILA
|
X 10-9 |
X 10-9 |
X 10-9 |
X 10-9 |
X 10-9 |
X 10-9 |
|
A2B5
|
4,68 (7,09)
|
2,67 (4,04) |
2,51 (3,80) |
1,66 (2,51)
|
0,91 (1,38) |
0,66 (1) |
|
A2K15
|
0,09 (52,10)
|
0,05 (26,52)
|
0,049 (26,26) |
0,026 (13,68)
|
0,008 (4,21)
|
0,0019 (1)
|
Relative risk to unrelated donors in parenthesis
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
THE POTENTIAL NUMBER OF CELLS AND SYSTEM SIZE OF INDIVIDUALS AND POPULATIONS
B.P. PAVLOVIĆ
Veterinarski fakultet, Beograd
The cell and the individual are basic biotic systems. An integrated set of biotic functions occur in them. A potential number of these systems are determined by the biotic characteristics of the species. Two species characteristics, the individual size (as the final number of cell division generations in it, k) and the reproductive potential, have been analysed. Cell division, in almost all species, produces two cells, and the cell number of the individual (L*) is a function of cell division generation (i, i = 0 do k): Li = 21. To relate cell and individual reproduction, let one individual produce two individuals after k-generations of synchronized cell divisions (at the end of its life). An individual generation internal (j = 0, 1, 2, . . .) includes k + 1 cell generations (i = 0, 1, 2,. . ., k). A population cell number (Ljj) is obtained from the relation Ljj=Nj2J. The number of single-cell individual generations (j.u) is related to the number of multi-cell individual generations (jv), and with the final individual size (kv), by the equation: ju=jv(kv+I)+i. The higher k is, the wider the oscillations of Lji are, abut there is a slower increase of Nj in the population. Some aspects of these intrinsic features of biotic systems have been considered in connection with the domination of haploid or diploid states, with cell transfers to the next generation, with the number of biotic systems achieved, and with their size or duration. The maximal size of the biotic space is determined by an integer sum of the systems (cell-division, individual-reproduction), while mutations and (re)combinations of genetic information take place with in this space.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
DISEQUILIBRIUM PATTERN ANALYSIS BETWEEN A AND B LOCI OF THE HLA SYSTEM IN SERBIA
R. SIMONOVIĆ, D. PAUNOVIĆ, I. STOLIĆ i V.D. MILETIĆ
Zavod za transfuziju krvi Srbije, Beograd
This work is part of a larger study on genetic variability of some blood markers in our population. The linkage disequilibrium values (D) for HLA-A and HLA-B locus haplotypes in a sample of 1329 unrelated individuals involved in paternity cases were analysed. Among 48 significant D values, the four haplotypes A1BS, (0.781), A1B37 (0.819), Awl9B70 (0.938) and Aw33B14 (0.819) expressed the highest positive D values. An application of disequilibrium pattern analysis (DPA) for the populaiton of Serbia identified three haplotypes from the entire set of 33 graphs of 12 HLA-A and 21 HLA-B allelic combinations: A1B8, A3B7 and Aw33B14. The strongest pattern indicating selection was the combination of the B8 allele with the A locus alleles.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
THE MITE PROCTOLAELAPS REGALIS AS A POSSIBLE VECTOR FOR HORIZONTAL TRANSFER OF THE P ELEMENT BETWEEN DROSOPHILA SPECIES
M. STAMENKOVIĆ-RADAK, J.B. CLARK i M. KID WELL
Department of Ecology and Evolutionary Biology, University of Arizona,
Tuscon, USA i Odeljenje za genetiku, Institut za bioloska istraživanja "Siniša
Stanković", Univerzitet u Beogradu, Beograd
The mite Proctolaelaps regalis has been recently identified as a possible vector in horizontal (mating independent) transfer of DNA sequences between Drosophila species (Houck ct al., 1991). Presently, four separate combinations of mixed Drosophila species cultures were set up in order to determine whether transfer of P elements from one species (P) to another (M) can be mediated by Proctolaelaps regalis. Samples of M species flies were taken from mixtures after several generations to determine the possible presence of the P element in the genome by a gonadal sterility assay and the polymcrase chain reaction (PCR). Mites from the mixtures were also checked for the presence of the P element. Coexistence of two Drosophila species with the mite Proctolaelaps regalis in these laboratory conditions could serve as a suitable model-system for the study and detection of lateral gene transfer. The differences between the species involved in these experiments make such an event rare, but possible. The feeding behaviour, as well as life history characteristics of Proctolaelaps regalis seem to provide conditions similar to those present in the method of microinjection of Drosophila embryos used in P element transformation studies. The data related to the pattern and nature of the acquisition of P element DNA by mites contributes to understanding this phenomenon which could be of considerable evolutionary significance.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
SELECTION FOR A DIFFERENT TIME UNTIL THE FIRST MATING IN Drosophila melanogaster
Snežana STANIĆ 1 i D.
MARINKOVIĆ 2
1 Institut za biologiju PMF, Kragujevac
2 Institut za zoologiju, Biološki fakultet Univerziteta u Beogradu,
Beograd
In view of the evolutionary importance of
the mating process in Drosophila the object of this study was the
selection for different time periods until the first mating in Drosophila
melanogaster to be able to obtain lines with individuals that have mainly
fast or slow mating. The number of offspring was noted in each generation of
selected lines. In order to observe possible influences due to conditions of
competition in considered fitness components, the selection was made in two
replies: I one pair of individuals was selected for producing the next
generation II ten pairs of individuals were kept in each bottle to produce the
next generation of Drosophila melanogaster. After nine generations of
selection we obtained slow lines whose time period to the first mating was 2863
sec (competition excluded) and 2402 sec (competition included) and fast lines
whose time periods were 100 sec and 160 sec, respectively. The mean time period
until the first mating within selected lines varied but there was some
response. Variability was less expressed in fast than in low lines.
Quantitative-genetic analysing of the obtained results showed higher
heritability in slow lines. Heritability coefficients in the case of the
selection for slow mating were h2 = 0.614 and h2 = 0.386 while in the case of fast mating they were h2 = 0.0241 and h2 = 0.0243. Mean heritability
values of this metric character per generation were derived from the ratio R/SD (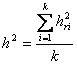 ). Variability of the number of offspring in
selected lines was seen, while according to correlation coefficient values
there was no regularity in the response to correlation.
). Variability of the number of offspring in
selected lines was seen, while according to correlation coefficient values
there was no regularity in the response to correlation.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
INDIVIDUAL VARIABILITY OF
A-AMYLASE ACTIVITY IN Drosophila subobscura
Vesna STOJILJKOVIĆ
Biološki fakultet, Beograd
In this study an experiment was performed to investigate the mechanisms of genetic regulation of ά-amylase activity in Drosophila subobscura individuals homozygous for the S or F allele of the Amy locus. The nature of genetic variation for ά-amylase activity was studied by means of analyses of variance among full-sib and half-sib families. The results indicate that different types of regulatory mechanisms are present in F and S homozygotes. Since additive genetic variance is higher in the S line, in the control of ά-amylase activity in S homozygotes a greater number of loci should be included, than in F homozygotes. In the F line the genetic variation consists primarily of additive variance, where as in the S line it seems that regulatory genes have additive and epistatic effects.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
EFFECTS OF LONG-TERM SELECTION FOR HIGH AND LOW LARVAL DENSITY OF LIFE-HISTORY TRAITS OF THE BEAN WEEVIL (Acanlhoscelides obtectus)
O. STOJKOVIĆ
Laboratorija za evolucionu biologiju, Institut za biološka istraživanja "Siniša Stanković", Beograd
After more than 40 generations of selection for low (r-) and high (K-) larval density various life-history traits of bean weevils (Acanlhoscelides obtectus) were investigated in order to test predictions made by the r/K selection theory. Some of our experimental results support theoretical predictions. Thus, compared to those from K-selected population, weevils from the r-selected population have a higher early and overall fecundity and live longer. However, contrary to the theory, egg-to-adult development time was longer, although not significantly, in the K-selected population. A significant interaction between population and larval density for development time of females and males as well as for longevity of females, suggests that effects of larval crowding on these traits are genotype-specific. Analysis of the components of genetic variation shows that long-term selection for high larval density left significant amounts of genetic variability to the population that can be expressed under different larval crowding conditions.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
THE EFFECTS OF ANTIOXIDANTS ON LONGEVITY IN SHORT- AND LONG-LIVED LINES OF BEAN WEEVILS (Acanthoscelides obleclus)
Darka ŠEŠLIJA i D. BLAGOJEVIĆ
Institut za biološka istraživanja "Siniša Stanković, Beograd
In the present study we have analyzed the effects of different antioxidants (ascorbic acid, glutathione and a mixture of ascorbic acid, glutathione, superoxide dismutase and sucrose) on longevity differences between weevils that had been selected for early- and late-reproduction. We have shown here that longevity can be significantly increased by exogenously applied antioxidants only in the lines with a short life-span. The longevity of the long-lived lines is not affected by applied antioxidants. These results are consistent with the hypothesis that differences in longevity between lines may involve the genes which control antioxidative defence in the bean weevil.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
THE INFLUENCE OF REPRODUCTIVE SUCCESS IN Drosophila subobscura INDIVIDUALS HOMOZYGOUS FOR THE S OR F ALLELE OF THE AMY-LOCUS ON THE VIABILITY OF THE PROGENY DEPENDING ON THE SUBSTRATE COMPOSITION
Tatjana TERZIĆ i M. ANĐELKOVIĆ
Odeljenje za genetiku, Institut za biološka istraživanja "Siniša Stanković", Beograd
The existence of frequency-dependent selection - "rare male effect" (RME) as a special kind of selection and its role in maintaining stable genetic polymorphisms, represents an insufficiently explained phenomenon of population genetics. In the present study, a polymorphism for the Amy-locus in Drosophila subobscura was used as a model-system. The well known biochemical and physiological role of the alpha-amylase and the precisely defined substrate for this enzyme provide the possibility of connecting the influence of the frequency of the genotypes for the Amy-locus on male mating success in Drosophila subobscura with some fitness components depending on some environmental factors. For this reason, the influence of the mating frequency on viability depending on the mating type and substrate composition was examined. Different genotypes for the Amy-locus in Drosophila subobscura were kept under outbreeding conditions, while some environmental components (varying content of starch in the substrate) and the influence of RME on total genotype fitness through viability as a fitness component after mating were studied. Mean viability values on starch and maltose showed a higher survival rate of heterogametic (SfFm; FfSm) comparing to that of homogametic (SfSm; FfFm) matings. The higher survival rate of heterogametic matings, for which RME was detected, could be related to positive heterosis.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
THE GENETIC DISTANCE BETWEEN THREE SPECIES OF THE GENUS Apodemus
Ljiljana VAPA, Ivana KARANOVIĆ, Dragana RADOVIĆ, J. PURGER i M. BOKOROV
Prirodno-matematički fakultet, Novi Sad
In spite of an increasing number of various molecular techniques isozyme elekctrophoresis is still widely applied and represents a valuable tool in the field of biochemical systematics. In the present paper data are given on allozyme variation at 11 loci of six different enzymes (ICD, E.C.I.1.1.42; LDH, E.C.I.1.1.27; SOD, E.C.1.15.1.1; MDH, E.C.I.1.37; ME, E.C.1.1.1.37; 6-PGD, E.C.I.1.1.44) obtained by the method of starch gel electrophoresis. Three species of the genus Apodemus (A. sylvaticus, A. flavicollis and A. agrarius) were trapped at Doroslovo (Vojvodina). Genetic identity (I) and genetic distance (D) were calculated on the basis of allelic frequency, while genetic relationships between the three species of the genus Apodemus were presented in the UPGMA dendrogram. A low value of genetic distance (D = 0.25) was obtained between A. sylvaticus and A. flavicollis, whereas it was high between A. agrarius and A. flavicolils (D = 1.1) and between A. agariuis and A. sylvaticus (D = 0.8).
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
CORRELATION OF STRUCTURAL COMPLEXITY OF O CHROMOSOME AND THE GENETIC LOAD IN Drosophila suboboscura
G. ŽIVANOVIĆ, Mirjana MILANOVIĆ i M. ANĐELKOVIĆ
Odeljenje za genetiku, Institut za biološka istraživanja "Siniša Stanković", Beograd
Inversion polymorphism represents a well known form of genetic polymorphism in Drosophila. The phenomenon of a high degree of inversion polymorphism in D. subobscura poses the question of the adaptive significance of inversions as coadaptive complexes. If these inversions represent coadaptive complexes, one should expect a lower level of genetic loads for complex structural types in relation to structural types with simple inversions. In this connection, analyses of inversion polymorphism of O chromosomes and genetic loads linked to gene loci of this chromosome were performed in D. subobscura. The results obtained throughout this stsudy provide the possibility of a better insight into the correlation of structural type complexity and level of genetic loads.
Published in Book of Abstracts „THE FIRST CONGRESS OF SERBIAN GENETICISTS“
Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, June 08-11, 1994
© 1994 Serbian Genetics Society
THE EFFECT OF THE AGING ON THE IN Drosophila melanogaster GENETIC LOAD
Jelena ŽIVANOV-ČURLIS i Estera MRČARICA
Institut za biologiju, Medicinski fakultet, Niš
The impact of the aging of male parents on the genetic load of the progeny was studied. Tests -were carried out by analyzing recessive harmful mutations on chromosomc-2. An experiment was done with the fruit fly Drosophila melanogaster cultivated on a yeast medium under optimal laboratory conditions. In addition to the wild flies line, the Cy/Pm laboratory line with dominant marker-genes was also used for the purpose of obtaining homozygotes for chromosome-2. A total of 54 chromosomcs-2 obtained by the usual technique after three crossbreedings in homozygous combination were analyzed. The +/Cy males from the F1-gencration were crossbred twice: at the ages of 1-5 and 25-30 days. Viability of homozygotes for chromosomc-2 was established based on the expected number ratio of the +/+ : +/Cy flics which amounted to 33.3 : 66.7 percent. Flies with heterozygous combinations of chromosomes were concurrently observed. The experimental results show that the difference in the viability of the homozygous progeny of young and older males was significant (t = 24.82; df = 106; p < 0,05). The average variability of homozygotes for chrocosomc-2 with the progeny of young males was 28.27 percent (heterozygotes 32.32 percent) while that of the progeny of older males was 21.32 percent (heterozygotes 34.32 percent). Compared to the heterozygous combinations harmful recessive mutations decreased the viability of homozygotes by 12.53 percent on average in the progeny of young males and by 37.88 percent on average in the progeny of old males. Analysis of chromosomcs-2 for the presence of genes of importance to viability indicated considerable differences in the frequency of lethals and supervitals between the progeny of young and older individuals. With progeny from the young males, lethals amounted to 12.96 percent while supervitals amounted to 29.63 percent; with progeny from the older males; lethals amounted to 27.78 percent while supervitals amounted to 7.41 percent only. The above data obviously show that the genetic load in the gene fund of progeny increases with the age of the male parent which results in a decreased average viability.